POTD 19 October: Level Of Nodes
Given an integer X and an undirected acyclic graph with V nodes, labeled from 0 to V-1, and E edges, find the level of the node labeled as X.
Level: It is the minimum number of edges you must travel from node 0 to some target.
If there doesn't exist such a node that is labeled as X, return -1.
Example:
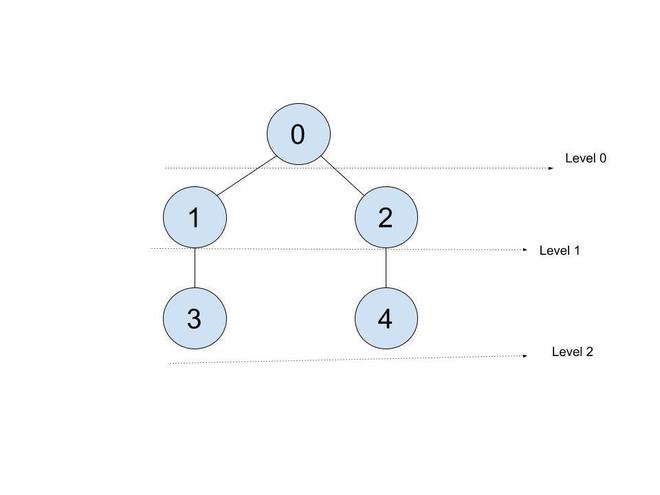
Input: V = 5, Edges = {{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 4}}, X = 3
Output: 2
Explanation: Starting from vertex 0, at level 0 we have node 0, at level 1 we have nodes 1 and 2 and at level 2 we have nodes 3 and 4. So the answer is 2
Input: V = 5, Edges = {{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {1, 3}, {2, 4}}, X = 5
Output: -1
Explanation: Vertex 5 is not present in the given graph so answer is -1
-660.jpg)
The given problem can be solved with the help of level order traversal. We can perform a BFS traversal in order to find the level of the given vertex
Follow the steps mentioned below to implement the idea:
- Find the maximum vertex of the graph and store it in a variable (say maxVertex).
- create adjacency list adj[] of size maxVertex+1.
- Check if X is present or not, if not then return -1.
- To traverse the graph, create a queue for level order traversal.
- Push vertex 0 in a queue, and set a counter level to 0.
- Create a visited array of size maxVertex+1 to mark the visited nodes.
- Start BFS traversal if the value of X is found in front of the queue then return the level.
- Keep popping nodes from the queue till it becomes empty and increment the counter level
- In one iteration, push all the unvisited nodes in the queue connected with the current node
- Increment the level variable to jump to the next level.
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
C++
class Solution {
public:
int bfs(vector<int> adj[], int V, int vis[],
int level[], int X)
{
if (X >= V)
return -1;
// storing 0 or first vertex in x.
int x = 0;
// creating a queue and pushing x into it.
queue<int> q;
q.push(x);
// marking x as visited and its level will be 0.
vis[x] = 1;
level[x] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
// storing first element of queue and popping
// it.
int curr = q.front();
q.pop();
// traversing adjacent vertices of current
// vertex.
for (int i : adj[curr]) {
// if vertex is not visited, we push it in
// the queue, mark it as visited and store
// its level.
if (!vis[i]) {
q.push(i);
level[i] = level[curr] + 1;
vis[i] = 1;
}
}
}
// returning level of node X.
return level[X];
}
// Function to find the level of node X.
int nodeLevel(int V, vector<int> adj[], int X)
{
// arrays to store level of each node and to mark
// nodes as visited.
int vis[V] = { 0 }, level[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
level[i] = -1;
}
return bfs(adj, V, vis, level, X);
}
};
class Solution {
public int bfs(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > adj,
int V, int[] vis, int[] level, int X)
{
if (X >= V)
return -1;
// Storing 0 or the first vertex in x.
int x = 0;
// Creating a queue and pushing x into it.
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(x);
// Marking x as visited, and its level will be 0.
vis[x] = 1;
level[x] = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
// Storing the first element of the queue and
// popping it.
int curr = q.poll();
// Traversing adjacent vertices of the current
// vertex.
for (int i : adj.get(curr)) {
// If the vertex is not visited, we push it
// in the queue, mark it as visited, and
// store its level.
if (vis[i] == 0) {
q.add(i);
level[i] = level[curr] + 1;
vis[i] = 1;
}
}
}
// Returning the level of node X.
return level[X];
}
// Function to find the level of node X.
public int nodeLevel(int V,
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > adj,
int X)
{
// Arrays to store the level of each node and to
// mark nodes as visited.
int[] vis = new int[V];
int[] level = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
level[i] = -1;
}
return bfs(adj, V, vis, level, X);
}
};
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def bfs(self, adj, V, vis, level, X):
if X >= V:
return -1
# Storing 0 or the first vertex in x.
x = 0
# Creating a queue and pushing x into it.
q = deque()
q.append(x)
# Marking x as visited, and its level will be 0.
vis[x] = 1
level[x] = 0
while q:
# Storing the first element of the queue and popping it.
curr = q.popleft()
# Traversing adjacent vertices of the current vertex.
for i in adj[curr]:
# If the vertex is not visited, we push it in the queue, mark
# it as visited, and store its level.
if vis[i] == 0:
q.append(i)
level[i] = level[curr] + 1
vis[i] = 1
# Returning the level of node X.
return level[X]
# Function to find the level of node X.
def nodeLevel(self, V, adj, X):
# Lists to store the level of each node and to mark nodes as visited.
vis = [0] * V
level = [-1] * V
return self.bfs(adj, V, vis, level, X)
Time Complexity: O(V + E) For traversing all of the nodes.
Auxiliary Space: O(V) to store all the nodes in the queue.