50 Computer Networks MCQs with Answers
Question 21
Consider a source computer(S) transmitting a file of size 106 bits to a destination computer(D)over a network of two routers (R1 and R2) and three links(L1, L2, and L3). L1connects S to R1; L2 connects R1 to R2; and L3 connects R2 to D.Let each link be of length 100 km. Assume signals travel over each link at a speed of 108 meters per second.Assume that the link bandwidth on each link is 1Mbps. Let the file be broken down into 1000 packets each of size 1000 bits. Find the total sum of transmission and propagation delays in transmitting the file from S to D?
Question 22
Consider a network with five nodes, N1 to N5, as shown below.
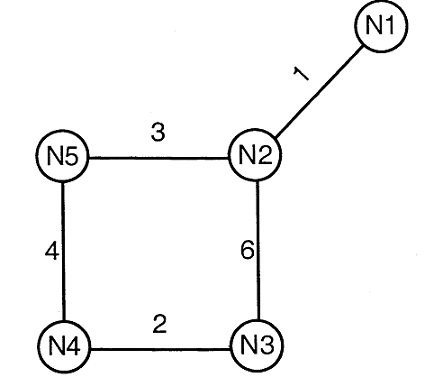 The network uses a Distance Vector Routing protocol. Once the routes have stabilized, the distance vectors at different nodes are as following.
N1: (0, 1, 7, 8, 4)
N2: (1, 0, 6, 7, 3)
N3: (7, 6, 0, 2, 6)
N4: (8, 7, 2, 0, 4)
N5: (4, 3, 6, 4, 0)
Each distance vector is the distance of the best known path at the instance to nodes, N1 to N5, where the distance to itself is 0. Also, all links are symmetric and the cost is identical in both directions. In each round, all nodes exchange their distance vectors with their respective neighbors. Then all nodes update their distance vectors. In between two rounds, any change in cost of a link will cause the two incident nodes to change only that entry in their distance vectors. 52. The cost of link N2-N3 reduces to 2(in both directions). After the next round of updates, what will be the new distance vector at node, N3.
The network uses a Distance Vector Routing protocol. Once the routes have stabilized, the distance vectors at different nodes are as following.
N1: (0, 1, 7, 8, 4)
N2: (1, 0, 6, 7, 3)
N3: (7, 6, 0, 2, 6)
N4: (8, 7, 2, 0, 4)
N5: (4, 3, 6, 4, 0)
Each distance vector is the distance of the best known path at the instance to nodes, N1 to N5, where the distance to itself is 0. Also, all links are symmetric and the cost is identical in both directions. In each round, all nodes exchange their distance vectors with their respective neighbors. Then all nodes update their distance vectors. In between two rounds, any change in cost of a link will cause the two incident nodes to change only that entry in their distance vectors. 52. The cost of link N2-N3 reduces to 2(in both directions). After the next round of updates, what will be the new distance vector at node, N3.
 The network uses a Distance Vector Routing protocol. Once the routes have stabilized, the distance vectors at different nodes are as following.
N1: (0, 1, 7, 8, 4)
N2: (1, 0, 6, 7, 3)
N3: (7, 6, 0, 2, 6)
N4: (8, 7, 2, 0, 4)
N5: (4, 3, 6, 4, 0)
Each distance vector is the distance of the best known path at the instance to nodes, N1 to N5, where the distance to itself is 0. Also, all links are symmetric and the cost is identical in both directions. In each round, all nodes exchange their distance vectors with their respective neighbors. Then all nodes update their distance vectors. In between two rounds, any change in cost of a link will cause the two incident nodes to change only that entry in their distance vectors. 52. The cost of link N2-N3 reduces to 2(in both directions). After the next round of updates, what will be the new distance vector at node, N3.
The network uses a Distance Vector Routing protocol. Once the routes have stabilized, the distance vectors at different nodes are as following.
N1: (0, 1, 7, 8, 4)
N2: (1, 0, 6, 7, 3)
N3: (7, 6, 0, 2, 6)
N4: (8, 7, 2, 0, 4)
N5: (4, 3, 6, 4, 0)
Each distance vector is the distance of the best known path at the instance to nodes, N1 to N5, where the distance to itself is 0. Also, all links are symmetric and the cost is identical in both directions. In each round, all nodes exchange their distance vectors with their respective neighbors. Then all nodes update their distance vectors. In between two rounds, any change in cost of a link will cause the two incident nodes to change only that entry in their distance vectors. 52. The cost of link N2-N3 reduces to 2(in both directions). After the next round of updates, what will be the new distance vector at node, N3.Question 23
Consider the data given in above question. Suppose the weights of all unused links in the previous question are changed to 2 and the distance vector algorithm is used again until all routing tables stabilize. How many links will now remain unused?
Question 24
Classless Inter-domain Routing (CIDR) receives a packet with address 131.23.151.76. The router’s routing table has the following entries:
Prefix Output Interface Identifier 131.16.0.0/12 3 131.28.0.0/14 5 131.19.0.0/16 2 131.22.0.0/15 1The identifier of the output interface on which this packet will be forwarded is ______.
Question 25
Two computers C1 and C2 are configured as follows. C1 has IP address 203.197.2.53 and netmask 255.255.128.0. C2 has IP address 203.197.75.201 and netmask 255.255.192.0. which one of the following statements is true?
Question 27
In cryptography, the following uses transposition ciphers and the keyword is LAYER. Encrypt the following message. (Spaces are omitted during encryption)
WELCOME TO NETWORK SECURITY !
Question 30
If there are N people in the world and are using secret key encryption/decryption for privacy purpose, then number of secret keys required will be:
There are 50 questions to complete.
Last Updated :
Take a part in the ongoing discussion