Reconnaissance (Recon) is the first and most critical phase of ethical hacking, focused on systematically gathering information about a target to understand its digital, physical, and human attack surface.
- Involves information gathering about systems, networks, and people
- Helps map a target’s digital footprint and infrastructure
- Can be passive (stealthy) or active (interactive and detailed)
- Used by both defenders and attackers to identify potential vulnerabilities
Types of Reconnaissance
Below are the two types of reconnaissance:
1. Passive Reconnaissance
It focuses on observation rather than engagement, making it stealthy but less detailed than active methods.
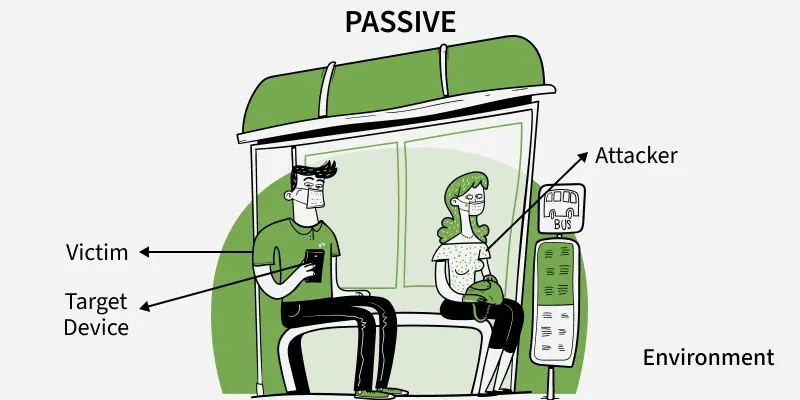
Information gathering without directly interacting with the target systems.
- Undetectable by the target
- Uses publicly available information
- No logs generated on target systems
- Lower risk, but potentially limited information
Example: Like researching a company through newspaper articles and public records without ever calling them.
2. Active Reconnaissance
It involves hands-on probing of a target, trading stealth for more precise and up-to-date intelligence.
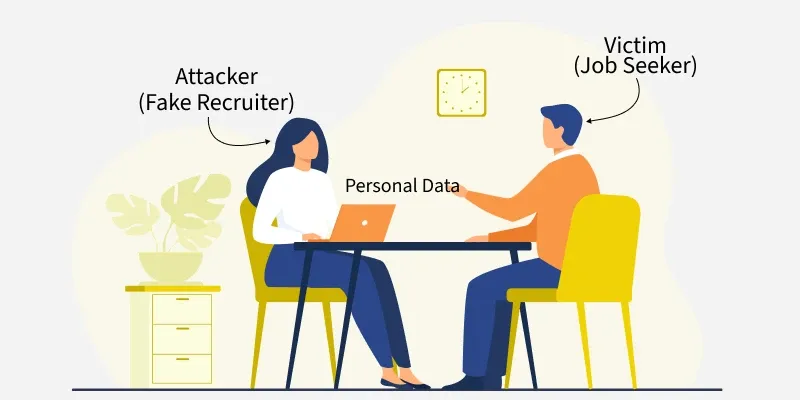
Direct interaction with target systems to gather information.
- Direct queries to target systems
- Potentially detectable (leaves traces)
- More detailed and current information
- Higher risk of detection
Example: Like calling a company directly to ask about their services or visiting their office.
Reconnaissance Categories
These reconnaissance techniques help security professionals and attackers alike map out targets, identify weaknesses, and plan further exploitation steps effectively.
1. In-Person Reconnaissance (Human Intelligence)
Physical observation and social engineering techniques.
Methods:
- Dumpster Diving: Searching discarded documents for sensitive information
- Shoulder Surfing: Observing people entering passwords or sensitive data
- Tailgating: Following authorized personnel into secure areas
- Social Engineering: Manipulating people to divulge information
Example: A security tester finds employee badges in a company's trash, revealing the badge format and employee naming conventions.
