Ever wondered how to tackle tricky problems in competitive programming? Well, basic geometry is your secret weapon! In this article, we're diving into the basics Geometric Algorithms. It's like a power-up for your problem-solving skills, giving you the tools to crack those coding challenges like a pro.
Table of Content
What are Geometric Algorithms?
Geometric algorithms are a set of computational techniques used in Competitive Programming to solve problems related to geometry and spatial relationships. These problems often involve points, lines, polygons, and other geometric objects.
Why to use Geometric Algorithms?
There are several questions which require basic geometric algorithms like:
- Vector Addition/Subtraction
- Dot Product and Cross Product
- Distance of a point from a line
- Intersection of Lines
- Intersection of Planes, etc.
1. Vector Addition/Subtraction:
Operations like addition and subtraction of two vectors can be simply done by performing the operation on the individual components of the vectors. Like if we have two vectors (x1, y1) and (x2, y2), then the sum of the two vectors is (x1+x2, y1+y2) and the difference between them is (x1-x2, y1-y2).
Implementation:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function to perform vector addition
vector<int> addVectors(const vector<int>& v1,
const vector<int>& v2)
{
vector<int> result;
if (v1.size() != v2.size()) {
cerr << "Vectors must be of the same size for "
"addition."
<< endl;
return result; // Returning an empty vector
// indicating an error
}
result.reserve(v1.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < v1.size(); ++i) {
result.push_back(v1[i] + v2[i]);
}
return result;
}
// Function to perform vector subtraction
vector<int> subtractVectors(const vector<int>& v1,
const vector<int>& v2)
{
vector<int> result;
if (v1.size() != v2.size()) {
cerr << "Vectors must be of the same size for "
"subtraction."
<< endl;
return result; // Returning an empty vector
// indicating an error
}
result.reserve(v1.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < v1.size(); ++i) {
result.push_back(v1[i] - v2[i]);
}
return result;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// Example vectors
vector<int> vector1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
vector<int> vector2 = { 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 };
// Perform vector addition
vector<int> sum = addVectors(vector1, vector2);
cout << "Vector Addition Result: ";
for (int value : sum) {
cout << value << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// Perform vector subtraction
vector<int> difference
= subtractVectors(vector1, vector2);
cout << "Vector Subtraction Result: ";
for (int value : difference) {
cout << value << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
import java.util.Arrays;
public class VectorOperations {
// Function for vector addition
public static int[] addVectors(int[] v1, int[] v2) {
int[] result = new int[v1.length];
// Check if vectors are of the same size for addition
if (v1.length != v2.length) {
System.out.println("Vectors must be of the same size for addition.");
// Returning an empty array indicating an error
return result;
}
// Perform vector addition
for (int i = 0; i < v1.length; i++) {
result[i] = v1[i] + v2[i];
}
return result;
}
// Function for vector subtraction
public static int[] subtractVectors(int[] v1, int[] v2) {
int[] result = new int[v1.length];
// Check if vectors are of the same size for subtraction
if (v1.length != v2.length) {
System.out.println("Vectors must be of the same size for subtraction.");
// Returning an empty array indicating an error
return result;
}
// Perform vector subtraction
for (int i = 0; i < v1.length; i++) {
result[i] = v1[i] - v2[i];
}
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example vectors
int[] vector1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int[] vector2 = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1};
// Perform vector addition
int[] sumResult = addVectors(vector1, vector2);
System.out.println("Vector Addition Result: " + Arrays.toString(sumResult));
// Perform vector subtraction
int[] differenceResult = subtractVectors(vector1, vector2);
System.out.println("Vector Subtraction Result: " + Arrays.toString(differenceResult));
}
}
def add_vectors(v1, v2):
result = []
if len(v1) != len(v2):
print("Vectors must be of the same size for addition.")
return result # Returning an empty list indicating an error
result = [x + y for x, y in zip(v1, v2)]
return result
def subtract_vectors(v1, v2):
result = []
if len(v1) != len(v2):
print("Vectors must be of the same size for subtraction.")
