Insert node into the middle of the linked list
Last Updated :
04 Sep, 2024
Given a linked list containing n nodes. The problem is to insert a new node with data x in the middle of the list. If n is even, then insert the new node after the (n/2)th node, else insert the new node after the (n+1)/2th node.
Examples:
Input: LinkedList = 1->2->4 , x = 3
Output: 1->2->3->4
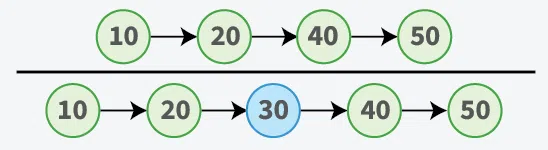
Input: LinkedList = 10->20->40->50 , x = 30
Output: 10->20->30->40->50
Explanation: The new element is inserted after the current middle element in the linked list and Hence, the output is 10->20->30->40->50.
[Expected Approach - 1] Using Two Traversal - O(n) Time and O(1) Space:
The idea is to first find the length of linked list and then insert node with value x after the half length of the linked list.
C++
// C++ implementation to insert node at the middle
// of the linked list
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *next;
Node(int x)
{
data = x;
next = nullptr;
}
};
// Function to insert a node at the middle
// of the linked list
Node *insertInMiddle(Node *head, int x) {
// If the list is empty
if (head == nullptr) {
return new Node(x);
}
Node *newNode = new Node(x);
Node *currNode = head;
int len = 0;
// Calculate the length of the linked list
while (currNode != nullptr) {
len++;
currNode = currNode->next;
}
// Calculate the position to insert the new node
int mid;
if (len % 2 == 0) {
mid = len / 2;
}
else {
mid = (len + 1) / 2;
}
currNode = head;
// Move to the position before where
// the new node will be inserted
while (mid > 1) {
currNode = currNode->next;
mid--;
}
// Insert the new node and adjust the links
newNode->next = currNode->next;
currNode->next = newNode;
return head;
}
void printList(Node *head) {
Node* curr = head;
while (curr != nullptr) {
cout << curr->data << " ";
curr = curr->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
// Creating the list 1->2->4->5
Node *head = new Node(1);
head->next = new Node(2);
head->next->next = new Node(4);
head->next->next->next = new Node(5);
int x = 3;
head = insertInMiddle(head, x);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// C implementation to insert node at the middle
// of the linked list
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
struct Node *createNode(int x);
// Function to insert a node at the middle
// of the linked list
struct Node *insertInMiddle(struct Node *head, int x) {
if (head == NULL) {
return createNode(x);
}
struct Node *newNode = createNode(x);
struct Node *currNode = head;
int len = 0;
// Calculate the length of the linked list
while (currNode != NULL) {
len++;
currNode = currNode->next;
}
int mid = (len % 2 == 0) ? len / 2 : (len + 1) / 2;
currNode = head;
// Move to the position before
// where the new node will be inserted
while (mid > 1) {
currNode = currNode->next;
mid--;
}
// Insert the new node and adjust the links
newNode->next = currNode->next;
currNode->next = newNode;
return head;
}
void printList(struct Node* head) {
struct Node* curr = head;
while (curr != NULL) {
printf("%d ", curr->data);
curr = curr->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
struct Node* createNode(int x) {
struct Node* newNode =
(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
int main() {
// Creating the list 1->2->4->5
struct Node *head = createNode(1);
head->next = createNode(2);
head->next->next = createNode(4);
head->next->next->next = createNode(5);
int x = 3;
head = insertInMiddle(head, x);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// Java implementation to insert node
// at the middle of the linked list
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x){
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
class GfG {
// Function to insert a node at
// the middle of the linked list
static Node insertInMiddle(Node head, int x){
if (head == null) {
return new Node(x);
}
Node newNode = new Node(x);
Node currNode = head;
int len = 0;
// Calculate the length of the linked list
while (currNode != null) {
len++;
currNode = currNode.next;
}
// Determine the middle position
int count
= (len % 2 == 0) ? (len / 2) : (len + 1) / 2;
currNode = head;
// Traverse to the middle node
while (count-- > 1) {
currNode = currNode.next;
}
// Insert the new node in the middle
newNode.next = currNode.next;
currNode.next = newNode;
return head;
}
