C++ Program For Recursive Selection Sort For Singly Linked List - Swapping Node Links
Last Updated :
23 Jul, 2025
Given a singly linked list containing n nodes. The problem is to sort the list using the recursive selection sort technique. The approach should be such that it involves swapping node links instead of swapping node data.
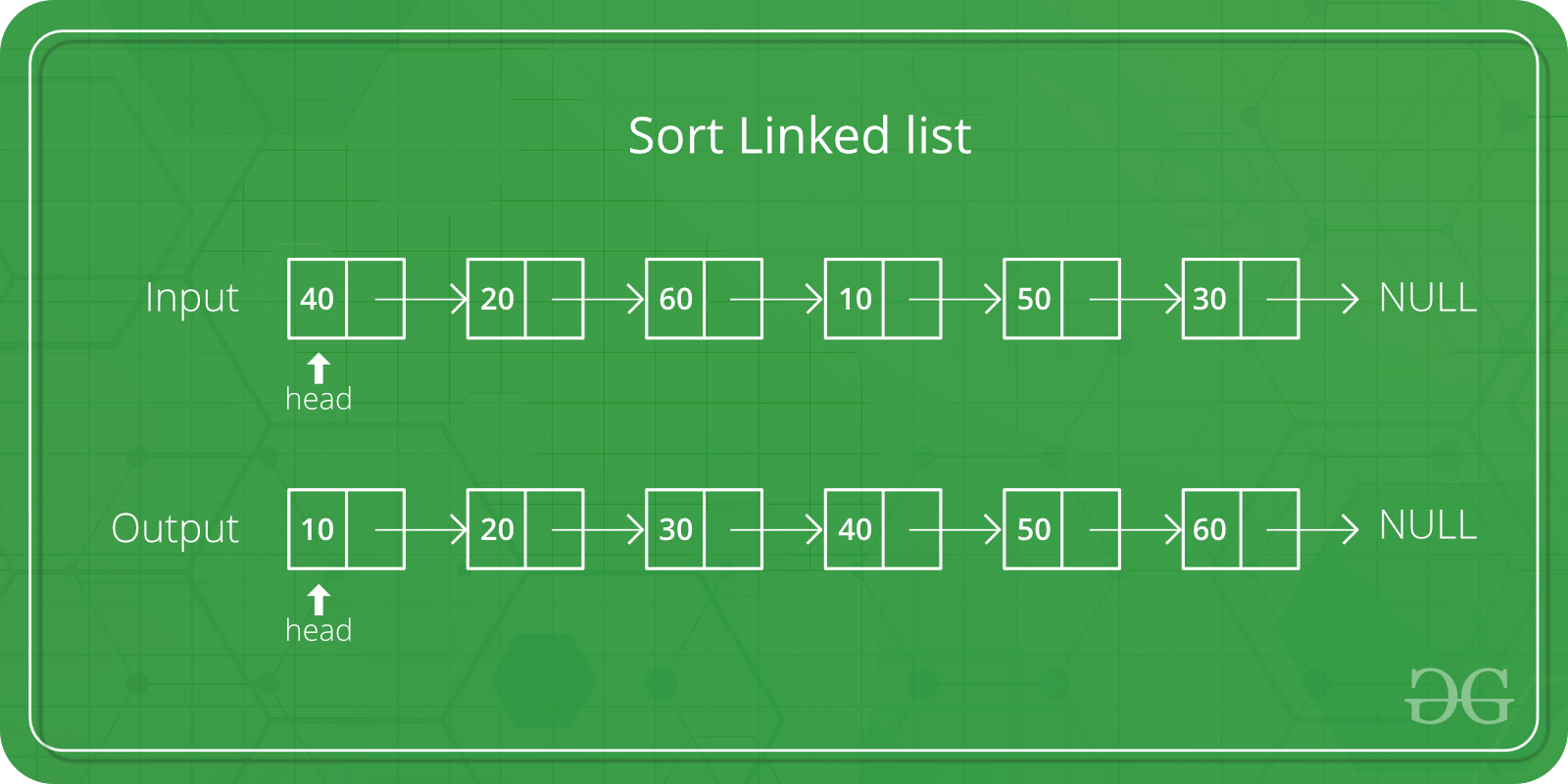
Examples:
Input: 10 -> 12 -> 8 -> 4 -> 6
Output: 4 -> 6 -> 8 -> 10 -> 12
In Selection Sort, we first find the minimum element, swap it with the beginning node and recur for the remaining list. Below is the recursive implementation of these steps for the linked list.