return result # Returning an empty list indicating an error
result = [x - y for x, y in zip(v1, v2)]
return result
# Example vectors
vector1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
vector2 = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
# Perform vector addition
sum_result = add_vectors(vector1, vector2)
print("Vector Addition Result:", *sum_result)
# Perform vector subtraction
difference_result = subtract_vectors(vector1, vector2)
print("Vector Subtraction Result:", *difference_result)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
// Function to perform vector addition
static List<int> AddVectors(List<int> v1, List<int> v2)
{
List<int> result = new List<int>();
if (v1.Count != v2.Count)
{
Console.WriteLine("Vectors must be of the same size for addition.");
return result; // Returning an empty list indicating an error
}
for (int i = 0; i < v1.Count; ++i)
{
result.Add(v1[i] + v2[i]);
}
return result;
}
// Function to perform vector subtraction
static List<int> SubtractVectors(List<int> v1, List<int> v2)
{
List<int> result = new List<int>();
if (v1.Count != v2.Count)
{
Console.WriteLine("Vectors must be of the same size for subtraction.");
return result; // Returning an empty list indicating an error
}
for (int i = 0; i < v1.Count; ++i)
{
result.Add(v1[i] - v2[i]);
}
return result;
}
// Driver code
static void Main()
{
// Example lists
List<int> vector1 = new List<int> { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
List<int> vector2 = new List<int> { 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 };
// Perform vector addition
List<int> sum = AddVectors(vector1, vector2);
Console.Write("Vector Addition Result: ");
foreach (int value in sum)
{
Console.Write(value + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
// Perform vector subtraction
List<int> difference = SubtractVectors(vector1, vector2);
Console.Write("Vector Subtraction Result: ");
foreach (int value in difference)
{
Console.Write(value + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Function for vector addition
function addVectors(v1, v2) {
let result = new Array(v1.length).fill(0);
// Check if vectors are of the same size for addition
if (v1.length !== v2.length) {
console.log("Vectors must be of the same size for addition.");
// Returning an empty array indicating an error
return result;
}
// Perform vector addition
for (let i = 0; i < v1.length; i++) {
result[i] = v1[i] + v2[i];
}
return result;
}
// Function for vector subtraction
function subtractVectors(v1, v2) {
let result = new Array(v1.length).fill(0);
// Check if vectors are of the same size for subtraction
if (v1.length !== v2.length) {
console.log("Vectors must be of the same size for subtraction.");
// Returning an empty array indicating an error
return result;
}
// Perform vector subtraction
for (let i = 0; i < v1.length; i++) {
result[i] = v1[i] - v2[i];
}
return result;
}
// Example vectors
let vector1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let vector2 = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1];
// Perform vector addition
let sumResult = addVectors(vector1, vector2);
console.log("Vector Addition Result: " + sumResult);
// Perform vector subtraction
let differenceResult = subtractVectors(vector1, vector2);
console.log("Vector Subtraction Result: " + differenceResult);
Output
Vector Addition Result: 6 6 6 6 6 Vector Subtraction Result: -4 -2 0 2 4
2. Dot Product and Cross Product:
The dot product of two vectors is simply the sum of the products of the corresponding elements. If we have two vectors (x1, y1) and (x2, y2), then the dot product of the two vectors is (x1 * x2) + (y1 * y2). The dot product of two vectors is a scalar quantity.
If we have two vectors in x-y plane (x1, y1) and (x2, y2), then the magnitude of cross product of two vectors is (x1 * y2) - (x2 * y1) and direction is in ±z direction. The cross product of two vectors is a vector quantity. Similarly, the cross product of two 3D vectors (x1, y1, z1) and (x2, y2, z2) is (y1*z2 - y2*z1, z1*x2 - z2*x1, x1*y2 - x2*y1).