static void printList(Node head)
{
Node curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
System.out.print(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating the list 1->2->4->5
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next = new Node(5);
int x = 3;
head = insertInMiddle(head, x);
printList(head);
}
}
# Python3 implementation to insert node
# at the middle of a linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# Function to insert a node at the
# middle of the linked list
def insertInMiddle(head, x):
if head is None:
return Node(x)
new_node = Node(x)
curr_node = head
length = 0
# Calculate the length of the linked list
while curr_node is not None:
length += 1
curr_node = curr_node.next
mid = length // 2 if length % 2 == 0 else (length + 1) // 2
curr_node = head
# Move to the position before
# where the new node will be inserted
while mid > 1:
curr_node = curr_node.next
mid -= 1
# Insert the new node and adjust the links
new_node.next = curr_node.next
curr_node.next = new_node
return head
def print_list(head):
curr = head
while curr is not None:
print(curr.data, end=" ")
curr = curr.next
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Creating the list 1->2->4->5
head = Node(1)
head.next = Node(2)
head.next.next = Node(4)
head.next.next.next = Node(5)
x = 3
head = insertInMiddle(head, x)
print_list(head)
// C# implementation to insert node
// at the middle of the linked list
using System;
class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int x){
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
class GfG {
// Function to insert a node at the middle of the linked
// list
static Node insertInMiddle(Node head, int x)
{
if (head == null) {
return new Node(x);
}
Node newNode = new Node(x);
Node currNode = head;
int len = 0;
// Calculate the length of the linked list
while (currNode != null) {
len++;
currNode = currNode.next;
}
// Determine the middle position
int count
= (len % 2 == 0) ? (len / 2) : (len + 1) / 2;
currNode = head;
// Traverse to the middle node
while (count-- > 1) {
currNode = currNode.next;
}
// Insert the new node in the middle
newNode.next = currNode.next;
currNode.next = newNode;
return head;
}
static void printList(Node head)
{
Node curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
Console.Write(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Creating the list 1->2->4->5
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next = new Node(5);
int x = 3;
head = insertInMiddle(head, x);
printList(head);
}
}
// Javascript implementation to insert node
// at the middle of the linked list
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Function to insert a node
// at the middle of the linked list
function insertInMiddle(head, x) {
if (head === null) {
return new Node(x);
}
let newNode = new Node(x);
let currNode = head;
let length = 0;
// Calculate the length of the linked list
while (currNode !== null) {
length++;
currNode = currNode.next;
}
let mid = (length % 2 === 0) ? length / 2
: (length + 1) / 2;
currNode = head;
// Move to the position before
// where the new node will be inserted
while (mid-- > 1) {
currNode = currNode.next;
}
// Insert the new node and adjust the links
newNode.next = currNode.next;
currNode.next = newNode;
return head;
}
function printList(head) {
let curr = head;
while (curr !== null) {
process.stdout.write(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
console.log();
}
// Creating the list 1->2->4->5
let head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next = new Node(5);
let x = 3;
head = insertInMiddle(head, x);
printList(head);
Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
[Expected Approach - 2] Using Single Traversal - O(n) Time and O(1) Space:
The idea is based on the tortoise and hare algorithm which uses two pointers, slow_ptr and fast_ptr to traverse the list. Here, slow_ptr moves one step at a time while fast moves two steps. When fast_ptr reaches the end or NULL then slow_ptr will point to the middle of the linked list. In this specific problem, our task is to insert a new node after the middle of the list. we initialize the fast_ptr to head->next (one node ahead to slow_ptr) then when the fast reaches at end or NULL then slow_ptr pointer will points just before where the insertion should occur. Now, we can insert the new node after slow_ptr.