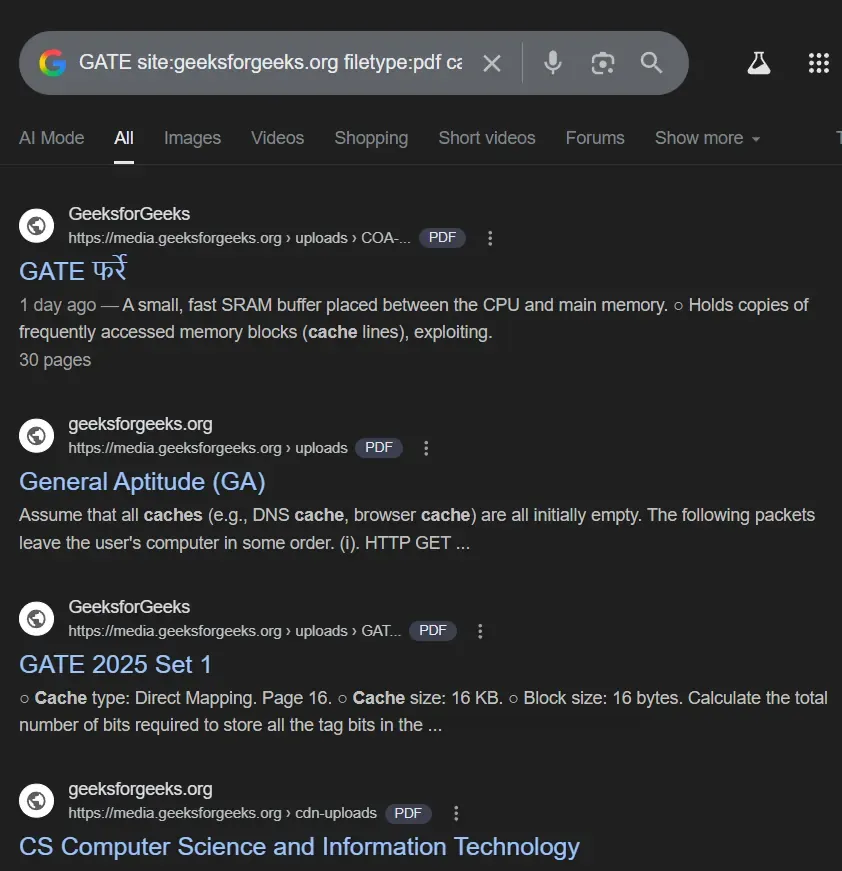
2. Google Dorking (Search Engine Intelligence)
Using advanced Google search operators to find sensitive information.
Common Dorks:
GATE site:geeksforgeeks.org filetype:pdf cache:geeksforgeeks.orgEnter this command to get GATE related PDF filetypes on the website of geeksforgeeks.org
3. Web-Based Reconnaissance
Gathering information from websites, web applications, and online services.
Techniques:
- Website Analysis: Technology stack, CMS versions, plugins
- Directory Enumeration: Finding hidden files and folders
- Subdomain Discovery: Identifying all subdomains
- Web Archive Analysis: Using Wayback Machine for historical data
Real Example: Discovering a forgotten subdomain dev.company.comthat contains development databases with test data.
4. IP Address-Based Reconnaissance
Information gathering using IP addresses and network infrastructure.
Methods:
- WHOIS Lookups: Domain and IP ownership information
- DNS Enumeration: Finding DNS records and configurations
- Network Scanning: Port scans, service identification
- Geolocation: Physical location of servers
Real Example: WHOIS lookup reveals that company.com uses AWS servers in Virginia, helping narrow down the infrastructure setup.
5. Social Media Intelligence (SOCMINT)
Extracting information from social media platforms.
Target Information:
- Employee details and roles
- Company culture and internal processes
- Technology preferences
- Personal information for social engineering
- Business relationships and partnerships
Real Example: LinkedIn reveals that the company's IT manager recently posted about migrating to Microsoft Azure, indicating their cloud infrastructure.
6. Physical Device Reconnaissance
Information gathering from physical devices and infrastructure.
Methods:
- Wi-Fi Network Analysis: SSID enumeration, security protocols
- Bluetooth Discovery: Nearby devices and services
- RF Analysis: Radio frequency monitoring
- IoT Device Discovery: Smart devices on networks
Real Example: Discovering an unsecured printer on the network that stores copies of all printed documents or Weak Wi-Fi signal Strength.