Implementation:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Function to calculate the dot product of two vectors
double dotProduct(const vector<double>& vec1,
const vector<double>& vec2)
{
double result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
result += vec1[i] * vec2[i];
}
return result;
}
// Function to calculate the cross product of two vectors
vector<double> crossProduct(const vector<double>& vec1,
const vector<double>& vec2)
{
vector<double> result(3, 0);
result[0] = vec1[1] * vec2[2] - vec1[2] * vec2[1];
result[1] = vec1[2] * vec2[0] - vec1[0] * vec2[2];
result[2] = vec1[0] * vec2[1] - vec1[1] * vec2[0];
return result;
}
int main()
{
// Example vectors
vector<double> vector1 = { 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 };
vector<double> vector2 = { 4.0, 5.0, 6.0 };
// Calculate and display the dot product
double dotResult = dotProduct(vector1, vector2);
cout << "Dot Product: " << dotResult << endl;
// Calculate and display the cross product
vector<double> crossResult
= crossProduct(vector1, vector2);
cout << "Cross Product: ";
for (double value : crossResult) {
cout << value << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class VectorOperations {
// Function to calculate the dot product of two vectors
public static double dotProduct(List<Double> vec1, List<Double> vec2) {
double result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
result += vec1.get(i) * vec2.get(i);
}
return result;
}
// Function to calculate the cross product of two vectors
public static List<Double> crossProduct(List<Double> vec1, List<Double> vec2) {
List<Double> result = Arrays.asList(0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
result.set(0, vec1.get(1) * vec2.get(2) - vec1.get(2) * vec2.get(1));
result.set(1, vec1.get(2) * vec2.get(0) - vec1.get(0) * vec2.get(2));
result.set(2, vec1.get(0) * vec2.get(1) - vec1.get(1) * vec2.get(0));
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example vectors
List<Double> vector1 = Arrays.asList(1.0, 2.0, 3.0);
List<Double> vector2 = Arrays.asList(4.0, 5.0, 6.0);
// Calculate and display the dot product
double dotResult = dotProduct(vector1, vector2);
System.out.println("Dot Product: " + dotResult);
// Calculate and display the cross product
List<Double> crossResult = crossProduct(vector1, vector2);
System.out.print("Cross Product: ");
for (double value : crossResult) {
System.out.print(value + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
class VectorOperations:
@staticmethod
def dot_product(vec1, vec2):
result = 0
for i in range(3):
result += vec1[i] * vec2[i]
return result
@staticmethod
def cross_product(vec1, vec2):
result = [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
result[0] = vec1[1] * vec2[2] - vec1[2] * vec2[1]
result[1] = vec1[2] * vec2[0] - vec1[0] * vec2[2]
result[2] = vec1[0] * vec2[1] - vec1[1] * vec2[0]
return result
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Example vectors
vector1 = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0]
vector2 = [4.0, 5.0, 6.0]
# Calculate and display the dot product
dot_result = VectorOperations.dot_product(vector1, vector2)
print("Dot Product:", dot_result)
# Calculate and display the cross product
cross_result = VectorOperations.cross_product(vector1, vector2)
print("Cross Product:", cross_result)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
// Function to calculate the dot product of two vectors
static double DotProduct(List<double> vec1, List<double> vec2)
{
double result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
result += vec1[i] * vec2[i];
}
return result;
}
// Function to calculate the cross product of two vectors
static List<double> CrossProduct(List<double> vec1, List<double> vec2)
{
List<double> result = new List<double> { 0, 0, 0 };
result[0] = vec1[1] * vec2[2] - vec1[2] * vec2[1];
result[1] = vec1[2] * vec2[0] - vec1[0] * vec2[2];
result[2] = vec1[0] * vec2[1] - vec1[1] * vec2[0];
return result;
}
static void Main()
{
// Example vectors
List<double> vector1 = new List<double> { 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 };
List<double> vector2 = new List<double> { 4.0, 5.0, 6.0 };
// Calculate and display the dot product
double dotResult = DotProduct(vector1, vector2);
Console.WriteLine("Dot Product: " + dotResult);
// Calculate and display the cross product
List<double> crossResult = CrossProduct(vector1, vector2);
Console.Write("Cross Product: ");
foreach (double value in crossResult)
{
Console.Write(value + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Function to calculate the dot product of two vectors
function dotProduct(vec1, vec2) {
let result = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
result += vec1[i] * vec2[i];
}
return result;
}
// Function to calculate the cross product of two vectors
function crossProduct(vec1, vec2) {
let result = [0, 0, 0];
result[0] = vec1[1] * vec2[2] - vec1[2] * vec2[1];
result[1] = vec1[2] * vec2[0] - vec1[0] * vec2[2];
result[2] = vec1[0] * vec2[1] - vec1[1] * vec2[0];
return result;
}
// Example vectors
const vector1 = [1.0, 2.0, 3.0];
const vector2 = [4.0, 5.0, 6.0];
// Calculate and display the dot product
const dotResult = dotProduct(vector1, vector2);
console.log("Dot Product: " + dotResult);
// Calculate and display the cross product
const crossResult = crossProduct(vector1, vector2);
console.log("Cross Product: " + crossResult.join(" "));
Output
Dot Product: 32 Cross Product: -3 6 -3
3. Distance from a point to a line:
Suppose we are given point A and a line L and we need to calculate the distance between the point and the line (say h), we can simply do it using Cross Product of vectors.
