An enum, short for "enumerated type", is a special data type in programming languages that allows us to define a set of named constants. These constants are essentially unchangeable variables that represent a fixed collection of possible values. Each contants can be accessed by its name. Enums are very similar to constants but they offer more data structure. we will learn about creating enums in JavaScript, exploring their significance in code organization and readability, along with practical implementation approaches using closures and other techniques.
These are the following approaches:
Using Object Literal with Object.freeze()
In this approach, we are using Object.freeze() method. Let's consider the sizes of a T-shirt: Small, Medium, Large and Extra Large. Now let's create an object which represents this available T-shirt sizes and then freeze it using Object.freeze(). This method freezes an object, preventing any additions, deletions, or modifications to its properties.
Example: This example shows the creation of enums using Object.freeze() method.
const TShirtSizes = Object.freeze({
SMALL: 'S',
MEDIUM: 'M',
LARGE: 'L',
EXTRA_LARGE: 'XL'
});
console.log(TShirtSizes.MEDIUM);
Output
M
Note: If we try to change the TShirtSizes object then it will throw TypeError, because we had enabled Strict mode.
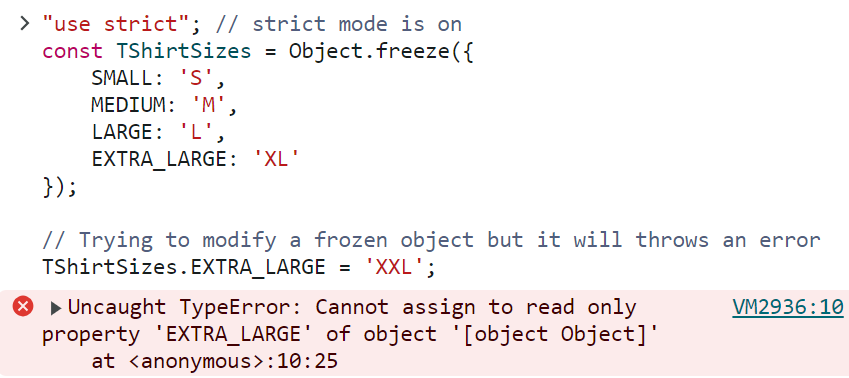
"use strict"; // strict mode is on
const TShirtSizes = Object.freeze({
SMALL: 'S',
MEDIUM: 'M',
LARGE: 'L',
EXTRA_LARGE: 'XL'
});
// Trying to modify a frozen
// object but it will throws an error
TShirtSizes.EXTRA_LARGE = 'XXL';
Output: As demonstrated earlier, attempting to modify the enum after freezing it results in no change, but if strict mode is enabled, it will throw a TypeError.
Note: It's a common convention in many programming languages, including JavaScript, to write enum constants in all capital letters to distinguish them from other variables and constants.
Using ES6 Symbols
- We firstly create an object TShirtSizes
- Inside the object, we define symbols for each size using Symbol()
- The orderTShirt function takes a size argument.
- We had performed a strict comparison (!==) between the argument and each enum member (symbol) to ensure a valid size is provided.
- If a valid size is used, then the order is been processed.
- If anyone attempt to use an invalid string value (e.g. "Medium") throws an error due to the strict comparison with symbols.
Example: This example shows how to create an enum using ES6 Symbols.
const TShirtSizes = {
SMALL: Symbol('Small'),
MEDIUM: Symbol('Medium'),
LARGE: Symbol('Large'),
EXTRA_LARGE: Symbol('Extra Large')
};
function orderTShirt(size) {
if (size !== TShirtSizes.SMALL &&
size !== TShirtSizes.MEDIUM &&
size !== TShirtSizes.LARGE &&
size !== TShirtSizes.EXTRA_LARGE) {
throw new Error('Invalid T-Shirt size!');
}
console.log(`Processing order for
size: ${String(size)}`);
}
orderTShirt(TShirtSizes.MEDIUM);
Output
Processing order for
size: Symbol(Medium)
Let's see if we try to provide a string argument:
const TShirtSizes = {
SMALL: Symbol('Small'),
MEDIUM: Symbol('Medium'),
LARGE: Symbol('Large'),
EXTRA_LARGE: Symbol('Extra Large')
};
function orderTShirt(size) {
if (size !== TShirtSizes.SMALL &&
size !== TShirtSizes.MEDIUM &&
size !== TShirtSizes.LARGE &&
size !== TShirtSizes.EXTRA_LARGE) {
throw new Error('Invalid T-Shirt size!');
}
console.log(`Processing order for
size: ${String(size)}`);
}
orderTShirt("Medium");
Output:

Using Closures
- Inside the Immediately Invoked Function Expression (IIFE), we define an object Enum containing the enum values.
- We then return the result of calling createEnum(Enum), effectively creating a closure over the Enum object, allowing read-only access to its values through the returned function.
Example: This example shows how to create an enum using Closures.
const Colors = (function () {
const Enum = {
RED: 'RED',
GREEN: 'GREEN',
BLUE: 'BLUE'
};
return (key) => {
return Enum[key];
};
})();
console.log(Colors('RED'));
console.log(Colors('GREEN'));
console.log(Colors('BLUE'));
Output
RED GREEN BLUE
Note: Attempting to modify the enum directly will result in an error, as the values cannot be modified after the closure is created.
const Colors = (function () {
const Enum = {
RED: 'RED',
GREEN: 'GREEN',
BLUE: 'BLUE'
};
return (key) => {
return Enum[key];
};
})();
// Attempting to modify the enum
// This will throw an Reference error
Colors('RED') = 'YELLOW';
Output: This error occurs when trying to assign a new value to the enum, which is not allowed because the enum is created using closures, providing read-only access to its values.
