OpenMP | Hello World program
Last Updated :
11 Jul, 2025
Imagine running a program that can split its work across multiple parts of your computer’s processor, making it faster and more efficient. This is the power of parallel programming, and tools like OpenMP make it accessible even for beginners. By tapping into the ability to run tasks simultaneously, you can unlock new possibilities for your code, whether you're building simple experiments or complex applications.
 OpenMP | Hello World program
OpenMP | Hello World programIn this article, we’ll walk through creating a parallel "Hello World" program using OpenMP in C/C++/Fortran. We’ll cover the essential steps, from including the necessary header files to setting up parallel regions and controlling the number of threads. You’ll also see how to compile and run the program, along with an explanation of the output and how threads work together in parallel.
Prerequisite:
Steps to Create a Parallel Program
Step 1:
Include the header file: We have to include the OpenMP header for our program, along with the standard header files.
//OpenMP header
#include <omp.h>
Step 2:
Specify the parallel region: In OpenMP, we need to mention the region that we are going to make as parallel using the keyword pragma omp parallel. The pragma omp parallel is used to fork additional threads to carry out the work enclosed in the parallel. The original thread will be denoted as the master thread with thread ID 0. Code for creating a parallel region would be,
#pragma omp parallel
{
//Parallel region code
}
So, here we include
#pragma omp parallel
{
printf("Hello World... from thread = %d\n",
omp_get_thread_num());
}
Step 3:
Set the number of threads: we can set the number of threads to execute the program using the external variable.
export OMP_NUM_THREADS=5
Diagram of parallel region
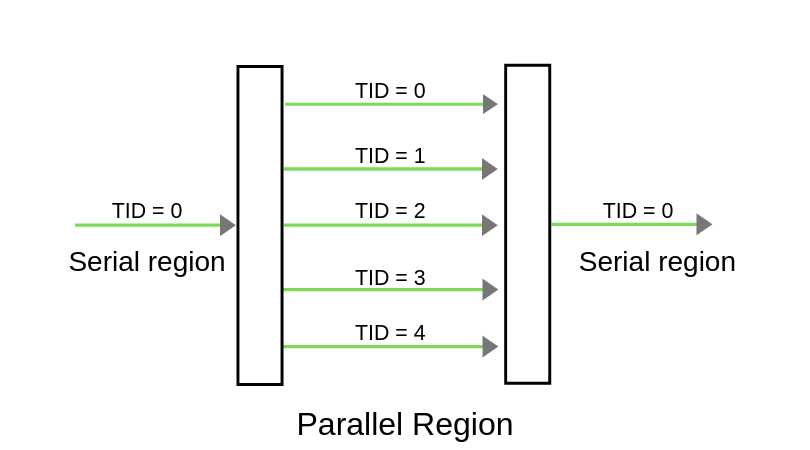
As per the above figure, Once the compiler encounters the parallel regions code, the master thread(thread which has thread id 0) will fork into the specified number of threads. Here it will get forked into 5 threads because we will initialise the number of threads to be executed as 5, using the command export OMP_NUM_THREADS=5. Entire code within the parallel region will be executed by all threads concurrently. Once the parallel region ended, all threads will get merged into the master thread.
Step 4:
Compile:
gcc -o hello -fopenmp hello.c
Execute:
./hello
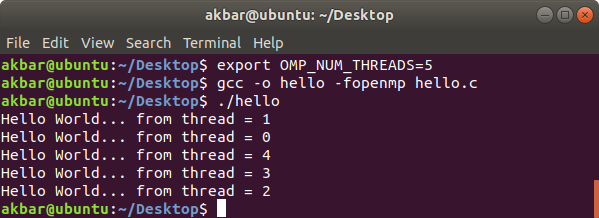
Below is the complete program with the output of the above approach:
Program: Since we specified the number of threads to be executed as 5, 5 threads will execute the same print statement at the same point of time. Here we can't assure the order of execution of threads, i.e Order of statement execution in the parallel region won't be the same for all executions. In the below picture, while executing the program for first-time thread 1 gets completed first whereas, in the second run, thread 0 completed first. omp_get_thread_num() will return the thread number associated with the thread.
OpenMP Hello World program
// OpenMP program to print Hello World
// using C language
// OpenMP header
#include <omp.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
// Beginning of parallel region
#pragma omp parallel
{
printf("Hello World... from thread = %d\n",
omp_get_thread_num());
}
// Ending of parallel region
}
Output
When run for 1st time:
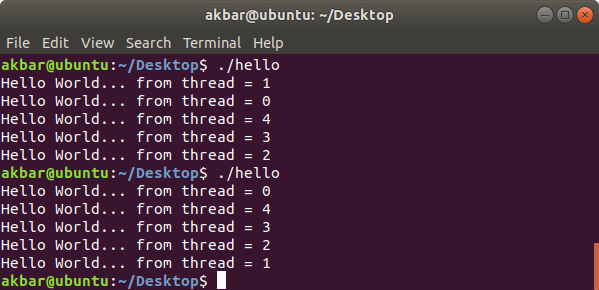
When run for multiple time:
Order of execution of threads changes every time.
Must Read
Conclusion
Parallel programming with OpenMP makes your code run faster by splitting tasks across multiple threads, like having a team of workers tackle a job together. By following simple steps like including the OpenMP header, setting up parallel regions, and choosing the number of threads, even beginners can create efficient programs that make the most of modern processors.
Explore
C Basics
Arrays & Strings
Pointers and Structures
Memory Management
File & Error Handling
Advanced Concepts