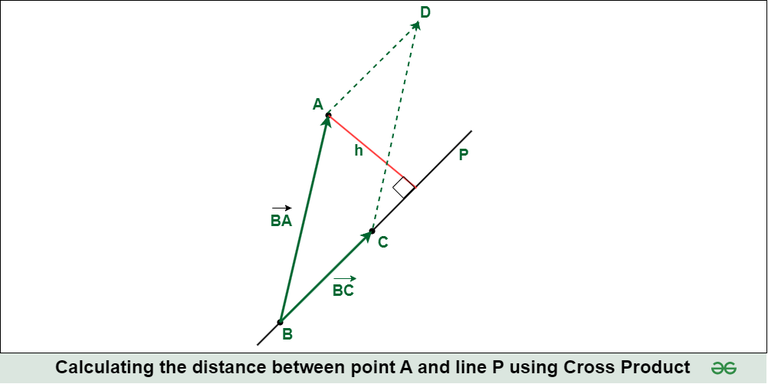
Let's say we take 2 points on the line L, say B and C so the distance between the point and the line would simply be:
[Tex]h = ( \,|\overrightarrow{\rm BA}| X |\overrightarrow{\rm BC}|) \,/(|\overrightarrow{\rm BC}|) [/Tex]
where the numerator is the magnitude of Cross Product of vector B to A and B to C and the denominator is the magnitude of vector B to C.
From the above diagram, we can see that the area of the parallelogram ABCD =
[Tex] (|\overrightarrow{\rm BA}| X |\overrightarrow{\rm BC}|) [/Tex]
Also, we know that area of a parallelogram = base * height = [Tex](|\overrightarrow{\rm BC}|) * h [/Tex]
So, using the above two equations, we can calculate the height h,
[Tex]h = ( \,|\overrightarrow{\rm BA}| X |\overrightarrow{\rm BC}|) \,/(|\overrightarrow{\rm BC}|) [/Tex]
Note: We can use the same formula for 3D vectors also.
