CSS (Cascading Styling Sheet) is the language that defines the presentation of a document written in a markup language like HTML. CSS is the language that transforms a basic HTML structure into a user-friendly and visually beautiful webpage. It can change the font, color, size, and spacing of content, split it into multiple columns, or add animations and other features.
In this CSS Tutorial, we'll learn all the basic to advanced concepts of CSS such as CSS properties, selectors, functions, media queries, and more.
What is CSS?
CSS, or Cascading Style Sheets, is the secret sauce that styles all the websites you visit. It's a simple language that controls how HTML elements (like text, images, and buttons) are displayed on a webpage. With CSS, you can change the font size and color, add backgrounds, and control the layout, transforming a basic webpage into a visually appealing and user-friendly experience.

CSS has 3 ways to style your HTML:
- Inline: Add styles directly to HTML elements (limited use).
- Internal: Put styles inside the HTML file in a <style> tag.
- External: Create a separate CSS file (.css) and link it to your HTML.
Table of Content
Basic CSS Example
In this example, we will use all of them with different properties.
<!-- File name: index.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- Importing External CSS -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="style.css" />
<!-- Using Internal CSS -->
<style>
h2 {
color: green;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Using Inline CSS -->
<h2 style="text-align: center;">Welcome To GFG</h2>
<p>CSS Tutorial - GeeksforGeeks</p>
</body>
</html>
/* External CSS */
/* File name: style.css */
p {
text-align: center;
}
Output:

CSS Example Output
Also Check: Recent Articles on CSS
CSS Tutorial
Introduction to Modern CSS
CSS Fundamentals
Understanding CSS basics is necessary whether you're an experienced developer or just starting your web journey. Let's explore some key CSS concepts.
CSS Styling Techniques
CSS describes how HTML elements should be presented on the web page. It provides colors, positions to the HTML elements, etc., create animations, and amplify your web page.
- CSS Fonts
- CSS Colors
- CSS Backgrounds
- CSS Borders
- CSS Grid
- CSS Flexbox
- CSS Images
- CSS Lists
- CSS Counters
- CSS Columns
- CSS Conditional Rules
- CSS Logical Properties
- CSS Math functions
CSS Responsive Design and Media Queries
While developing a site, it has to be mobile-friendly and responsive. Here, we discuss all the concepts that help you make your website responsive.
Advanced CSS Topics
Let's Move further with the Advanced CSS. Learn advanced styling techniques and master your modern web design and development skills in 2024.
CSS Online Quizzes
To achieve a solid understanding of CSS, it’s essential to engage with CSS quizzes and MCQs. These CSS quizzes can enhance your ability to solve similar questions and improve your problem-solving skills.
Here are some quiz articles related to CSS 3:
CSS Practical Projects
Getting only the theoretical knowledge will be of no use unless and until you don’t work on some real-time projects. Working on such HTML & CSS projects will test your CSS knowledge and you will get some hands-on experience.
- Design GeeksforGeeks logo
- Meet the Team Page Design
- Tribute Page Design
- Design a web page
- Contact Us Page Design
- Create Browsers Window
- Design Email Newsletter
CSS Interview Preparation
- Don't miss our CSS Interview Questions and Answers before going for your interview.
- CSS CheastSheet for Beginners (2024) - A Basic Guide to CSS
CSS Preprocessors
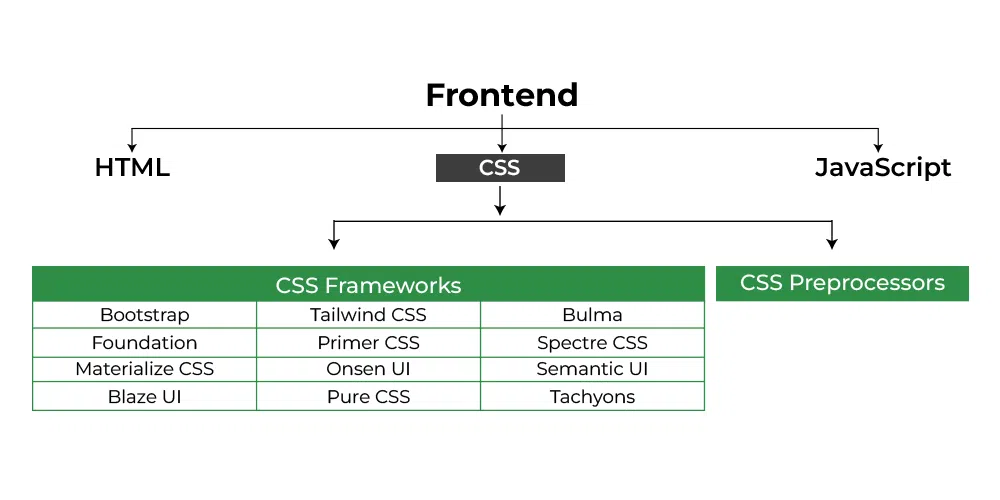
CSS Preprocessors introduce features like variables, nesting, and mixins to enhance the functionality, maintainability, and organization of stylesheets. Some popular preprocessors are:
CSS Frameworks
CSS frameworks are pre-prepared libraries of CSS code and sometimes JavaScript, designed to simplify and expedite the process of web development.
