The Context API in React provides a way to pass data through the component tree without having to pass props down manually at every level. When working with TypeScript and Next.js, leveraging the Context API allows for a more organized and type-safe approach to managing the global state. In this tutorial, we'll explore using Context API with TypeScript in a Next.js application.
Prerequisites:
Approach
- First, define the context using React.createContext(). This will be the container for your global state.
- Use a Context Provider component to wrap the parts of your application that need access to the global state. Pass the state and any functions to modify it as values to the Provider.
- Use the useContext() hook to consume the context within functional components. This hook takes the context object created with createContext() and returns the current context value.
- Create a useCounter hook with useContext to access context values, throwing an error if the context is unavailable.
- Wrap the main component with CounterProvider in _app.tsx to make context available throughout the app.
- Utilize useCounter hook in components to access the counter state and functions, enabling interaction with the counter.
Steps to Setup the Application
Step 1: Create a NextJS application by using this command
npx create-next-app@latest myappStep 2: Navigate to project directory
cd myappProject Structure:
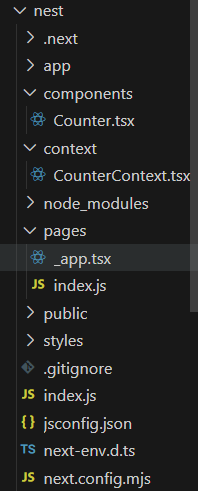
The updated dependencies in package.json file will look like:
{
"dependencies": {
"react": "^17.0.2",
"react-dom": "^17.0.2",
"next": "^11.1.2"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@types/react": "^17.0.38",
"@types/react-dom": "^17.0.11",
"typescript": "^4.5.4"
}
}
Example: Implementation to show how to use Context API with Typescript and NextJS by building a counter app.
/* styles/globals.css */
.counter-container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
font-size: 300%;
position: absolute;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
top: -15%;
}
.counter {
font-size: 120%;
position: relative;
top: 10vh;
}
.buttons {
display: flex;
margin-top: 20vh;
}
.increment,
.decrement {
font-size: 60%;
margin: 0 5px;
border-radius: 8%;
color: white;
padding: 5px 10px;
}
.increment {
background-color: green;
}
.decrement {
background-color: red;
}
// context/CounterContext.tsx
import React, { createContext, useContext, useState } from "react";
interface CounterContextType {
counter: number;
increment: () => void;
decrement: () => void;
}
const CounterContext = createContext<CounterContextType | undefined>(undefined);
export const CounterProvider: React.FC = ({ children }) => {
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(0);
const increment = () => setCounter(counter + 1);
const decrement = () => setCounter(counter - 1);
return (
<CounterContext.Provider value={{ counter, increment, decrement }}>
{children}
</CounterContext.Provider>
);
};
export const useCounter = () => {
const context = useContext(CounterContext);
if (!context) {
throw new Error("useCounter must be used within a CounterProvider");
}
return context;
};
// pages/_app.tsx
import React from "react";
import { AppProps } from "next/app";
import { CounterProvider } from "../context/CounterContext";
import "../styles/globals.css";
function MyApp({ Component, pageProps }: AppProps) {
return (
<CounterProvider>
<Component {...pageProps} />
</CounterProvider>
);
}
export default MyApp;
// components/Counter.tsx
import React from "react";
import { useCounter } from "../context/CounterContext";
const Counter: React.FC = () => {
const {
counter,
increment,
decrement } = useCounter();
return (
<div className="counter-container">
<div className="counter">{counter}</div>
<div className="buttons">
<button className="increment"
onClick={increment}>
Increment
</button>
<button className="decrement"
onClick={decrement}>
Decrement
</button>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default Counter;
Output:
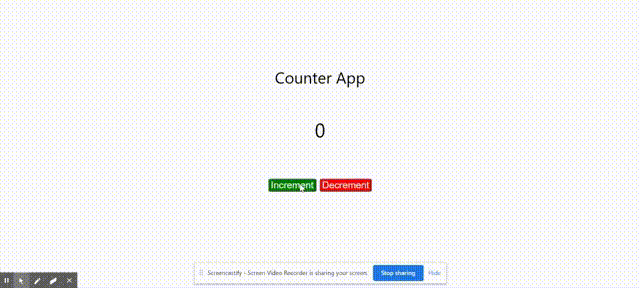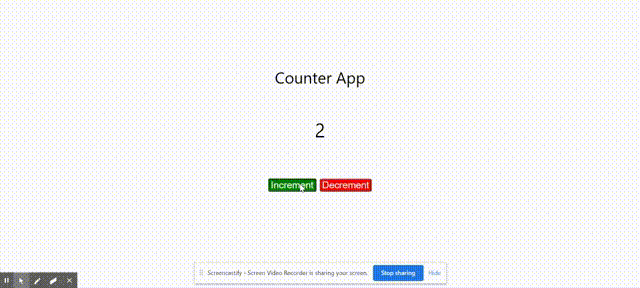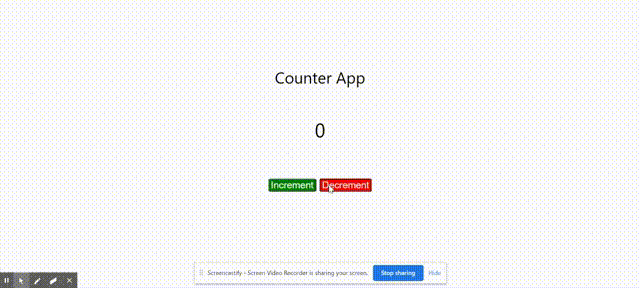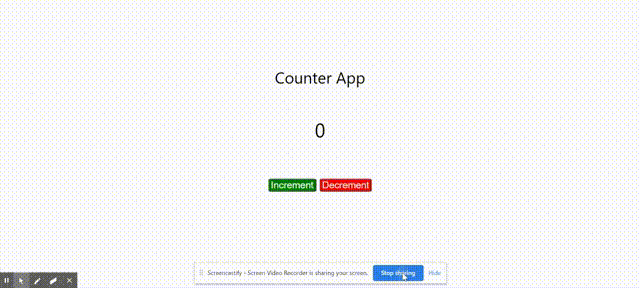
Output