Convex Lenses and Concave Lenses are the types of spherical lenses, which are optical devices that are transparent in nature. There are several differences between Convex and Concave Lenses which we will cover in this article in detail such as their distinct characteristics and uses.
Knowing the difference between Convex and Concave Lenses is critical in grasping their function in different optical systems such as binoculars, optical microscopes, telescopes, etc.
This article explores the difference between convex and concave lens in detail including their definition with diagrams and key characteristics as well.

Table of Content
Convex Lenses and Concave Lens
Convex lens- Thicker in the middle and thinner on the edges, a convex lens is able to form real images by converging light rays when the object is outside the focal point and virtual images when it's closer than the focal length.
Concave lens: Forming only virtual images, a concave lens is thinner at the center and thicker at the edges, diverging light rays. It has a virtual focal point instead of a real one and rays appear to originate from it.
What is Convex Lens?
With a curved shape that bulges from the centre and tapers towards the edges, a convex lens - also referred to as a converging lens, is an optical device that is transparent. The lens is able to converge parallel rays of light that pass through it due to the fact that it's thicker at the centre than it is at the edges.
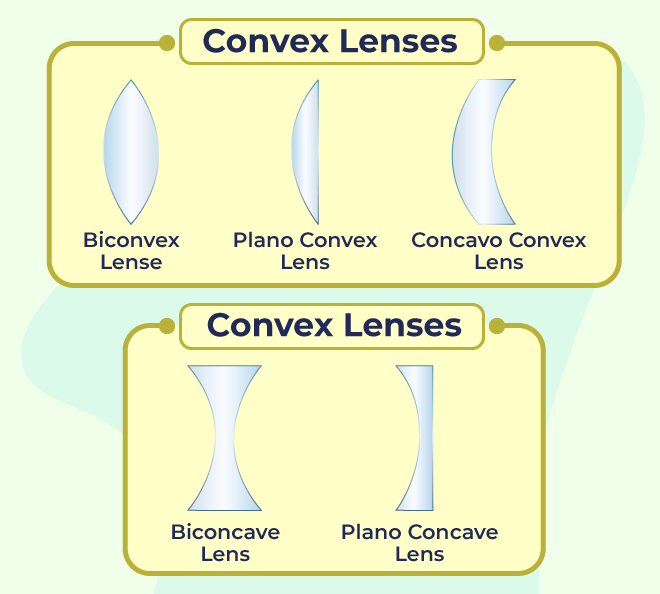
Types of Convex Lens
- Biconvex Lens: The lens has a shape, on both sides bulging towards the center. It is commonly used in magnifying glasses and simple camera lenses.
- Plano Convex Lens: This lens has one side (plano). The other side is curved outward. It is designed to focus rays to a specific point and is often found in optical instruments and projectors.
- Concavo Convex: This lens has convex face and concave face. In this lens convex face has smaller curvature.
What is Concave Lens?
A transparent optical device with a curved shape that curves inward, creating thinner centres and thicker edges is known as a concave lens or diverging lens. When passing through this type of lens, parallel rays of light spread apart or diverge, unlike convex lenses that converge light rays.
Types of Concave Lens
- Biconcave Lens: The lens curves inward on both sides causing it to become thinner towards the center. This design disperses rays. Creates virtual images. It is commonly used in eyeglasses for nearsightedness.
- Plano Concave Lens: Similar to the lens this one also has one side (plano) but curves inward on the other side. It diverges light. Finds application in specific optical systems, like beam expansion setups.
Difference Between Convex and Concave Lens
Convex lens
- A convex lens is thicker at its center and thinner at its edges, bulging outward like the exterior of a sphere.
- It is also known as a converging lens because it focuses parallel rays of light that pass through it.
- A convex lens converges parallel rays of light to a focal point on the opposite side of the lens from the light source.
- It can form real and inverted images when objects are placed beyond its focal point, and it can create virtual and upright images when objects are placed between the lens and its focal point.
- Convex lenses are commonly used in magnifying glasses, cameras, telescopes, and binoculars to focus and magnify distant objects.
