Gate IT 2008
Question 61
Data transmitted on a link uses the following 2D parity scheme for error detection:
Each sequence of 28 bits is arranged in a 4×7 matrix (rows r0 through r3, and columns d7 through d1) and is padded with a column d0 and row r4 of parity bits computed using the Even parity scheme. Each bit of column d0 (respectively, row r4) gives the parity of the corresponding row (respectively, column). These 40 bits are transmitted over the data link.
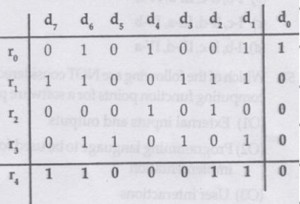
The table shows data received by a receiver and has n corrupted bits. What is the minimum possible value of n?

The table shows data received by a receiver and has n corrupted bits. What is the minimum possible value of n?
Question 62
Two popular routing algorithms are Distance Vector(DV) and Link State (LS) routing. Which of the following are true?
(S1) Count to infinity is a problem only with DV and not LS routing
(S2) In LS, the shortest path algorithm is run only at one node
(S3) In DV, the shortest path algorithm is run only at one node
(S4) DV requires lesser number of network messages than LS
(S1) Count to infinity is a problem only with DV and not LS routing
(S2) In LS, the shortest path algorithm is run only at one node
(S3) In DV, the shortest path algorithm is run only at one node
(S4) DV requires lesser number of network messages than LS
Question 63
Which of the following statements are TRUE?
(S1) TCP handles both congestion and flow control
(S2) UDP handles congestion but not flow control
(S3) Fast retransmit deals with congestion but not flow control
(S4) Slow start mechanism deals with both congestion and flow control
(S1) TCP handles both congestion and flow control
(S2) UDP handles congestion but not flow control
(S3) Fast retransmit deals with congestion but not flow control
(S4) Slow start mechanism deals with both congestion and flow control
Question 64
The three way handshake for TCP connection establishment is shown below.
[caption width="800"]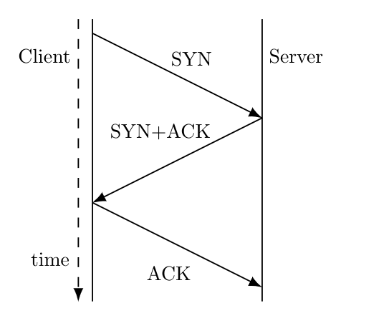 [/caption]
[/caption]
Which of the following statements are TRUE?
(S1) Loss of SYN + ACK from the server will not establish a connection
(S2) Loss of ACK from the client cannot establish the connection
(S3) The server moves LISTEN → SYN_RCVD → SYN_SENT → ESTABLISHED in the state machine on no packet loss
(S4) The server moves LISTEN → SYN_RCVD → ESTABLISHED in the state machine on no packet loss.
Question 65
The total number of keys required for a set of n individuals to be able to communicate with each other using secret key and public key crypto-systems, respectively are:
Question 66
A Binary Search Tree (BST) stores values in the range 37 to 573. Consider the following sequence of keys.
Suppose the BST has been unsuccessfully searched for key 273. Which all of the above sequences list nodes in the order in which we could have encountered them in the search?
I. 81, 537, 102, 439, 285, 376, 305
II. 52, 97, 121, 195, 242, 381, 472
III. 142, 248, 520, 386, 345, 270, 307
IV. 550, 149, 507, 395, 463, 402, 270
Suppose the BST has been unsuccessfully searched for key 273. Which all of the above sequences list nodes in the order in which we could have encountered them in the search?
Question 67
A Binary Search Tree (BST) stores values in the range 37 to 573. Consider the following sequence of keys.
I. 81, 537, 102, 439, 285, 376, 305
II. 52, 97, 121, 195, 242, 381, 472
III. 142, 248, 520, 386, 345, 270, 307
IV. 550, 149, 507, 395, 463, 402, 270
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
I. 81, 537, 102, 439, 285, 376, 305
II. 52, 97, 121, 195, 242, 381, 472
III. 142, 248, 520, 386, 345, 270, 307
IV. 550, 149, 507, 395, 463, 402, 270
Which of the following statements is TRUE?
Question 69
Student (school-id, sch-roll-no, sname, saddress)
School (school-id, sch-name, sch-address, sch-phone)
Enrolment(school-id sch-roll-no, erollno, examname)
ExamResult(erollno, examname, marks)
What does the following SQL query output?
C
School (school-id, sch-name, sch-address, sch-phone)
Enrolment(school-id sch-roll-no, erollno, examname)
ExamResult(erollno, examname, marks)
What does the following SQL query output?
SELECT sch-name, COUNT (*)
FROM School C, Enrolment E, ExamResult R
WHERE E.school-id = C.school-id
AND
E.examname = R.examname AND E.erollno = R.erollno
AND
R.marks = 100 AND S.school-id IN (SELECT school-id
FROM student
GROUP BY school-id
HAVING COUNT (*) > 200)
GROUP By school-id
/* Add code here. Remove these lines if not writing code */
Question 70
A binary tree with n > 1 nodes has n1, n2 and n3 nodes of degree one, two and three respectively. The degree of a node is defined as the number of its neighbors.
n3 can be expressed as
n3 can be expressed as
There are 82 questions to complete.
Last Updated :
Take a part in the ongoing discussion