Factorization of a quadratic equation is a key algebraic technique where a quadratic expression is rewritten as the product of two binomials. This method simplifies solving quadratic equations, rewriting algebraic expressions, and understanding the geometric properties of quadratic functions, such as their x-intercepts.
A quadratic equation is typically in the form ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a, b, and c are constants. The goal of factorization is to express the equation as a product of binomials, like K(px + q)(rx + s) = 0. By setting each binomial equal to zero, we can solve for x to find the equation’s roots.
Factorization not only helps in solving equations but also provides insight into the behavior of quadratic functions on a graph. The techniques for factorizing quadratic equations vary depending on the specific problem, but they all aim to simplify the equation and reveal its roots.
Methods to Factorize Quadratic Equations
There are several methods to factorize quadratic equations, each suited for different types of equations. The primary methods are:
Factoring Using Splitting Middle-Term
This method splits the middle term into two parts that add up to the middle coefficient and multiply to the product of the first and last coefficients.
- Step 1: Identify the quadratic equation ax2 + bx + c = 0.
- Step 2: Find two numbers whose sum is b (the coefficient of x) and whose product is ac (the product of the coefficients of x2 and the constant term).
- Step 3: Rewrite the middle term using these two numbers.
- Step 4: Group the terms into two pairs.
- Step 5: Factor out the common factor from each pair.
- Step 6: Factor out the common binomial factor from the resulting expression.
Example: Factorize 2x2 + 7x + 3.
Identify the quadratic equation: 2x2 + 7x + 3
Find two numbers: We need two numbers that add to 7 and multiply by 2 * 3 = 6. These numbers are 6 and 1
Rewrite the middle term: 2x2 + 6x + x + 3
Group the terms: (2x2 + 6x) + (x + 3)
Factor out the common factor: 2x(x + 3) + 1(x + 3)
Factor out the common binomial factor: (2x + 1)(x + 3)Thus, 2x2 + 7x + 3 = (2x + 1)(x + 3)
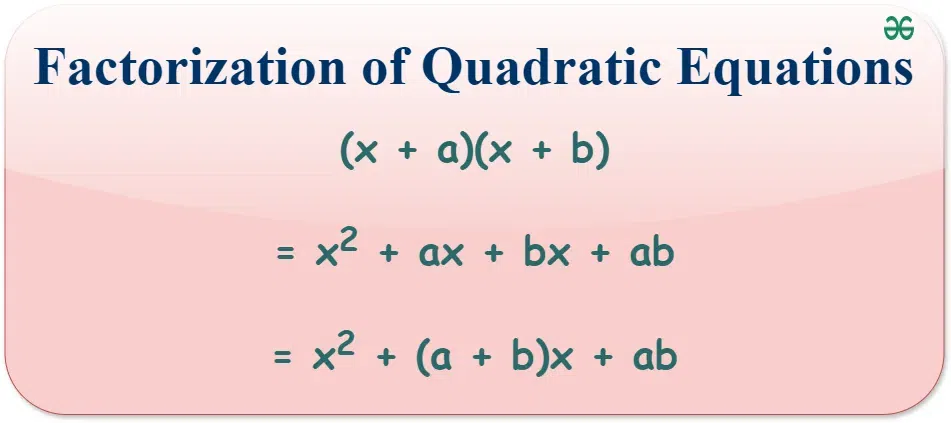
Factoring Quadratic Equation using Formula
This method uses a specific formula to factorize the quadratic equation.
- Step 1: Identify the quadratic equation in the form ax2 + bx + c.
- Step 2: Use the factorization formula: If a ≠ 1, use the formula for ax2 + bx + c.
- Step 3: Rewrite the equation based on the identified formula.
- Step 4: Simplify to find the factors.
Example: Factorize x2 + 5x + 6.
Identify the quadratic equation: x2 + 5x + 6
Use the factorization formula: x2 + (a + b)x + ab = (x + a)(x + b)Here, a = 2 and b = 3, since 2 + 3 = 5 and 2 × 3 = 6
Rewrite the equation: (x + 2)(x + 3)Thus, x2 + 5x + 6 = (x + 2)(x + 3).