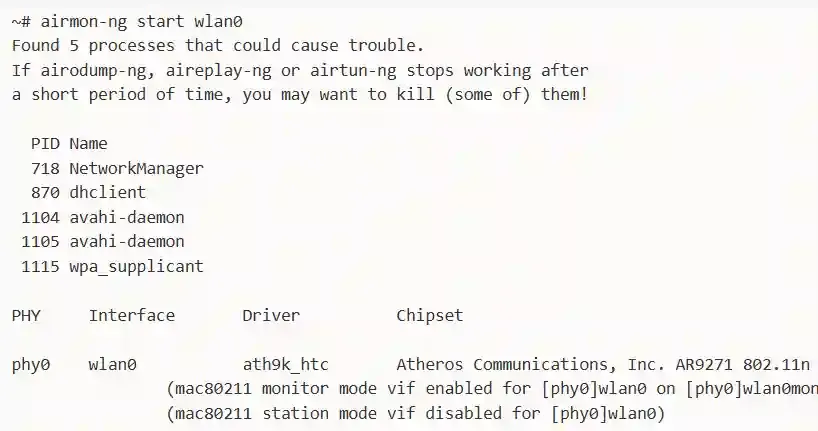
7. Email Intelligence (EMAILINT)
Gathering information through email addresses and email infrastructure.
Techniques:
- Email Harvesting: Collecting email addresses from websites
- Email Verification: Checking if emails exist
- Email Header Analysis: Tracing email origins
- Email Pattern Discovery: Understanding naming conventions
Real Example: Finding that a company uses firstname.lastname@company.com format helps create targeted phishing campaigns.
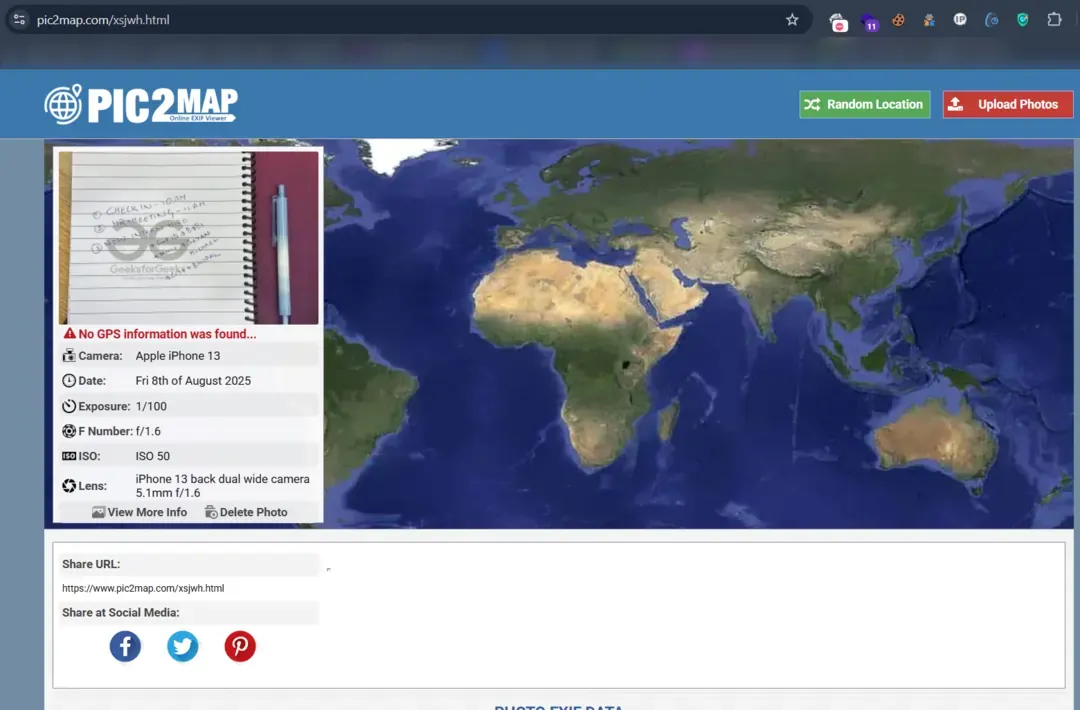
8. Digital Footprints & Metadata Analysis
Analyzing digital traces left by targets.
Sources:
- Document Metadata: Author names, software versions, creation dates
- Image EXIF Data: GPS coordinates, camera details, timestamps
- Code Repositories: GitHub profiles, commit histories
- Forum Posts: Technical discussions revealing infrastructure
Real Example: A PDF on the company website contains metadata showing it was created by "John.Smith" on a Windows 10 machine, revealing an employee name and OS information.