recurSelectionSort(head)
if head->next == NULL
return head
Initialize min = head
Initialize beforeMin = NULL
Initialize ptr = head
while ptr->next != NULL
if min->data > ptr->next->data
min = ptr->next
beforeMin = ptr
ptr = ptr->next
if min != head
swapNodes(&head, head, min, beforeMin)
head->next = recurSelectionSort(head->next)
return head
swapNodes(head_ref, currX, currY, prevY)
head_ref = currY
prevY->next = currX
Initialize temp = currY->next
currY->next = currX->next
currX->next = temp
The swapNodes(head_ref, currX, currY, prevY) is based on the approach discussed here but it has been modified accordingly for the implementation of this post.
C++
// C++ implementation of recursive
// selection sort for singly linked
// list | Swapping node links
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A Linked list node
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// Function to swap nodes 'currX'
// and 'currY' in a linked list
// without swapping data
void swapNodes(struct Node** head_ref,
struct Node* currX,
struct Node* currY,
struct Node* prevY)
{
// Make 'currY' as new head
*head_ref = currY;
// Adjust links
prevY->next = currX;
// Swap next pointers
struct Node* temp = currY->next;
currY->next = currX->next;
currX->next = temp;
}
// Function to sort the linked list using
// recursive selection sort technique
struct Node* recurSelectionSort(struct Node* head)
{
// If there is only a single node
if (head->next == NULL)
return head;
// 'min' - pointer to store the node
// having minimum data value
struct Node* min = head;
// 'beforeMin' - pointer to store
// node previous to 'min' node
struct Node* beforeMin = NULL;
struct Node* ptr;
// traverse the list till the last node
for (ptr = head; ptr->next != NULL;
ptr = ptr->next)
{
// if true, then update 'min' and
// 'beforeMin'
if (ptr->next->data < min->data)
{
min = ptr->next;
beforeMin = ptr;
}
}
// If 'min' and 'head' are not same,
// swap the head node with the 'min' node
if (min != head)
swapNodes(&head, head, min, beforeMin);
// Recursively sort the remaining list
head->next = recurSelectionSort(head->next);
return head;
}
// Function to sort the given linked list
void sort(struct Node** head_ref)
{
// If list is empty
if ((*head_ref) == NULL)
return;
// Sort the list using recursive
// selection sort technique
*head_ref = recurSelectionSort(*head_ref);
}
// Function to insert a node at the
// beginning of the linked list
void push(struct Node** head_ref,
int new_data)
{
// Allocate node
struct Node* new_node =
(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
// Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// Link the old list to the
// new node
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
// Move the head to point to
// the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// Function to print the linked list
void printList(struct Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL)
{
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct Node* head = NULL;
// Create linked list
// 10->12->8->4->6
push(&head, 6);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 8);
push(&head, 12);
push(&head, 10);
cout <<
"Linked list before sorting:n";
printList(head);
// Sort the linked list
sort(&head);
cout <<
"Linked list after sorting:n";
printList(head);
return 0;
}
Output:
Linked list before sorting:
10 12 8 4 6
Linked list after sorting:
4 6 8 10 12
Time Complexity: O(n2)
Auxiliary Space: O(n)
Please refer complete article on Recursive selection sort for singly linked list | Swapping node links for more details!
Explore
DSA Fundamentals
Data Structures
Algorithms
Advanced
Interview Preparation
Practice Problem