A quadratic function can be represented in the form f(x) = ax2 + bx + c, where x is variable, a, b, and c are constants, and a ≠ 0. It is also a type of polynomial function whose greatest degree is 2. The graph of a quadratic function is parabolic in shape, which can open either upwards or downwards depending on the sign of a. If a > o then the parabola opens upwards, and if a <0 then the parabola opens downward. The vertex of the parabola is an important point that represents either the maximum or minimum value of the function, depending on the direction in which the parabola opens.
In this article, we are going to learn how we can find the vertex of a quadratic function using various methods such as the vertex formula method, completing the square method, and the graphical method.
Table of Content
What is Vertex of a Quadratic Function?
Vertex of a quadratic function is a critical point where the function reaches its maximum or minimum value, depending on the orientation of the parabola (which is the graph of the quadratic function). In mathematical terms, a quadratic function can be expressed in the standard form:
f(x) = ax2 + bx + c
Here, a, b, and c are constants, and x is the variable. The vertex of the quadratic function is the point (h, k), where:
- h = -b/2a
- k = f(h) = f(-2ab)
Methods to Find Vertex of a Quadratic Function
Different methods to find the vertex of a Quadratic Function are:
- Using Vertex Formula
- Completing Square Method
- By Graphical Analysis
Using Vertex Formula
The vertex of a quadratic function of standard form f(x) = ax2 + bx + c can be found using the vertex formula:
- h = -b/2a
- k = f(h)
The (h, k) coordinates represent the vertex of the quadratic function.
The x-coordinate of the vertex is h and the y-coordinate of the vertex is k. h is found by substituting -b/2a in the function and y-coordinate is the value of the function at h.
Step-by-Step Procedure
Step 1: Identify the coefficients a and b in the quadratic function f(x) = ax2 + bx + c
Step 2: Calculate the x-coordinate of the vertex using h = -b/2a
Step 3: Substitute the value of h into function, f(k) to find the y-coordinate of the vertex k.
Step 4: Coordinate of the vertex is (h, k).
Derivation of Vertex Formula
The vertex formula can be derived by completing the square for the quadratic function f(x) = ax2 + bx + c:
First we write the quadratic equation in standard form:
f(x) = ax2 + bx + c
Factor out the coefficient a from the quadratic function and linear terms:
f(x) = a (x2 + (b/a)x) + c
Complete the square present inside paranthesis in above equation:
f(x) = a (x2 + (b/a)x + (b/2a)2 - (b/2a)2) + c
f(x) = a(x + b/2a)2 - a(b/2a)2 + c
Now, simplify the equation:
f(x) = a(x + b/2a)2 - b2/4a + c
The vertex form of the quadratic equation can be represented in the form:
f(x) = a(x - h)2 + k
where h = -b/2a and k = c - b2/4a
Completing Square Method
Using completing the square method we can convert the quadratic equation of form ax2 + bx + c to vertex form a(x - h)2 + k, where (h, k) is the vertex.
Steps for Completing Square Method
First start with the standard form of the quadratic equation of the form: ax2 + bx + c
If a ≠ 1, factor out a from the quadratic and linear term:
f(x) = a(x2 + bx/a) + c
Now, add and subtract the square of half the coefficient of x inside the parentheses:
f(x) = a(x2 + bx/a + (b/2a)2 - (b/2a)2) + c
Simplify the equation:
f(x) = a(x + b/2a)2 - a(b/2a)2+ c
The vertex form of the quadratic function is given as:
f(x) = a(x - h)2 + k
where h = -b/2a and k = c - b2/4a
Cooridnates of vertex is (h , k)
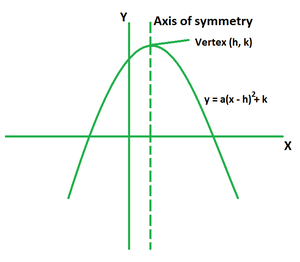
By Graphical Analysis
In graphical analysis we plot the quadratic function and identify the vertex visually i.e. by looking. This method is very useful for understanding the behaviour of the quadratic function and it is also used to confirm the results obtained using algebraic methods.
Steps for Graphical Analysis
Step 1: Plot the quadratic function. We will use graphing calculator or software to plot the function: f(x) = ax2 + bx + c
Step 2: Identify the Axis of symmetry. The axis of symmetry is the vertical line that passes through the vertex. It can be found using the formula x = -b/2a
Step 3: Vertex is the point where the parabola intersects the axis of symmetry. The coordinates of vertex is (h, k).
Applications of Vertex of a Quadratic Function
Vertex of a quadratic function has various real-world applications. Some of them are mentioned below:
- Physics: The vertex represents the highest point (maximum height) or lowest point (ground level) of the trajectory in projectile motion. For example, in the equation h(t) = -16t2 + 64t + 5, the vertex gives the maximum height of the projectile.
