The Greenhouse Effect is a natural process that occurs in Earth’s atmosphere, where certain greenhouse gases trap heat from the sun and keep the planet’s temperature within a range suitable for life. The greenhouse effect is important for maintaining the balance of the Earth’s climate. However, human activities such as burning fossil fuels have caused an increase in the concentration of greenhouse gases, leading to global warming.
In this article, we will cover the greenhouse effect cause and effect along with ways to prevent its adverse effects.
Greenhouse Effect Definition
When the sunrays are absorbed in the Earth’s atmosphere by greenhouse gases it increases the temperature of the earth. This process is known as the greenhouse effect.
What is Greenhouse Effect?
A greenhouse is a glass structure used to grow plants. The sun’s beams warm the plants and the air in the greenhouse. The trapped heat cannot leave, therefore warming the greenhouse, which is required for plant growth. The same may be said for the atmosphere. The sun heats the earth’s atmosphere during the day. Heat is reflected into the atmosphere as the ground cools at night.
Heat is absorbed by greenhouse gases in the earth’s atmosphere during this process. This is what keeps the surface of the Earth warm and allows life to exist. Carbon dioxide absorbs heat and strongly contributes to global warming. In addition to carbon dioxide, greenhouse gases such as methane, ozone, CFCs, and nitrous oxide have a significant role.
Diagram of Greenhouse Effect
The greenhouse effect diagram demonstrating the process is given below:
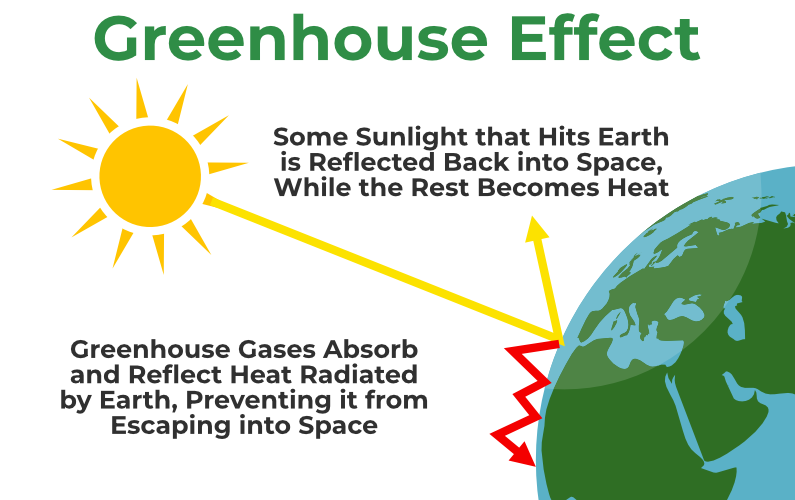
What are Greenhouse Gases?
Greenhouse Gases Definition: Gases which absorb the infraraid radition from the surface of earth and cause the greenhouse effect is known as Greenhouse Gases.
The atmosphere contains several chemical substances that serve as greenhouse gases. These gases allow sunlight to readily flow through the Earth’s atmosphere and heat the land and oceans. This heat is released by the warmed Earth in the form of infrared light, which is invisible to the human eyes. Some infrared light emitted by the Earth returns to space via the atmosphere.
Green house gases major producer are factories, deforestation, automobiles pollution, etc. Greenhouse gases, on the other hand, will prevent all infrared light from passing through the atmosphere. They absorb some of it and return it to the Earth. The greenhouse effect is a naturally occurring phenomenon that keeps the Earth’s surface warm. It is critical to our survival on our planet. The Earth’s average surface temperature would be around 60 degrees Fahrenheit (15.56 °C) colder without the greenhouse effect, making our existing way of life unthinkable.
Greenhouses gases can further be divided into 2 types:
- Direct Greenhouse Gases: Gases that directly absorb the rays are known as direct greenhouse gases. Examples: Ozone, Carbon dioxide.
- Indirect Greenhouse Gases: They are not capable to absorb rays on their own, but they form those gases that absorb the rays, such gases known as indirect greenhouse gases. Example: Methane, Carbon monoxide.
Diagram of Greenhouse Gases
The diagram of greenhouse gases is given below:

Greenhouse Effect and Global Warming
The greenhouse effect is a natural process for maintaining Earth’s temperature, where greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, keeping the planet warm enough to sustain life. However, human activities like burning fossil fuels and deforestation intensify this effect, leading to global warming.
Global warming refers to the overall increase in Earth’s average temperature due to the increased greenhouse effect, causing significant environmental changes such as rising sea levels, melting polar ice caps, and extreme weather events. Addressing greenhouse gas emissions is crucial to mitigating the impacts of global warming and preserving the planet for future generations.