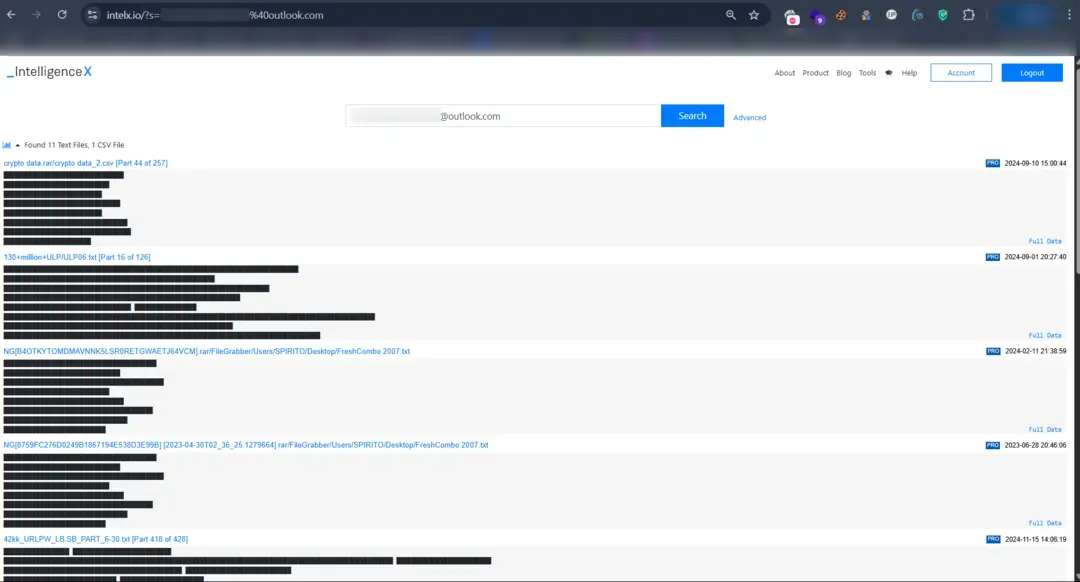
9. Data Breach & Leaked Database Analysis
Leveraging compromised data from previous breaches.
Sources:
- HaveIBeenPwned: Email breach checking
- Pastebin Sites: Leaked credentials and data dumps
- Dark Web Marketplaces: Sold databases and credentials
- Public Data Breaches: Analysis of known breaches
Real Example: Discovering that several company email addresses were compromised in the 2019 Collection #1 breach, potentially providing password patterns.
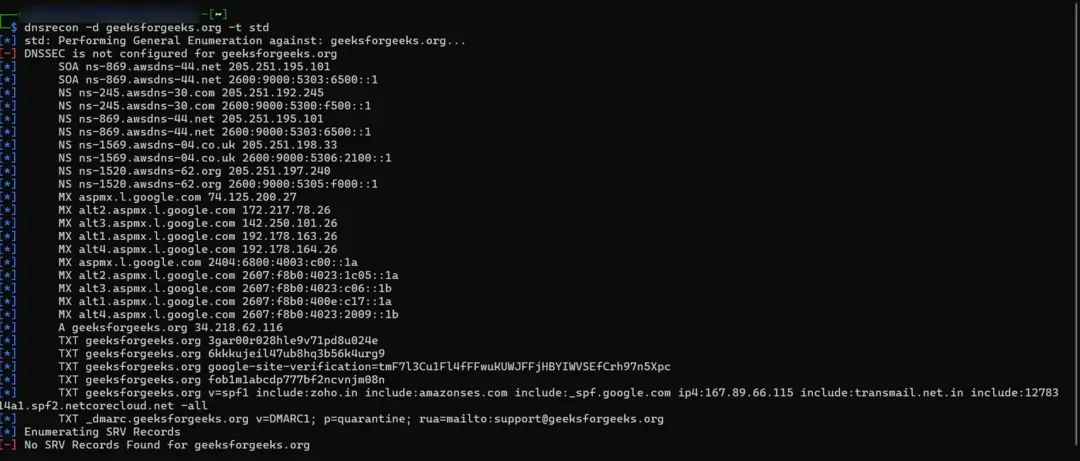
10. DNS Intelligence
Deep analysis of DNS infrastructure and configurations.
