In R programming language, the cbind() function is used to combine multiple vectors, matrices or data frames by columns. The name cbind stands for column bind and it joins objects horizontally.
Syntax:
cbind(..., deparse.level = 1)
Parameters:
- x1, x2, ...: Objects to be combined such as vectors, matrices or data frames
1. Combining Vectors using cbind()
We create two numeric vectors and combine them as columns.
vector1 <- c(1, 2, 3)
vector2 <- c(4, 5, 6)
combined <- cbind(vector1, vector2)
print(combined)
Output:

In this example, we use the cbind() function to combine them into a matrix, where each becomes a separate column.
2. Combining Matrices using cbind()
We create two matrices with the same number of rows and combine them.
matrix1 <- matrix(1:4, nrow = 2)
matrix2 <- matrix(5:8, nrow = 2)
combined <- cbind(matrix1, matrix2)
print(combined)
Output:
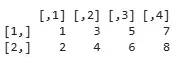
In this example, we use the cbind() function to combine them by columns, resulting in a new matrix where columns from the first are followed by those from the second.
3. Combining Data Frames using cbind()
We define two data frames and combine them column-wise.
df1 <- data.frame(A = 1:3, B = c("X", "Y", "Z"))
df2 <- data.frame(C = c("a", "b", "c"), D = c(TRUE, FALSE, TRUE))
combined <- cbind(df1, df2)
print(combined)
Output:
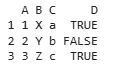
In this example, we use the cbind() function to combine them by columns, resulting in a new data frame where columns from the first are followed by those from the second.