SQL
Question 11
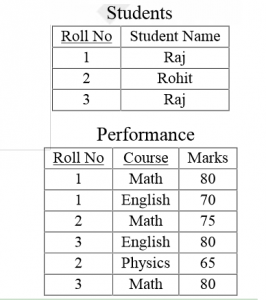
Consider the set of relations shown below and the SQL query that follows.
Students: (Roll_number, Name, Date_of_birth) Courses: (Course number, Course_name, Instructor) Grades: (Roll_number, Course_number, Grade)
select distinct Name
from Students, Courses, Grades
where Students. Roll_number = Grades.Roll_number
and Courses.Instructor = Korth
and Courses.Course_number = Grades.Course_number
and Grades.grade = A
Which of the following sets is computed by the above query?
Question 12
Given relations r(w, x) and s(y, z), the result of
SELECT DISTINCT w, x
FROM r, s
is guaranteed to be same as r, provided
Question 13
In SQL, relations can contain null values, and comparisons with null values are treated as unknown. Suppose all comparisons with a null value are treated as false. Which of the following pairs is not equivalent?
Question 14
Consider the following three table to store student enrollements in different courses.
Student(EnrollNo, Name) Course(CourseID, Name) EnrollMents(EnrollNo, CourseID)
What does the following query do?
SELECT S.Name
FROM Student S, Course C, Enrollments E
WHERE S.EnrollNo = E.EnrollNo AND
C.Name = "DBMS" AND
E.CourseID = C.CourseID AND
S.EnrollNo IN
(SELECT S2.EnrollNo
FROM Student S2, Course C2, Enrollments E2
WHERE S2.EnrollNo = E2.EnrollNo AND
E2.CourseID = C2.CourseID
C2.Name = "OS")
Question 15
Consider the following Employee table
ID salary DeptName 1 10000 EC 2 40000 EC 3 30000 CS 4 40000 ME 5 50000 ME 6 60000 ME 7 70000 CS
How many rows are there in the result of following query?
SELECT E.ID
FROM Employee E
WHERE EXISTS (SELECT E2.salary
FROM Employee E2
WHERE E2.DeptName = \'CS\'
AND E.salary > E2.salary)
Question 16
Question 17
Consider the following relation
Cinema (theater, address, capacity)Which of the following options will be needed at the end of the SQL query
SELECT P1. address FROM Cinema P1Such that it always finds the addresses of theaters with maximum capacity?
Question 18
A company maintains records of sales made by its salespersons and pays them commission based on each individual\'s total sales made in a year. This data is maintained in a table with following schema:
salesinfo = (salespersonid, totalsales, commission)
In a certain year, due to better business results, the company decides to further reward its salespersons by enhancing the commission paid to them as per the following formula:
If commission < = 50000, enhance it by 2%
If 50000 < commission < = 100000, enhance it by 4%
If commission > 100000, enhance it by 6%
The IT staff has written three different SQL scripts to calculate enhancement for each slab, each of these scripts is to run as a separate transaction as follows:
| T1 | Update salesinfo Set commission = commission * 1.02 Where commission < = 50000; |
| T2 | Update salesinfo Set commission = commission * 1.04 Where commission > 50000 and commission is < = 100000; |
| T3 | Update salesinfo Set commission = commission * 1.06 Where commission > 100000; |
Which of the following options of running these transactions will update the commission of all salespersons correctly
Question 19
A table \'student\' with schema (roll, name, hostel, marks), and another table \'hobby\' with schema (roll, hobbyname) contains records as shown below:
The following SQL query is executed on the above tables:
| Roll | Name | Hostel | Marks |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1798 | Manoj Rathod | 7 | 95 |
| 2154 | Soumic Banerjee | 5 | 68 |
| 2369 | Gumma Reddy | 7 | 86 |
| 2581 | Pradeep Pendse | 6 | 92 |
| 2643 | Suhas Kulkarni | 5 | 78 |
| 2711 | Nitin Kadam | 8 | 72 |
| 2872 | Kiran Vora | 5 | 92 |
| 2926 | Manoj Kunkalikar | 5 | 94 |
| 2959 | Hemant Karkhanis | 7 | 88 |
| 3125 | Rajesh Doshi | 5 | 82 |
| Roll | Hobbyname |
|---|---|
| 1798 | chess |
| 1798 | music |
| 2154 | music |
| 2369 | swimming |
| 2581 | cricket |
| 2643 | chess |
| 2643 | hockey |
| 2711 | volleyball |
| 2872 | football |
| 2926 | cricket |
| 2959 | photography |
| 3125 | music |
| 3125 | chess |
select hostel from student natural join hobby where marks > = 75 and roll between 2000 and 3000;Relations S and H with the same schema as those of these two tables respectively contain the same information as tuples. A new relation S’ is obtained by the following relational algebra operation: S’ = ∏hostel ((σs.roll = H.roll (σmarks > 75 and roll > 2000 and roll < 3000 (S)) X (H)) The difference between the number of rows output by the SQL statement and the number of tuples in S’ is
Question 20
In an inventory management system implemented at a trading corporation, there are several tables designed to hold all the information. Amongst these, the following two tables hold information on which items are supplied by which suppliers, and which warehouse keeps which items along with the stock-level of these items.
Supply = (supplierid, itemcode)
Inventory = (itemcode, warehouse, stocklevel)
For a specific information required by the management, following SQL query has been written
Select distinct STMP.supplierid
From Supply as STMP
Where not unique (Select ITMP.supplierid
From Inventory, Supply as ITMP
Where STMP.supplierid = ITMP.supplierid
And ITMP.itemcode = Inventory.itemcode
And Inventory.warehouse = \'Nagpur\');
For the warehouse at Nagpur, this query will find all suppliers who
There are 66 questions to complete.
Last Updated :
Take a part in the ongoing discussion