Methods:
- Zone Transfers: Attempting to download DNS zone files
- DNS Cache Snooping: Checking DNS resolver caches
- Reverse DNS Lookups: Finding domains associated with IP ranges
- DNS History: Tracking historical DNS changes
Tools for Reconnaissance
Web-Based Tools
| Category | Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| WHOIS/DNS | whois.net, dnsdumpster.com | Domain information, DNS records |
| Subdomains | Sublist3r.online, crt.sh | Subdomain discovery |
| Google Dorking | Google.com, DorkSearch.com | Advanced search queries |
| Social Media | Sherlock-project.github.io | Username searches across platforms |
| hunter.io, have-i-been-pwned.com | Email discovery and breach checking | |
| Website Analysis | builtwith.com, wappalyzer.com | Technology stack identification |
| Archives | web.archive.org | Historical website data |
| IP Intelligence | shodan.io, censys.io | Internet-connected device search |
Leaked Data Base | Intelx.io, cracking.org | Leaked Database Website and Forum |
Kali Linux CLI Tools
Network & DNS Reconnaissance
- Commands for DNS Enumeration -
dnsrecon -d example.com -t std
dig example.com ANY
fierce -dns example.com
- Commands for Subdomain discovery -
sublist3r -d example.com
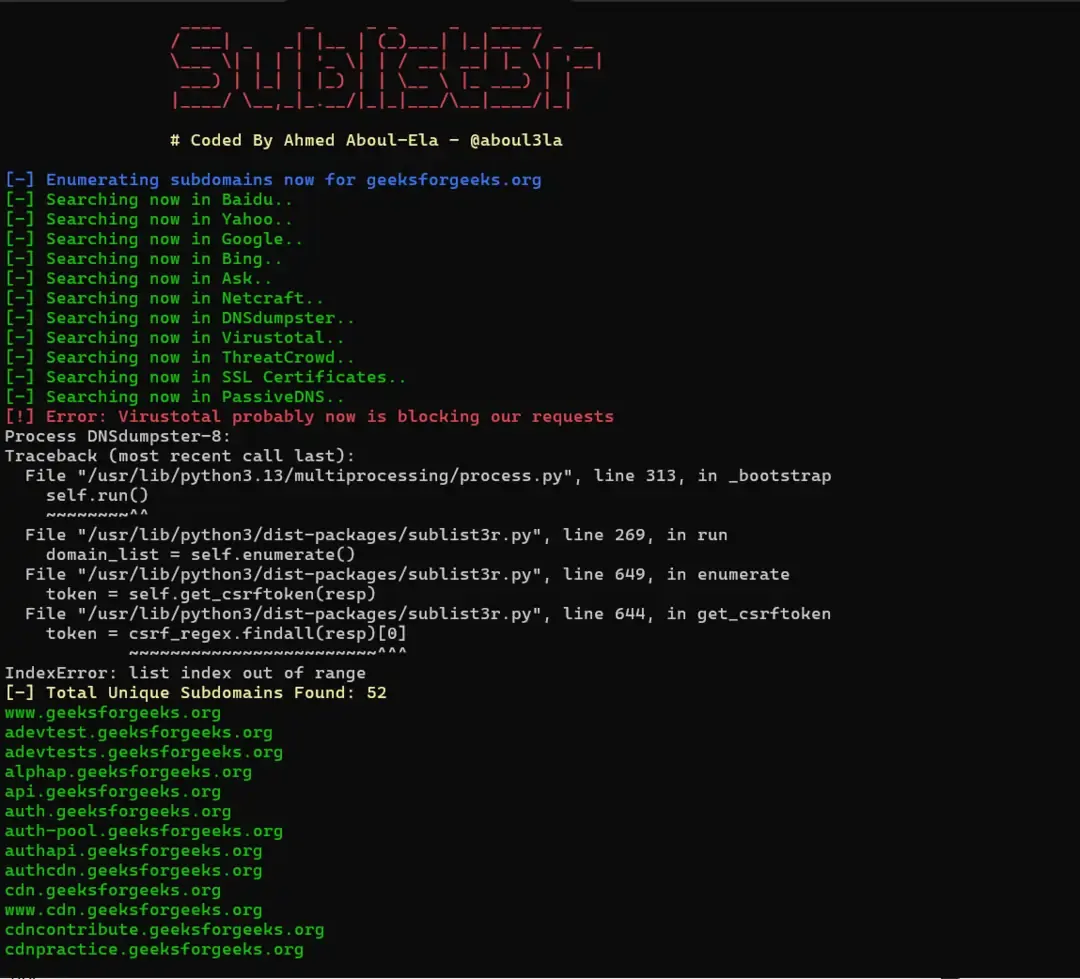
- Commands for Network scanning -
nmap -sS -A XX.XX.XX.XX
masscan -p1-65535 XX.XX.XX.XX --rate=10000
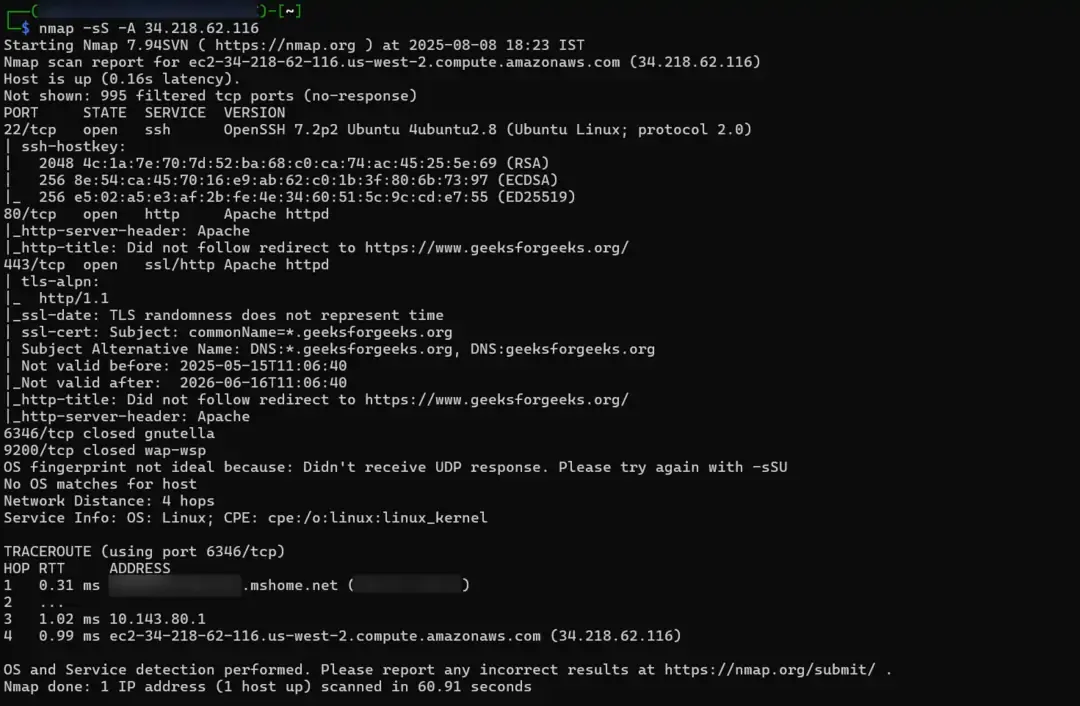
Web Application Reconnaissance
- Directory/File Discovery
dirb http://example.com///
gobuster dir -u http://example.com/// -w /usr/share/wordlists/dirb/common.txt
dirsearch -u http://example.com///
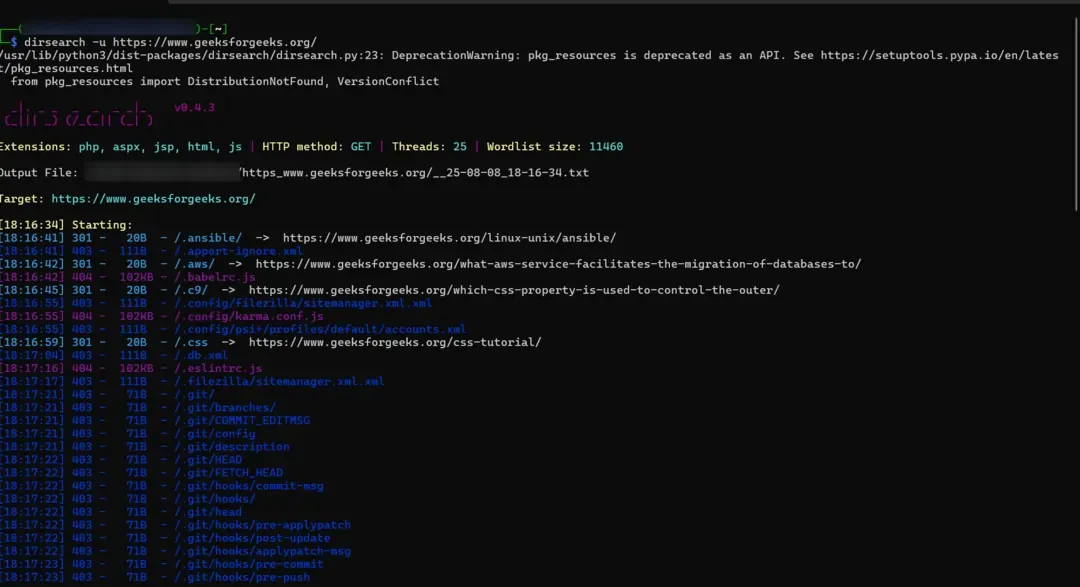
- Web Technology Identification
whatweb http://example.com///
wapiti -u http://example.com///
- Web crawling
wget --spider --recursive --no-verbose --output-file=spider.log http://example.com///Social Media & OSINT
