CSS Flexbox, short for Flexible Box Layout, offers a streamlined way to design adaptable and visually appealing layouts. It works primarily in one dimension (row or column) to intelligently distribute space among elements within a container.
This results in clean alignment and responsive designs that work seamlessly across different screen sizes – perfect for crafting both smaller components and overall webpage structure.
Features of flexbox:
- A lot of flexibility is given.
- Arrangement & alignment of items.
- Proper spacing
- Order & Sequencing of items.
- Bootstrap 4 is built on top of the flex layout.
Before the Flexbox Model:
- Block: It is used to make sections in web pages.
- Inline: It is used for text.
- Table: It is used for two-dimensional table data.
- Positioned: It is used for the explicit position of an element.
There are 2 main components of the Flexbox:
- Flex Container: The parent "div" which contains various divisions is called a flex container.
- Flex Items: The items inside the container "div" are flex items.
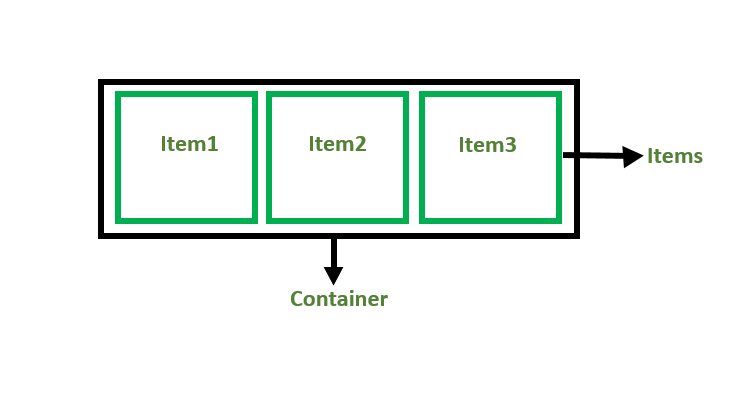
For creating the flexbox, we need to create a flex container along with setting the display property to flex.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Flexbox Tutorial</title>
<style>
.flex-container {
display: flex;
background-color: #32a852;
}
.flex-container div {
background-color: #c9d1cb;
margin: 10px;
padding: 10px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>GeeksforGeeks</h2>
<h4> Flexbox</h4>
<div class="flex-container">
<div>Item1</div>
<div>Item2</div>
<div>Item3</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Output:

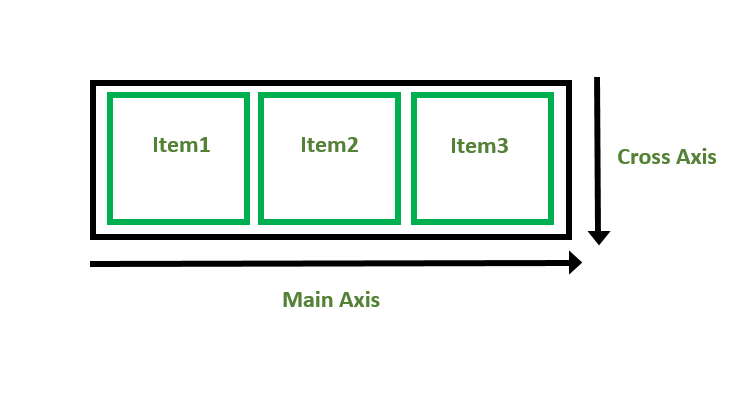
Flexbox Axes: While working with Flexbox, we deal with 2 axes:
- Main Axis
- Cross Axis
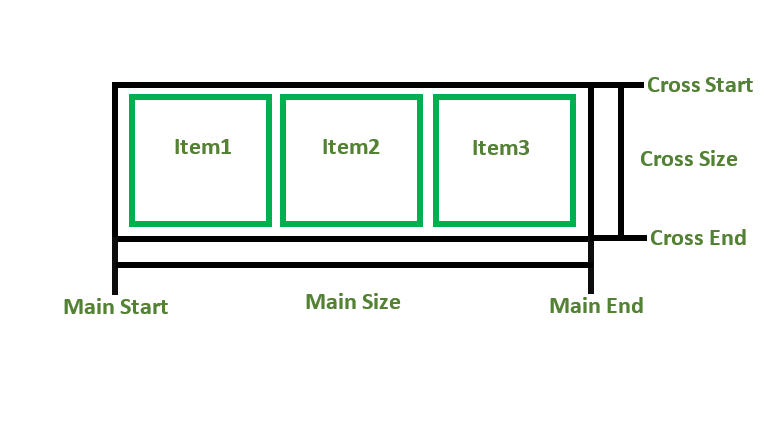
Main Axis:
- By default, the main axis runs from left to right.
- Main Start: The start of the main axis is called Main Start.
- Main Size: The length between Main Start and Main End is called Main Size.
- Main End: The endpoint is called Main End.
- Main And Cross Axis
left to right:
flex-direction: row;right to left:
flex-direction: row-reverse;top to bottom:
flex-direction: column;bottom to top:
flex-direction: column-reverse;Cross Axis:
The cross axis will be perpendicular to the main axis.
- By default, Cross Axis runs perpendicular to the Main Axis i.e. from top to bottom.
- Cross Start: The start of the Cross axis is called Cross Start.
- Cross Size: The length between Cross Start and Cross End is called Cross Size.
- Cross End: The endpoint is called Cross End.
Supported Browsers:
- Google Chrome 29.0
- Firefox 22.0
- Microsoft Edge 11.0
- Opera 48.0
- Safari 10.0