DNS stands for Domain Name System. For the implementation of the simple DNS resolver in Java is allowed to translate the domain names into the corresponding IP addresses in the programmatically. Domain Name System (DNS) plays a crucial component of internet communication and translates human-readable domain names such as "example.com" and "google.com" are converted into machine-readable IP addresses such as "93.184.216.34" and "142.251.42.110".
In Java, you also implement the DNS resolver with the help of the "InetAddress" class can be provided in the "java.net" package. This class provides the methods to perform the DNS lookups and retrieve the IP addresses combined with the domain names. Implementing the DNS resolver in Java is used for the different network applications where you will need to programmatically resolve the domain names to the IP addresses like building the network tools, custom DNS clients, and web crawlers.
Prerequisites:
The following are the prerequisites that are used to implement a simple DNS resolver in Java:
- Java Programming
- Networking Concepts
- Exception Handling
- Testing Environment
Note: The above prerequisite knowledge is helpful to implement the DNS resolver in Java as described in the subsequent sections.
Implementation of a Simple DNS Resolver in Java
Step 1: Open Eclipse and create a Dynamic web project and Create a Java class for DNS resolver in the Dynamic web project, and name it as "DNSResolver".
The below figure shows the path of the DNSResolver.java class file.
Step 2: Write the following DNS resolver code in DNSResolver. java file.
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public class DNSResolver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Obtain domain name from user input
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter domain name: ");
String domain = scanner.nextLine();
scanner.close();
// DNS resolution code will go here
try {
// Perform DNS lookup
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName(domain);
System.out.println("IP Address for " + domain + " is: " + address.getHostAddress());
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
System.out.println("Unable to resolve host: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
In the above example,
- Import the "java.net.InetAddress" used for resolving the DNS.
- We use "getByName()" method of the "InetAddress" class to resolved IP address for given domain by the programmer.
- We catch the "UnknownHostException" for handling the cases where will be the domain did not be solved the error or exception.
Step 3: Run the program
- we can run the program by right click on the "DNSResolver.java" file.
- After that we can select the "Run As" > "Java Application".
- After completion of run the file, the output will be shown as below in your console window.
- If you have any errors or exceptions, the above code will be handled the exceptions and if domain cannot be resolved, it will print the error message in the console window.
Output:
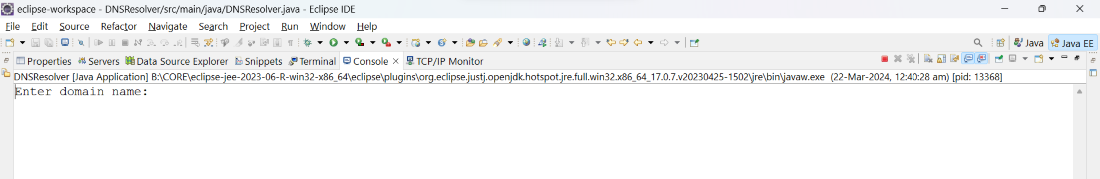
Before Enter the domain name
- After you run the program, it will ask the domain name.
- After you enter the domain name, it will show the IP address of the given domain name as shown below.
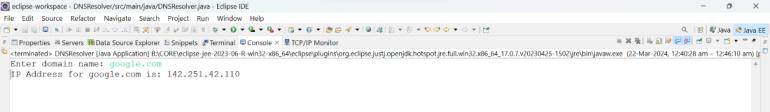
After enter the domain name
Step 4: Test with different domains
You can test the DNS resolver with the different domains at the time of execution in your console window.