- Username recon using sherlock tool -
sherlock username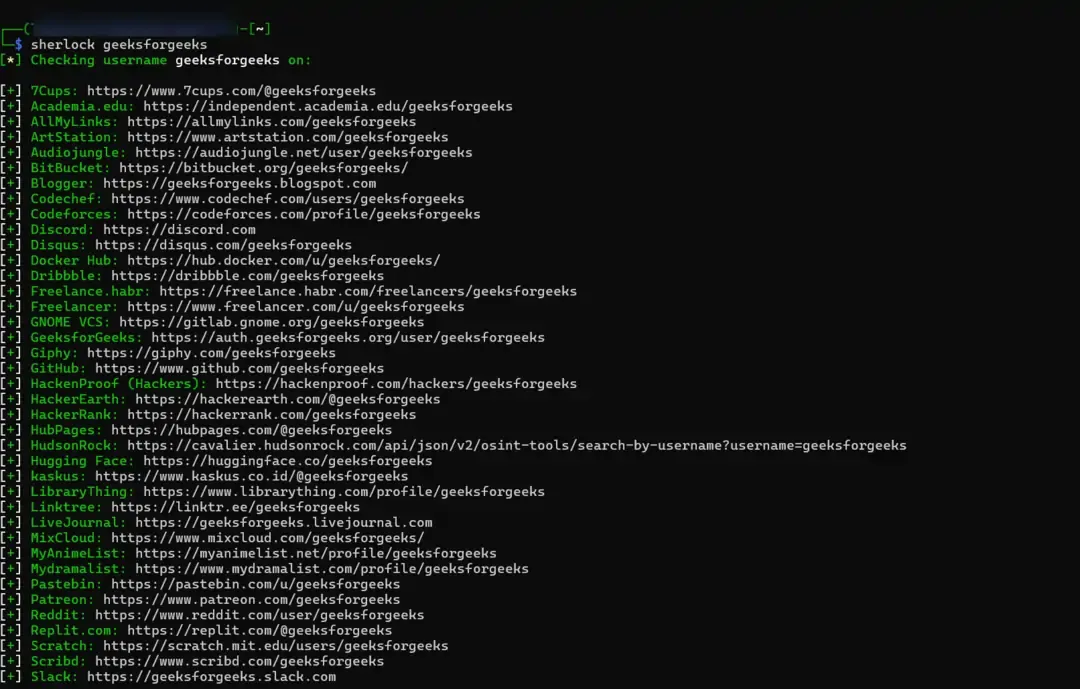
- Email harvesting
theharvester -d example.com -l 500 -b google
maltego (GUI-based OSINT framework)
- Metadata analysis
exiftool document.pdf
metagoofil -d example.com -t pdf -l 100 -n 25 -o results/
Specialized Tools
- WHOIS information
whois example.com- SSL Certificate analysis
sslscan target.com
sslyze target.com
- Shodan Enumeration
shodan host 192.XX.XX.XXFramework Tools
- Recon-ng for Modular reconnaissance framework
recon-ng- Spiderfoot for Automated OSINT Framework
spiderfoot -s example.com- Killshot for Framework and Vulnerability Testing
git clone https://github.com/bahaabdelwahed/killshot%3C/span>Note: Killshot is an open-source tool that integrates various pentesting tools. You may need to visit GitHub and refer to the README.txt file to understand its functionality and commands.