Implementation:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Method to get the magnitude of a vector
double getMagnitude(vector<int>& v)
{
return sqrt(v[0] * v[0] + v[1] * v[1] + v[2] * v[2]);
}
// Method to calculate the cross product of two vectors v1
// and v2
void getCrossProduct(vector<int>& v1, vector<int>& v2,
vector<int>& crossProduct)
{
crossProduct[0] = v1[1] * v2[2] - v1[2] * v2[1];
crossProduct[1] = v1[2] * v2[0] - v1[0] * v2[2];
crossProduct[2] = v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0];
}
int main()
{
// Point from which we need to calculate the distance
vector<int> pointA = { 1, 4, -2 };
// Points on the line P
vector<int> pointB = { 3, 1, -2 };
vector<int> pointC = { 6, -2, 1 };
// vector BA
vector<int> vecBA
= { pointA[0] - pointB[0], pointA[1] - pointB[1],
pointA[2] - pointB[2] };
// vector BC
vector<int> vecBC
= { pointC[0] - pointB[0], pointC[1] - pointB[1],
pointC[2] - pointB[2] };
// vector to store the cross prduct
vector<int> crossProduct(3);
getCrossProduct(vecBA, vecBC, crossProduct);
// Variable to store the distance of point A from line P
double dist
= getMagnitude(crossProduct) / getMagnitude(vecBC);
cout << dist;
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
// Class to hold the methods
public class Main {
// Method to get the magnitude of a vector
public static double getMagnitude(int[] v) {
return Math.sqrt(v[0] * v[0] + v[1] * v[1] + v[2] * v[2]);
}
// Method to calculate the cross product of two vectors v1 and v2
public static int[] getCrossProduct(int[] v1, int[] v2) {
int[] crossProduct = new int[3];
crossProduct[0] = v1[1] * v2[2] - v1[2] * v2[1];
crossProduct[1] = v1[2] * v2[0] - v1[0] * v2[2];
crossProduct[2] = v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0];
return crossProduct;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Point from which we need to calculate the distance
int[] pointA = { 1, 4, -2 };
// Points on the line P
int[] pointB = { 3, 1, -2 };
int[] pointC = { 6, -2, 1 };
// vector BA
int[] vecBA = { pointA[0] - pointB[0], pointA[1] - pointB[1], pointA[2] - pointB[2] };
// vector BC
int[] vecBC = { pointC[0] - pointB[0], pointC[1] - pointB[1], pointC[2] - pointB[2] };
// vector to store the cross product
int[] crossProduct = getCrossProduct(vecBA, vecBC);
// Variable to store the distance of point A from line P
double dist = getMagnitude(crossProduct) / getMagnitude(vecBC);
System.out.println(dist);
}
}
import math
# Method to get the magnitude of a vector
def get_magnitude(v):
return math.sqrt(v[0] * v[0] + v[1] * v[1] + v[2] * v[2])
# Method to calculate the cross product of two vectors v1
# and v2
def get_cross_product(v1, v2):
cross_product = [0, 0, 0]
cross_product[0] = v1[1] * v2[2] - v1[2] * v2[1]
cross_product[1] = v1[2] * v2[0] - v1[0] * v2[2]
cross_product[2] = v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0]
return cross_product
# Point from which we need to calculate the distance
pointA = [1, 4, -2]
# Points on the line P
pointB = [3, 1, -2]
pointC = [6, -2, 1]
# vector BA
vecBA = [pointA[0] - pointB[0], pointA[1] - pointB[1], pointA[2] - pointB[2]]
# vector BC
vecBC = [pointC[0] - pointB[0], pointC[1] - pointB[1], pointC[2] - pointB[2]]
# vector to store the cross product
cross_product = get_cross_product(vecBA, vecBC)
# Variable to store the distance of point A from line P
dist = get_magnitude(cross_product) / get_magnitude(vecBC)
print(dist)
using System;
public class MainClass {
// Method to calculate the magnitude of a vector
static double GetMagnitude(int[] v)
{
return Math.Sqrt(v[0] * v[0] + v[1] * v[1]
+ v[2] * v[2]);
}
// Method to calculate the cross product of two vectors
// v1 and v2
static void GetCrossProduct(int[] v1, int[] v2,
int[] crossProduct)
{
crossProduct[0] = v1[1] * v2[2] - v1[2] * v2[1];
crossProduct[1] = v1[2] * v2[0] - v1[0] * v2[2];
crossProduct[2] = v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0];