Factoring Quadratic Equation using Quadratic Formula
Quadratic formula also known as Shreedhara Acharya’s Formula is a standard method for solving any quadratic equation and can also be used for factorization. The quadratic formula is derived from the process of completing the square and is given by:
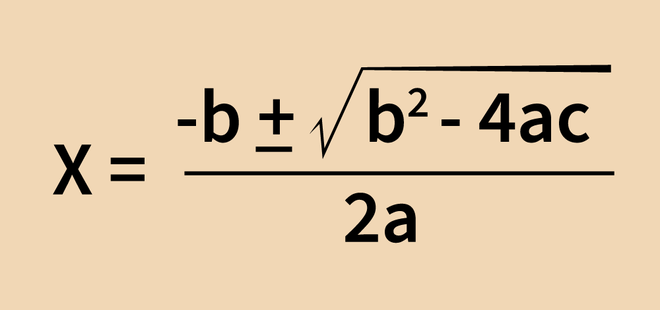
This formula gives the roots of the quadratic equation, which can then be used to factorize the quadratic expression.
- Step 1: Identify the quadratic equation in the form ax2 + bx + c
- Step 2: Apply the quadratic formula to find the roots x1 and x2
- Step 3: Rewrite the quadratic equation as a(x - x1)(x - x2)
Example: Factorize 3x2 - 2x - 8.
Identify the quadratic equation: 3x2 - 2x - 8
Apply the quadratic formula: x = (-(-2) ± √((-2)2 - 4.3.(-8)) / (2.3)Simplify the discriminant
x = x = (2 ± √(4 + 96)) / 6 = x = (2 ± √(100)) / 6 = x = (2 ± 10) / 6Find the roots: x1 = 2 and x2 = - 4/3
Rewrite the equation: 3 (x - 2) (x + 4/3)Thus, 3x2 - 2x - 8 = 3 (x - 2) (x + 4/3)
Factoring Quadratic Equations using Algebraic Identities
Algebraic identities can simplify the factorization process, particularly when dealing with specific forms of quadratic equations. They provide a straightforward method to factorize certain types of quadratic expressions.
- Step 1: Identify the quadratic equation in a recognizable identity form.
- Step 2: Apply the appropriate identity to factorize the expression.
Example: Factorize 4x2 - 9.
Identify the quadratic equation: 4x2 - 9 is in the form a2 - b2
Apply the identity: a2 - b2 = (a + b)(a - b), where a = 2x and b = 3
Rewrite the equation: (2x + 3)(2x - 3)Thus, 4x2 - 9 = (2x + 3)(2x - 3)
Application of Factorization of Quadratic Equations
The applications of Factorization of Quadratic equations are as follows:
- Solving Quadratic Equations: Factorization makes the process of finding the roots of quadratic equations easier, which is very important in algebra and calculus.
- Graphing Quadratic Functions: Knowledge of the factors assists when searching for the x-intercepts of the function which also assists in graph sketching.
- Physics Problems: Most of the projectiles are governed by quadratic equations and hence the function can model many physical occurrences.
- Optimization Problems: Quadratics have applications in finding the maximum and minimum values which are commonly used cases in the field of economics and engineering.
- Geometry: Factorization helps in solving geometric problems involving areas and dimensions.
Read More,
Solved Examples of Factorization of Quadratic Equations
Example 1: Factorize: x2 - 5x + 6.
To factorixe: x2 - 5x + 6
⇒ x2 - 2x - 3x + 6
⇒ x(x - 2) - 3(x - 2)
⇒ (x - 2)(x - 3)
Example 2: Factorize: x2 - 6x + 9.
x2 - 6x + 9
⇒ x2 - 2.3x + (3)2Comparing with a2 - 2ab + b2 = (a - b)2
⇒ (x - 3)2
Example 3: Factorize: x2 + x - 12.
x2 + x - 12
⇒ x2 +4x - 3x + 12
⇒ x(x + 4) - 3(x + 4)
⇒ (x + 4)(x - 3)
Example 4: Factorize: x2 + 8x + 16.
x2 + 8x + 16
⇒ x2 + 2.4x + (4)2Comparing with a2 + 2ab + b2 = (a + b)2
⇒ (x + 4)2