Replacing All Occurrences of Specified Element of Java Vector
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
The replaceAll() method of java.util.Collections class is used to Replaces all occurrences of one specified value in a list with another. More formally, replaces with newVal each element e in list such that (oldVal==null ? e==null : oldVal.equals(e)). (This method has no effect on the size of the list.)
Let's consider the following vector:
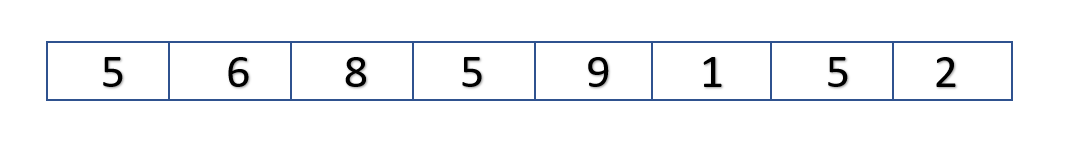 VECTOR BEFORE REPLACING
VECTOR BEFORE REPLACING
Now in this vector we have to replace all occurrences of 5 with a given value. Let's say the value here is -1. After replacing our vector should become as shown below:
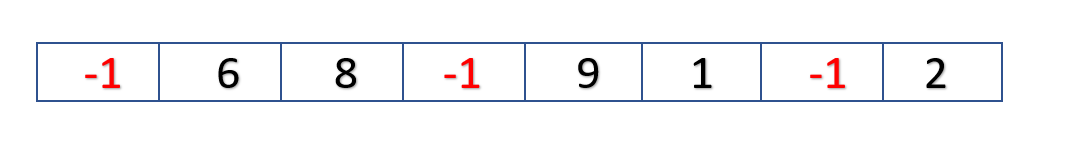 VECTOR AFTER REPLACING
VECTOR AFTER REPLACING
Approach:
A naive way to approach this problem is to traverse the entire vector and while traversal if the element in vector is equal the specified element then replace it with the given value.
However, in Java, we have a Built-in method replaceAll() as a part of Java Collections which does the same.
Syntax:
public static boolean
replaceAll(List list, T oldVal, T newVal)
Parameters: This method takes the following argument as a Parameter
- list – the list in which replacement is to occur.
- oldVal – the old value to be replaced.
- newVal – the new value with which oldVal is to be replaced.
Return Value: This method returns true if list contained one or more elements e such that (oldVal==null ? e==null : oldVal.equals(e)).
Code:
Java
// Java program to replace all occurrences
// of Specified Element of Java Vector
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.Collections;
class GFG {
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// Create a vector
Vector<Integer> storage =new Vector<Integer>(6);
// adding elements to the vector
storage.add(5);
storage.add(6);
storage.add(8);
storage.add(5);
storage.add(9);
storage.add(1);
storage.add(5);
storage.add(2);
// val to replace with
int val=-1;
// printing the vector before replacing
System.out.println("Vector before Replacing is: " + storage);
// using Collections.replaceAll to replace all occurrences of the element
Collections.replaceAll(storage,5,val);
//printing the vector after replacing
System.out.println("Vector after Replacing is: " + storage);
}
}
OutputVector before Replacing is: [5, 6, 8, 5, 9, 1, 5, 2]
Vector after Replacing is: [-1, 6, 8, -1, 9, 1, -1, 2]
Now let's consider a Vector having String instead of Integer values:
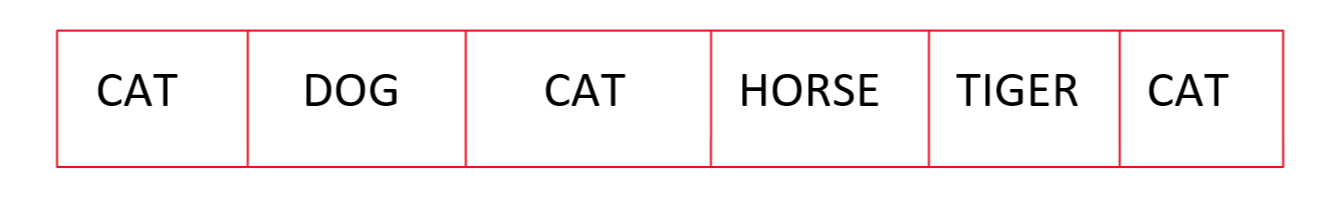 VECTOR BEFORE REPLACING
VECTOR BEFORE REPLACING
Now in this vector, we have to replace all occurrences of CAT with a given String. Let's say the string here is LION. After replacing our vector should become as shown below:
 VECTOR AFTER REPLACING
VECTOR AFTER REPLACING
Code:
Java
// Java program to replace all occurrences
// of Specified Element of Java Vector
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.Collections;
class GFG {
public static void main (String[] args) {
// Create a vector
Vector<String> storage =new Vector<String>(6);
// adding elements to the vector
storage.add("CAT");
storage.add("DOG");
storage.add("CAT");
storage.add("HORSE");
storage.add("TIGER");
storage.add("CAT");
// val to replace with
String val="LION";
// printing the vector before replacing
System.out.println("Vector before Replacing is: " + storage);
// using Collections.replaceAll to replace all occurrences of specified element
Collections.replaceAll(storage,"CAT",val);
//printing the vector after replacing
System.out.println("Vector after Replacing is: " + storage);
}
}
OutputVector before Replacing is: [CAT, DOG, CAT, HORSE, TIGER, CAT]
Vector after Replacing is: [LION, DOG, LION, HORSE, TIGER, LION]
Explore
Java Basics
OOP & Interfaces
Collections
Exception Handling
Java Advanced
Practice Java