Wireless Encryption Methods in Cisco
Last Updated :
13 Nov, 2022
Wireless encryption uses authentication protocols to secure your wireless network. A password or network key is required when a user or device attempts to connect. An unsecured wireless network can allow unauthorized users to access the network to obtain personal information or use your Internet connection to conduct malicious or illegal activities. Network speed and performance can be degraded when other people use your network without your knowledge.
- 64-bit encryption: This configuration requires a password of 10 characters if using hexadecimal digits (0-9 and A-F) and 8 characters if using ASCII characters.
- 128-bit encryption: This configuration requires passwords of 26 characters when using hexadecimal digits and 14 characters when using ASCII characters.
Types of Wireless Encryption:
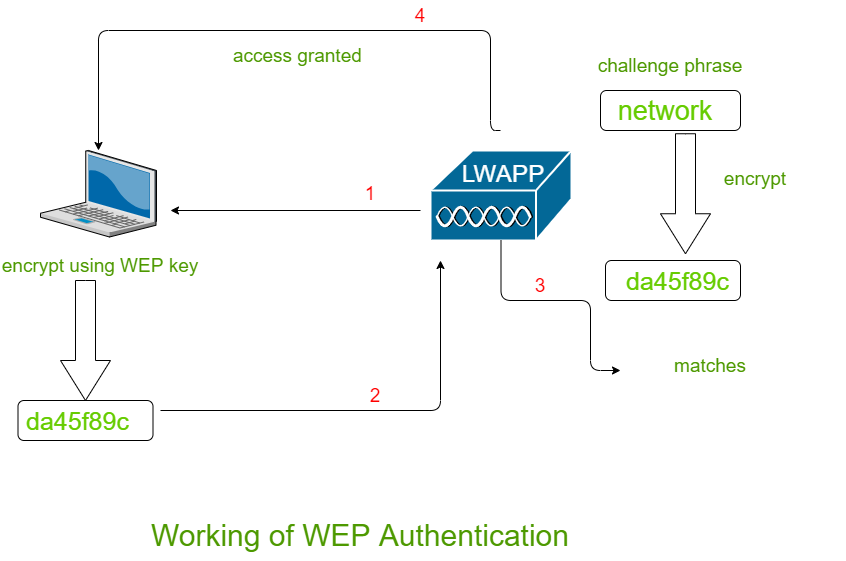
In wireless networks, protection is provided using an authentication process through wireless encryption. Each time a user or device tries to connect, a password or network key is required. Unauthorized users may access your wireless network and obtain personal information, or they may use your internet connection for nefarious or unlawful purposes if it is not secure. If others use your network without your awareness, your network performance or speed may suffer.
1. WPA: Wi-Fi Alliance created Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) in 2003. It is necessary to create a new protocol because of WEP’s flaws. Wi-Fi Protected Access is used (WPA). WPA used 256-bit WPA-PSK encryption (Pre-shared Key). Additional security measures have emerged with WPA. “Message Integrity Check” and “Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)” are two of these new security techniques. The message content is now more safe from hackers thanks to the Message Integrity Check mechanism. The key system had modified the top-per-packet with TKIP. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) would eventually be adopted in place of TKIP. WPA was available in two different modes. Both of these WPA modes are used, with one being used by businesses and the other by individuals. The WPA Modes include:
- Personal Mode (WPA-EAP)
- Enterprise Mode (WPA-PSK)
2. WPA2: Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) was created in 2006. It was an improved version of the original WPA. WPA2 makes weaker WPA components stronger. To provide more secure networks, WPA2 offered improved encryption and authentication techniques. AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and CCMP were these techniques (Counter Cipher Mode with Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol). These mechanisms were utilized in place of the earlier TKIP system. TKIP was also utilized for interoperability, but only as a backup.
Note: WPA2 may be beneficial for home networks, but it is insecure for business networks.
3. AES: Encrypting the top-secret data was the protocols’ primary goal. It has been speculated that deploying AES on tiny networks may eventually increase security. Applications of AES are given below:
- Wireless Security
- Encrypted Browsing
- General File Encryption
- Processor Security
For more details, you can refer to the article: Types of Wireless Security Encryption
Wireless Encryption Methods in Cisco:
However, because it is one of the industry standards algorithms and complies with the IEEE 802.11i standard, AES is the preferable method to utilize for protecting a wireless network.AES performs the same tasks as TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol), but it also leverages information from the MAC header to add a sequence number to the encrypted data header and enables destination hosts to determine whether the non-encrypted bits have been altered. Linksys is the Cisco subsidiary responsible for wireless devices for Small Office Home Office (SOHO). Instead of WPA or WPA2, Linksys APs may use something known as a Pre-shared Key (PSK). The following are comparable PSKs:
- WPA2 is the same as PSK or PSK2 with TKIP
- WPA2 is the same as PSK or PSK2 with AES
- PSK2 without a specified encryption method is the same as WPA2
A wireless LAN can be secured in three ways:
- Disable APs’ SSID broadcasting
- Activate MAC address filtering and only permit recognized clients.
- Utilize WPA2 (or at least WPA)
Note: Be careful; relying solely on the first two security measures won’t adequately protect your network. Even SSIDs that are not broadcast can be found using specialized software like Netstumbler, and MAC addresses can be copied.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...