- Engineering: The vertex of the function helps in designing structures and analyzing stress and strain in materials.
- Economics: The vertex is used to find the maximum profit or minimum cost in optimization problems. For example, in the profit function P(x) = -5x2 + 100x - 300, the vertex gives the quantity of items that maximizes profit. For example, in the cost function C(x) = 2x2 - 16x + 100, the vertex gives the quantity of items that minimizes cost.
Practice Questions on Vertex of a Quadratic Function
Q1. Find the vertex of the quadratic function f(x) = 3x2 - 6x + 2
Solution:
Identify the coefficient in given quadratic function: a = 3, b = -6 and c = 2
Calculate the x-coordinate of the vertex using formula h = -b/2a:
h = -(-6/2 × 3) = 6/6 = 1
Substitute the value of h = 1 in given function to find the y-coordinate:
k = f(1) = 3(1)2 - 6(1) + 2 = 3 - 6 + 2 = -1
Coordinates of vertex are (1 , -1).
Q2. Find the vertex of the quadratic function f(x) = -2x2 + 8x - 5
Solution:
Identify the coefficient in given quadratic function: a = -2, b = 8 and c = -5
Calculate the x-coordinate of the vertex using formula h = -b/2a:
h = -(-8/2 × (-2)) = -(8/-4) = 2
Substitute the value of h = 1 in given function to find the y-coordinate:
k = f(2) = -2(2)2 + 8(2) - 5 = -8 + 16 - 5 = 3
Coordinates of vertex are (2 , 3).
Q3. Find the vertex of the quadratic function f(x) = x2 - 4x + 6
Solution:
Identify the coefficient in given quadratic function: a = 1, b = -4 and c = 6
Calculate the x-coordinate of the vertex using formula h = -b/2a:
h = -(-4/2 × 1) = (4/2) = 2
Substitute the value of h = 1 in given function to find the y-coordinate:
k = f(2) = (2)2 - 4(2) + 6 = 4 - 8 + 6 = 2
Coordinates of vertex are (2 , 2).
Q4. Find the vertex of the quadratic function f(x) = -x2 + 2x - 1
Solution:
Identify the coefficient in given quadratic function: a = -1, b = 2 and c = -1
Calculate the x-coordinate of the vertex using formula h = -b/2a:
h = -(-2/2 × (-1)) = -(2/-2) = 1
Substitute the value of h = 1 in given function to find the y-coordinate:
k = f(2) = -(1)2 + 2(1) - 1 = -1 + 2 - 1 = 0
Coordinates of vertex are (1 , 0).
Q5. Find the vertex of the quadratic function f(x) = 2x2 + 3x + 1
Solution:
Identify the coefficient in given quadratic function: a = 2, b = 3 and c = 1
Calculate the x-coordinate of the vertex using formula h = -b/2a:
h = -(3/2 × 2) = -3/4
Substitute the value of h = -3/4 in given function to find the y-coordinate:
k = f(-3/4) = 2(-3/4)2 + 3(-3/4) + 1
k = 2 × (9/16) - 9/4 + 1
k = 18/16 - 36/16 + 16/16
k = 18 - 36 + 16/16
k = -2/16 = -1/8
Coordinates of vertex are (-3/4 , -1/8).
Projectile Motion Problem
Q6. A ball is thrown into the air with an initial velocity. The height h(t) of the ball at time t is given by h(t) = -16t2 + 64t + 5. Find the maximum height of the ball.
Solution:
First identify the coefficients: a = -16, b = 64, and c = 5
Now, we calculate the t-coordinate of the vertex:
t = -b/2a = - 64/2 × (-16) = -64/-32 = 2
Now, we substitute t =2 into the function to find the height:
h(2) = -16(2)2 + 64(2) + 5
= -16 × 4 + 128 + 5= -64 + 128 + 5
= 69
So, the maximum height of the ball is 69 units.
Cost Minimization Problem
Q7. A company incurs a cost C(x) to produce x units of a product. The cost function is C(x) = 2x2 - 16x + 100. Find the quantity of items that minimizes cost.
Solution:
First we identify the coefficients from given equation: a = 2, b = -16, and c = 100
Calculate the x -coordinates of the vertex
x = -b/2a = -(-16)/2 × 2 = 16/4 = 4
So, the quantity of items that minimizes cost is 4 units
Conclusion
The vertex of a quadratic function is a fundamental topic in algebra and precalculus. The vertex of a quadratic function provides overall behaviour such as axis of symmetry, maximum or minimum value etc. There are some common methods of finding vertex of quadratic function such as the vertex formula, completing the square, and graphical analysis.