Below is the working of above algorithm:
Code Implementation:
C++
// C++ implementation to insert node at the middle
// of the linked list
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *next;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = nullptr;
}
};
// Function to insert a node
// at the middle of the linked list
Node *insertInMiddle(Node *head, int x) {
// If the list is empty
if (head == nullptr) {
return new Node(x);
}
else {
// Create a new node
Node *newNode = new Node(x);
// Assign values to the slow and fast pointers
Node *slow = head;
Node *fast = head->next;
// Move slow and fast pointers to find the middle
while (fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
// Insert the newNode and adjust the links
newNode->next = slow->next;
slow->next = newNode;
return head;
}
}
void printList(Node *head) {
Node* curr = head;
while (curr != nullptr) {
cout << curr->data << " ";
curr = curr->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
// Creating the list 1->2->4->5
Node *head = new Node(1);
head->next = new Node(2);
head->next->next = new Node(4);
head->next->next->next = new Node(5);
int x = 3;
head = insertInMiddle(head, x);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// C implementation to insert node at the middle
// of the linked list
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
struct Node *createNode(int x);
// Function to insert a node
// at the middle of the linked list
struct Node *insertInMiddle(struct Node *head, int x) {
// If the list is empty
if (head == NULL) {
return createNode(x);
}
else {
// Create a new node
struct Node *newNode = createNode(x);
// Assign values to the slow and fast pointers
struct Node *slow = head;
struct Node *fast = head->next;
// Move slow and fast pointers to find the middle
while (fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
// Insert the newNode and adjust the links
newNode->next = slow->next;
slow->next = newNode;
return head;
}
}
void printList(struct Node *head) {
struct Node* curr = head;
while (curr != NULL) {
printf("%d ", curr->data);
curr = curr->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
struct Node *createNode(int x) {
struct Node *newNode =
(struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->data = x;
newNode->next = NULL;
return newNode;
}
int main()
{
// Creating the list 1->2->4->5
struct Node *head = createNode(1);
head->next = createNode(2);
head->next->next = createNode(4);
head->next->next->next = createNode(5);
int x = 3;
head = insertInMiddle(head, x);
printList(head);
return 0;
}
// Java implementation to insert node
// at the middle of the linked list
class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x){
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
class GfG {
// Function to insert a node at the
// middle of the linked list
static Node insertInMiddle(Node head, int x)
{
// If the list is empty, create a new node as the
// head
if (head == null) {
return new Node(x);
}
else {
// Create a new node
Node newNode = new Node(x);
Node slow = head;
Node fast = head.next;
// Move slow and fast pointers to find the
// middle
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// Insert the new node in the middle
newNode.next = slow.next;
slow.next = newNode;
return head;
}
}
static void printList(Node head)
{
Node curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
System.out.print(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating the list 1->2->4->5
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next = new Node(5);
int x = 3;
head = insertInMiddle(head, x);
printList(head);
}
}
# Python3 implementation to insert node
# at the middle of a linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# Function to insert a node
# at the middle of the linked list
def insertInMiddle(head, x):
# If the list is empty, create
# a new node as the head
if head is None:
return Node(x)
else:
# Create a new node
new_node = Node(x)
slow = head
fast = head.next
# Move slow and fast pointers to find the middle
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
# Insert the new node in the middle
new_node.next = slow.next
slow.next = new_node
return head
def print_list(head):
curr = head
while curr is not None:
print(curr.data, end=" ")
curr = curr.next
print()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Creating the list 1->2->4->5
head = Node(1)
head.next = Node(2)
head.next.next = Node(4)
head.next.next.next = Node(5)
x = 3
head = insertInMiddle(head, x)
print_list(head)
// C# implementation to insert node
// at the middle of the linked list
using System;
class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int x){
data = x;
next = null;
}
}
class GfG {
// Function to insert a node at the middle of the linked
// list
static Node insertInMiddle(Node head, int x){
// If the list is empty, create a new node as the
// head
if (head == null) {
return new Node(x);
}
else {
// Create a new node
Node newNode = new Node(x);
Node slow = head;
Node fast = head.next;
// Move slow and fast pointers to find the
// middle
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// Insert the new node in the middle
newNode.next = slow.next;
slow.next = newNode;
return head;
}
}
static void printList(Node head){
Node curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
Console.Write(curr.data + " ");
curr = curr.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
public static void Main(string[] args){
// Creating the list 1->2->4->5
Node head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next = new Node(5);
int x = 3;
head = insertInMiddle(head, x);
printList(head);
}
}
// Javascript implementation to insert node
// at the middle of the linked list
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
// Function to insert a node
// at the middle of the linked list
function insertInMiddle(head, x)
{
// If the list is empty, create
// a new node as the head
if (head === null) {
return new Node(x);
}
else {
// Create a new node
let newNode = new Node(x);
let slow = head;
let fast = head.next;
// Move slow and fast pointers to find the middle
while (fast !== null && fast.next !== null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// Insert the new node in the middle
newNode.next = slow.next;
slow.next = newNode;
return head;
}
}
function printList(head) {
let currNode = head;
while (currNode !== null) {
process.stdout.write(currNode.data + " ");
currNode = currNode.next;
}
console.log();
}
let head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next = new Node(5);
let x = 3;
head = insertInMiddle(head, x);
printList(head);
Time Complexity: O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem