GATE-CS-2006
Question 1
Question 2
Let X, Y, Z be sets of sizes x, y and z respectively. Let W = X x Y. Let E be the set of all subsets of W. The number of functions from Z to E is:
Question 3
Question 4
A relation R is defined on ordered pairs of integers as follows: (x,y) R(u,v) if x < u and y > v. Then R is:
Question 5
For which one of the following reasons does Internet Protocol (IP) use the timeto- live (TTL) field in the IP datagram header
Question 6
Question 7
S -> S * E S -> E E -> F + E E -> F F -> idConsider the following LR(0) items corresponding to the grammar above.
(i) S -> S * .E (ii) E -> F. + E (iii) E -> F + .EGiven the items above, which two of them will appear in the same set in the canonical sets-of-items for the grammar?
Question 8
You are given a free running clock with a duty cycle of 50% and a digital waveform f which changes only at the negative edge of the clock. Which one of the following circuits (using clocked D flip-flops) will delay the phase of f by 180°?
[caption width="800"]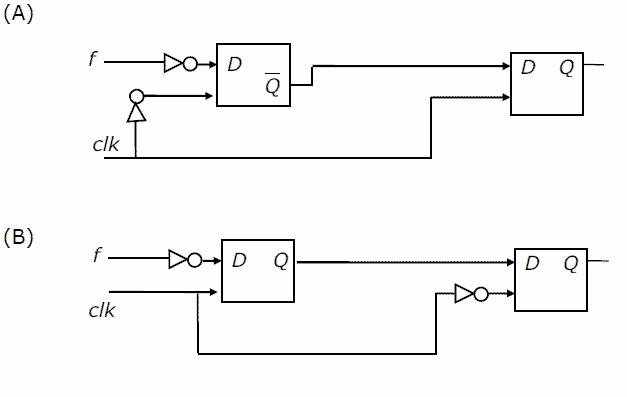 [/caption][caption width="800"]
[/caption][caption width="800"]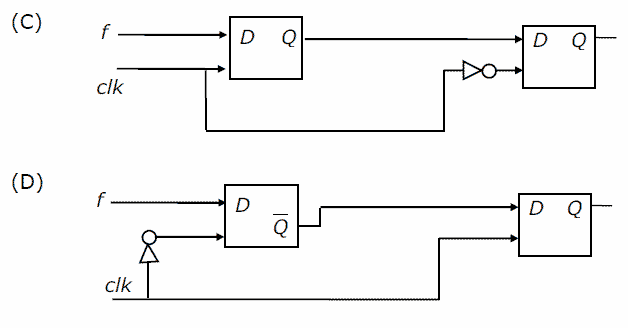 [/caption]
[/caption]Question 9
A CPU has 24-bit instructions. A program starts at address 300 (in decimal). Which one of the following is a legal program counter (all values in decimal)?
Question 10
There are 84 questions to complete.