These CSS frameworks provide a set of standardized, reusable components and a predefined structure, allowing developers to create responsive and aesthetically pleasing websites with reduced effort.
Other Resources
CSS Versions
- CSS1: The foundation, released in 1996, introduced basic styling capabilities for fonts, colors, and margins.
- CSS2: Expanded in 1998, adding positioning elements, pseudo-classes, and improved layout options.
- CSS 2.1: Further refinements in 2004, including improvements to inheritance and box model properties.
- CSS3: Introduced from 2001 onwards, CSS3 isn't a single version but a collection of modules adding features like animations, media queries, and web fonts. It's constantly evolving.
- CSS4 (Ongoing):
- CSS is continuously evolving.
- Recent developments focus on variables (custom properties), enhanced grid and flexbox layouts, subgrid, aspect-ratio property, and color manipulation functions.
Why learn CSS?
1. Enhance Visual Appeal: CSS allows you to style your web pages, making them visually appealing and engaging. Here’s why it matters:
- User Experience (UX): Well-designed websites attract and retain users. CSS enables you to create beautiful layouts, choose fonts, and apply colors that resonate with your audience.
- Branding: Consistent styling across your site reinforces your brand identity. CSS ensures your website aligns with your brand’s aesthetics.
2. Responsive Design: In today’s mobile-first world, responsive design is crucial. CSS empowers you to:
- Media Queries: Adapt your layout based on screen size (desktop, tablet, mobile).
- Flexbox and Grid: Create flexible, adaptive designs that look great on any device.
3. SEO Benefits: CSS indirectly impacts your site’s SEO. Here’s how:
- Page Load Speed: Well-organized CSS files load faster, improving user experience. Google considers page speed as a ranking factor.
- Structured Content: Properly styled HTML (thanks to CSS) enhances readability for search engines and users.
- Mobile Friendliness: Responsive CSS ensures your site performs well on mobile devices, positively affecting rankings.
4. Efficient Maintenance: CSS promotes clean code and separation of concerns:
- Modularity: Separate CSS files allow easy updates without affecting other parts of your site.
- Consistency: Apply styles consistently across your site using classes and IDs.
5. Career Opportunities: Learning CSS opens doors to various roles:
- Front-End Developer: Mastering CSS is essential for front-end development.
- Web Designer: CSS skills are fundamental for creating stunning web layouts.
- Full-Stack Developer: Understanding CSS complements back-end skills.
CSS - Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Full Form of CSS?
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets. It is a style sheet language used to describe the presentation and formatting of a document written in HTML or XML.
What are the types of CSS?
There are three types of CSS which are given below:
- Inline CSS: Inline CSS contains the CSS property in the body section attached to the element.
- Internal or Embedded CSS: The CSS ruleset should be within the HTML file in the head section i.e. the CSS is embedded within the HTML file.
- External CSS: External CSS contains a separate CSS file that contains only style properties with the help of tag attributes.
How do I link an external CSS file to an HTML document?
Use the <link> element within the <head> section of your HTML document. Example: <link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css">
What is the purpose of the 'box model' in CSS?
The box model is a fundamental concept in CSS that describes the layout of elements. It consists of content, padding, border, and margin, which collectively determine the size and spacing of an element.
How can I center an element horizontally and vertically in CSS?
To center horizontally, use margin: auto; on the element. For vertical centering, consider using Flexbox (display: flex; align-items: center; justify-content: center;) or Grid (display: grid; place-items: center;).
What is the difference between 'margin' and 'padding' in CSS?
Margin is the space outside an element, creating space between the element and its surrounding elements. Padding is the space inside an element, creating space between the element's content and its border.
How do media queries contribute to responsive design in CSS?
Media queries allow developers to apply styles based on characteristics such as screen width, height, or device orientation. They are crucial for creating responsive designs that adapt to different devices and screen sizes.