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Point from which we need to calculate the
// distance
int[] pointA = { 1, 4, -2 };
// Points on the line P
int[] pointB = { 3, 1, -2 };
int[] pointC = { 6, -2, 1 };
// Vector BA
int[] vecBA = { pointA[0] - pointB[0],
pointA[1] - pointB[1],
pointA[2] - pointB[2] };
// Vector BC
int[] vecBC = { pointC[0] - pointB[0],
pointC[1] - pointB[1],
pointC[2] - pointB[2] };
// Array to store the cross product
int[] crossProduct = new int[3];
// Calculate the cross product of vecBA and vecBC
GetCrossProduct(vecBA, vecBC, crossProduct);
// Variable to store the distance of point A from
// line P
double dist = GetMagnitude(crossProduct)
/ GetMagnitude(vecBC);
// Output the distance
Console.WriteLine(dist);
}
}
// Get the magnitude of a vector
const getMagnitude = (v) => {
return Math.sqrt(v[0] * v[0] + v[1] * v[1] + v[2] * v[2]);
};
// Calculate the cross product of two vectors v1 and v2
const getCrossProduct = (v1, v2, crossProduct) => {
crossProduct[0] = v1[1] * v2[2] - v1[2] * v2[1];
crossProduct[1] = v1[2] * v2[0] - v1[0] * v2[2];
crossProduct[2] = v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0];
};
// Main function
const main = () => {
// Point from which we need to calculate the distance
const pointA = [1, 4, -2];
// Points on the line P
const pointB = [3, 1, -2];
const pointC = [6, -2, 1];
// Vector BA
const vecBA = [pointA[0] - pointB[0], pointA[1] - pointB[1], pointA[2] - pointB[2]];
// Vector BC
const vecBC = [pointC[0] - pointB[0], pointC[1] - pointB[1], pointC[2] - pointB[2]];
// Vector to store the cross product
const crossProduct = [0, 0, 0];
getCrossProduct(vecBA, vecBC, crossProduct);
// Distance of point A from line P
const dist = getMagnitude(crossProduct) / getMagnitude(vecBC);
console.log(dist);
};
main();
Output
2.16025
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
4. Intersection Point of two lines:
We can find the intersection point of two lines in 2D using parametric equations. Parametric equations are a way of representing a curve in terms of one or more parameters. For a line in 2D, we can use the following parametric equation:
=> r = a + td
where a is the starting point of the line, t is a real parameter, d is the direction vector for the line and r is a point on the line.
So, for the first line the parametric equation will be, r1 = a1 + t1d1 and for the second line the parametric equation will be, r2 = a2 + t2d2. We can further simplify the second equation:
=> r2 - a2 = t2d2
Taking Cross Product with d2 vector on both sides.
=> (r2 - a2) X d2 = 0
As the lines intersect at any point, the value of r1 and r2 will be same at that intersection point. So, by substituting the value of r1 in the above equation,
=> (a1 + t1d1 - a2) X d2 = 0
=> t1 = ((a2 - a1) X d2) / (d1 X d2)
Now, we can find the intersection point by putting the value of t1 into r1 = a1 + t1d1
Implementation:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Since the product of 2D(x, y) vectors is a vector in z
// direction, we simply return the magnitude of the vector
double getCrossProduct(vector<double> v1, vector<double> v2)
{
return v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0];
}
vector<double> getDifference(vector<double> v1,
vector<double> v2)
{
vector<double> diff(2);
diff[0] = v2[0] - v1[0];
diff[1] = v2[1] - v1[1];
return diff;
}
vector<double> getSum(vector<double> v1, vector<double> v2)
{
vector<double> sum(2);
sum[0] = v1[0] + v2[0];
sum[1] = v1[1] + v2[1];
return sum;
}
int main()
{
// Points of lines
vector<double> pointA = { 1, 1 };
vector<double> pointB = { 4, 4 };
vector<double> pointC = { 1, 8 };
vector<double> pointD = { 2, 4 };
// direction vector d1
vector<double> d1 = getDifference(pointA, pointB);
// direction vector d2
vector<double> d2 = getDifference(pointC, pointD);
double t1
= getCrossProduct(getDifference(pointA, pointC), d2)