- They are also used in eyeglasses to correct farsightedness (hyperopia) and presbyopia.
Concave lens
- A concave lens is thinner at its center and thicker at its edges, curving inward to create a hollow or dented appearance.
- It is known as a diverging lens because it spreads out parallel rays of light that pass through it.
- A concave lens causes parallel rays of light to diverge as if they originated from a virtual focal point on the same side as the light source.
- It can only produce virtual and diminished images when objects are placed on the same side as the virtual focal point.
- Concave lenses are used in eyeglasses to correct nearsightedness (myopia) and in certain scientific instruments and devices to spread out light or correct optical aberrations.
Concave vs Convex Lens - Tabular Difference
There are various key differences between the Convex Lens and Concave Lens, which are listed in the following table:
| Characteristic | Convex Lens | Concave Lens |
|---|---|---|
| Lens Shape | Thicker at the center, bulging outward | Thinner at the center, curving inward |
| Focusing | Converging lens, brings parallel rays to a focus | Diverging lens, causes parallel rays to spread out |
| Principal Focus | Real, located on the side of incoming light | Virtual, located on the same side as incoming light |
| Image Formation | Can form real or virtual images | Always forms virtual, upright, and diminished images. |
| Magnification | Can have positive or negative magnification | Always has a negative magnification. |
| Lens Thickness | Thicker at the center | Thicker at the edges. |
| Lens Curvature | Curves Outward | Curves inward. |
| Focal Length | Positive focal length | Negative focal length |
| Lens Equation | 1/f = 1/v + 1/u | 1/f = 1/v - 1/u |
| Image Size | Can be larger, smaller, or same size as object | Always smaller than object. |
| Applications | Cameras, projectors, magnifying glasses | Corrective eyeglasses, optical experiments |
| Lens Aberrations | More prone to chromatic aberration | Less prone to chromatic aberration. |
| Field of View | Widens field of view for magnification | Narrows field of view for correction. |
| Lens Types | Biconvex, Plano Convex | Biconcave, Plano Concave |
Application of Convex and Concave Lens
There are various use cases where convex and concave lenses are used in our daily lives. Some of these use cases are discussed for each lens in the following headings.
Check: Image Formation by Lenses
Application of Convex Lens
Some common used cases of Convex Lens are:
- Camera Lenses: In cameras, convex lenses are utilized to concentrate light onto the image sensor or film. This process ensures that the resulting images are clear and well-defined.
- Magnifying Glasses: When magnifying small objects, magnifying glasses employ the use of virtual, enlarged images created by convex lenses.
- Eyeglasses: Additionally, these same convex lenses can rectify hyperopia (commonly known as farsightedness) by causing incoming light rays to converge before reaching the eye's lens.
- Projectors: By focusing beams of light onto a single point, projectors aid in projecting amplified images onto screens for visual representation.
- Telescopes: These optical devices have the capability to gather and concentrate distant light from celestial bodies and remote landscapes using convex lenses. Consequently, they allow us to observe such entities with accuracy.
Check: Lens Sign Convention
Application of Concave Lens
Some commonly used cases of Concave Lens are:
- Eyeglasses: Concave lenses serve the purpose of rectifying myopia by redirecting incoming light in a way that prevents it from focusing directly on the eye's lens.
- Laser Systems: These lenses find their application in various optical devices where the spread or divergence of light is required, such as beam expanders and laser systems.
- Galilean Telescopes: Within Galilean telescopes, concave lenses play a crucial role by producing a virtual image for amplification purposes.
- When it comes to viewing aids, these types of lenses can be seen incorporated into devices like peepholes or door viewers. Their function within such tools is to offer an extended field of view to the viewer.
- In ophthalmology, certain diagnostic and testing equipment relies on concave lenses to achieve accurate results.
- Additionally, they contribute significantly to projectors and display technology. By manipulating how light disperses, these lenses enable the creation of distinct optical effects while also improving visibility within projection systems.
Related Resources,