Mensuration is the branch of mathematics that deals with the measurement of various geometric figures and shapes. This includes calculating areas, volumes, and perimeters of two-dimensional shapes like squares, rectangles, circles, and triangles, as well as three-dimensional figures like cubes, cylinders, spheres, and cones.
These shapes can exist in 2 ways:
- Two-Dimensional Shapes - circle, triangle, square, etc.
- Three-Dimensional Shapes - cube, cuboid, cone, etc.
Difference Between 2D and 3D Shapes
2-Dimensional vs 3-Dimensional Shapes | |
|---|---|
| 2D Shape | 3D Shape |
| Any shape is 2D if it is bound by three or more straight lines in a plane. | A shape is a three-dimensional shape if there are several surfaces or planes around it. |
| There is no height or depth in these shapes. | In contrast to 2D forms, these are sometimes known as solid shapes and have height or depth. |
| These shapes just have length and width as their dimensions. | Since they have depth (or height), breadth, and length, they are referred to as three-dimensional objects. |
| We can calculate their perimeter and area. | Their volume, curved surface area, lateral surface area, or total surface area can all be calculated. |
Mensuration Terminologies
Here is the list of terms you will come across in mensuration class. We have provided the term, it's abbreviation, unit and definition for easy understanding.
| Terms | Abbreviation | Unit | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| Area | A | m2 or cm2 | The surface that the closed form covers is known as the area. |
| Perimeter | P | cm or m | A perimeter is the length of the continuous line that encircles the specified figure. |
| Volume | V | cm3 or m3 | A 3D shape's space is referred to as its volume. |
| Curved Surface Area | CSA | m2 or cm2 | The overall area is known as a Curved surface area if there is a curved surface. Example: Sphere. |
| Lateral Surface area | LSA | m2 or cm2 | The term "Lateral Surface area" refers to the combined area of all lateral surfaces that encircle the provided figure. |
| Total Surface Area | TSA | m2 or cm2 | The total surface area is the total of all the curved and lateral surface areas. |
| Square Unit | - | m2 or cm2 | A square unit is the area that a square of side one unit covers. |
| Cube Unit | – | m3 or cm3 | The space taken up by a cube with a single side. |
Mensuration Formula For 2D Shapes
The following table provides a list of all mensuration formulas for 2D shapes:
| Shape | Area (Square units) | Perimeter (units) | Figure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Square | a2 | 4a |  |
| Rectangle | l × b | 2(l + b) | 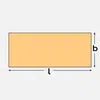 |
| Circle | πr2 | 2πr | 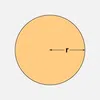 |
| Scalene Triangle | √[s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)], Where, s = (a+b+c)/2 | a + b + c | 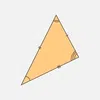 |
| Isosceles Triangle | ½ × b × h | 2a + b | 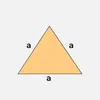 |
| Equilateral Triangle | (√3/4) × a2 | 3a |  |
| Right Angle Triangle | ½ × b × h | b + hypotenuse + h | 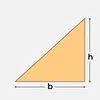 |
| Rhombus | ½ × d1 × d2 | 4 × side | 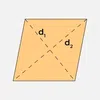 |
| Parallelograms | b × h | 2(l + b) | 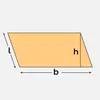 |
| Trapezium | ½ h(a + c) | a + b + c + d | 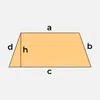 |
Learn More:
- Area of Trapezium
- Area of Polygons
- Area of General Quadrilateral
- Heron’s Formula
- Applications of Heron’s Formula
- Area of 2D Shapes
- Perimeter of circular figures
- Areas of sector and segment of a circle
- Areas of combination of plane figures
Mensuration Formula for 3D Shapes
The following table provides a list of all mensuration formulas for 3D shapes:
| Shape | Volume | Curved Surface Area or Lateral Surface Area | Total Surface Area | Figure |
| Cube | a3 | LSA = 4 a2 | 6a2 |  |
| Cuboids | l × b × h | LSA = 2h(l + b) | 2(lb +bh +hl) |  |
| Sphere | (4/3)πr3 | 4πr2 | 4πr2 |  |
| Hemisphere | (⅔)πr3 | 2πr2 | 3πr2 |  |
| Cylinder | πr2h | 2πrh | 2πrh + 2πr2 |  |
| Cone | (⅓)πr2h | πrl | πr(r + l) | 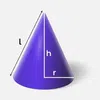 |
Learn More :
- Surface Area of Cube, Cuboid, and Cylinder
- Volume of Cube, Cuboid, and Cylinder
- Volume and Capacity
- Surface Area of 3D Shapes
- Volumes of Cubes and Cuboids
- Surface Areas and Volumes
- Volumes of a combination of solids
- Conversion of solids
- Frustum of a Cone
- Section of a Cone
- Conic Section
- Parabola
- Ellipse
- Hyperbola
Solved Problems on Mensuration
Let's solve some example problems on mensuration.
Problem 1: Find the volume of a cone if the radius of its base is 1.5 cm and its perpendicular height is 5 cm.
Solution:
Radius of the cone, r = 1.5 cm
Height of the cone, h = 5 cm∴ Volume of the cone, V = 13πr2h=13×227×(1.5)2×5= 11.79 cm3
Thus, the volume of the cone is 11.79 cm3.
Problem 2: The dimensions of a cuboid are 44 cm, 21 cm, 12 cm. It is melted and a cone of height 24 cm is made. Find the radius of its base.
Solution:
The dimensions of the cuboid are 44 cm, 21 cm and 12 cm.
Let the radius of the cone be r cm.
Height of the cone, h = 24 cm
It is given that cuboid is melted to form a cone.
∴ Volume of metal in cone = Volume of metal in cuboid
⇒(1/3)πr2h = 44 × 21 × 12(Volume of cuboid=Length×Breadth×Height)
⇒(1/3) × (22/7) × r2 × 24 = 44 × 21 × 12
⇒r = √(44 × 21 × 12 × 21) / (22 × 24)
=21 cmThus, the radius of the base of cone is 21 cm.
Problem 3: The radii of two circular ends of frustum shape bucket are 14 cm and 7 cm. The height of the bucket is 30 cm. How many liters of water can it hold? (1 litre = 1000 cm3).
Solution:
Radius of one circular end, r1 = 14 cm
Radius of other circular end, r2 = 7 cm
Height of the bucket, h = 30 cm∴ Volume of water in the bucket = Volume of frustum of cone
=(1/3)πh(r12 + r1r2 + r22)
=13×22/7 × 30 × (142 + 14 × 7 + 72)
=13×22/7 × 30 × 343 = 10780 cm3
=107801000 = 10.780 LThus, the bucket can hold 10.780 litres of water.