/ (getCrossProduct(d1, d2) * 1.0);
d1[0] *= t1;
d1[1] *= t1;
// Now, we can find the intersection point by putting
// the value of t1 into r1 = A + t1d1
vector<double> intersectionPoint = getSum(pointA, d1);
cout << intersectionPoint[0] << " "
<< intersectionPoint[1];
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
// Since the product of 2D(x, y) vectors is a vector in z
// direction, we simply return the magnitude of the vector
public static double getCrossProduct(double[] v1, double[] v2) {
return v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0];
}
public static double[] getDifference(double[] v1, double[] v2) {
double[] diff = new double[2];
diff[0] = v2[0] - v1[0];
diff[1] = v2[1] - v1[1];
return diff;
}
public static double[] getSum(double[] v1, double[] v2) {
double[] sum = new double[2];
sum[0] = v1[0] + v2[0];
sum[1] = v1[1] + v2[1];
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Points of lines
double[] pointA = { 1, 1 };
double[] pointB = { 4, 4 };
double[] pointC = { 1, 8 };
double[] pointD = { 2, 4 };
// direction vector d1
double[] d1 = getDifference(pointA, pointB);
// direction vector d2
double[] d2 = getDifference(pointC, pointD);
double t1 = getCrossProduct(getDifference(pointA, pointC), d2) / getCrossProduct(d1, d2);
d1[0] *= t1;
d1[1] *= t1;
// Now, we can find the intersection point by putting
// the value of t1 into r1 = A + t1d1
double[] intersectionPoint = getSum(pointA, d1);
System.out.println(intersectionPoint[0] + " " + intersectionPoint[1]);
}
}
from typing import List
# Since the product of 2D(x, y) vectors is a vector in z
# direction, we simply return the magnitude of the vector
def getCrossProduct(v1: List[float], v2: List[float]) -> float:
return v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0]
def getDifference(v1: List[float], v2: List[float]) -> List[float]:
diff = [0.0, 0.0]
diff[0] = v2[0] - v1[0]
diff[1] = v2[1] - v1[1]
return diff
def getSum(v1: List[float], v2: List[float]) -> List[float]:
sum = [0.0, 0.0]
sum[0] = v1[0] + v2[0]
sum[1] = v1[1] + v2[1]
return sum
# Points of lines
pointA = [1, 1]
pointB = [4, 4]
pointC = [1, 8]
pointD = [2, 4]
# direction vector d1
d1 = getDifference(pointA, pointB)
# direction vector d2
d2 = getDifference(pointC, pointD)
t1 = getCrossProduct(getDifference(pointA, pointC), d2) / getCrossProduct(d1, d2)
d1[0] *= t1
d1[1] *= t1
# Now, we can find the intersection point by putting
# the value of t1 into r1 = A + t1d1
intersectionPoint = getSum(pointA, d1)
print(intersectionPoint[0], intersectionPoint[1])
// Function to calculate the cross product of two 2D vectors
function getCrossProduct(v1, v2) {
return v1[0] * v2[1] - v1[1] * v2[0];
}
// Function to calculate the difference between two 2D vectors
function getDifference(v1, v2) {
return [v2[0] - v1[0], v2[1] - v1[1]];
}
// Function to calculate the sum of two 2D vectors
function getSum(v1, v2) {
return [v1[0] + v2[0], v1[1] + v2[1]];
}
// Main function
function main() {
// Points of lines
const pointA = [1, 1];
const pointB = [4, 4];
const pointC = [1, 8];
const pointD = [2, 4];
// Direction vector d1
const d1 = getDifference(pointA, pointB);
// Direction vector d2
const d2 = getDifference(pointC, pointD);
// Calculate t1
const t1 = getCrossProduct(getDifference(pointA, pointC), d2) / getCrossProduct(d1, d2);
// Calculate the scaled direction vector d1
const scaledD1 = [d1[0] * t1, d1[1] * t1];
// Calculate the intersection point by adding the scaled direction vector to pointA
const intersectionPoint = getSum(pointA, scaledD1);
// Output the intersection point
console.log(intersectionPoint[0] + " " + intersectionPoint[1]);
}
// Invoke the main function
main();
Output
2.4 2.4
Click here to know about finding the intersection point using equation of lines.
Practice Problems on Basic Geometry for Competitive Programming:
Problem | Problem Link |
|---|---|