Also Read: Global Warming
Causes of Greenhouse Effect
Due to some process that directly accelerates the greenhouse effect. Those causes are:
Burning of Fossil Fuels
Transportation and power generation both rely on fossil fuels. When fossil fuels are burned, carbon dioxide is released. As the world’s population has expanded, so has the use of fossil fuels. As a result, the atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases has risen.
Deforestation
Plants take carbon dioxide and release it as oxygen. Cutting down trees causes a huge increase in greenhouse gases, which causes global warming.
Farming
Fertilizers include nitrous oxide, which adds to the greenhouse effect on the environment.
Industrial Waste and Landfills
Industries and industries emit hazardous gases into the atmosphere. Landfills also emit CO2 and methane, both of which contribute to global warming.
Effects of Greenhouse Effect
Some of the effects of the greenhouse effect are discussed below:
Global Warming
It is the progressive rise in the average temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere. The fundamental source of this environmental issue is the growing amount of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane emitted by the combustion of fossil fuels, as well as emissions from vehicles, factories, and other human activities.
Depletion of the Ozone Layer
The ozone layer shields the Earth from the sun’s damaging UV rays. It can be found at higher heights of the stratosphere. The depletion of the ozone layer allows harmful UV radiation to reach the earth’s surface, potentially causing skin cancer and catastrophic climate change. The fundamental cause of this phenomenon is the accumulation of natural greenhouse gases such as chlorofluorocarbons, carbon dioxide, and methane, among others.
Smog and Air Pollution
Smoke and fog mix to create smog. It could be caused by both natural and man-made factors. Smog is caused by the accumulation of additional greenhouse gases such as nitrogen and sulfur oxides. Smog is caused by automobile and industrial emissions, agricultural fires, natural forest fires, and chemical reactions between these compounds.
Also Read: Air Pollution
Acidification of Water Bodies
Most of the world’s water bodies have become acidic as the total amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere has grown. When greenhouse gases and precipitation combine, acid rain is created. Water bodies become corrosive as a result. Precipitation also transports toxins to rivers, streams, and lakes, resulting in acidification.
Climate Change Due to Global Warming
Climate scientists agree that the global temperature has risen significantly during the last century. If global warming continues unabated, it will have far-reaching consequences. The rise in sea and ocean levels will be one of the most significant repercussions of global warming. This is already happening all around us. The melting of glaciers and polar ice caps will lead to global water levels rising. Aside from that, freshwater resources will be depleted.
Runway Greenhouse Effect
When the planet absorbs more light than it radiates back, this phenomenon is known as the Runway greenhouse effect. Such a phenomenon occurred on Venus many years ago.
The runway greenhouse effect anticipates in the following manner:
- When the temperature of the earth reaches the boiling point of the water, that time greenhouse effect starts. Due to the high temperature, water from the ocean starts evaporating, and the vapors also absorb more heat from the sun and which also increases the temperature of the earth. This directly speeds up the greenhouse effect, also known as a positive feedback loop.
- There is one other hypothesis for the runway greenhouse effect. Due to high temperatures due to the above-mentioned scenario, because of the high temperature, some chemical reactions start. Due to these chemical reactions from the rocks, CO2 is released into the atmosphere. As the temperature of the earth’s surface increases, it further speeds up the release of CO2 from the rocks, which gives rise to the runway greenhouse effect.
The increase in temperature is because of the greenhouse effect which causes the runway greenhouse effect. Due to this, the temperature of the earth increased and life can’t survive in the future.
How to Prevent Greenhouse Effect?
Increasingly rising temperature is harmful for the Earth. Some of the ways to prevent it are:
Reduce Carbon Emissions
The most effective way to prevent the greenhouse effect is to reduce carbon emissions. This can be achieved by using renewable energy sources, such as wind, solar, and hydro power, reducing dependence on fossil fuels, promoting energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable practices.
Promote Afforestation
Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and release oxygen, making afforestation a crucial measure for reducing greenhouse gas concentrations. Promoting afforestation, especially in urban areas, can also help to reduce air pollution and enhance the quality of life.
Also Read: Difference Between Afforestation And Deforestation
Reduce Waste
Landfills are a major source of greenhouse gas emissions. Reducing waste can help to reduce the amount of methane produced in landfills. This can be achieved by reducing, reusing, and recycling waste materials.
Also Read: Waste Disposal Types and methods
Adopt Sustainable Agricultural Practices
Agriculture is another major source of greenhouse gas emissions. Adopting sustainable agricultural practices, such as reducing fertilizer use, promoting organic farming, and adopting water conservation techniques, can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture.
Promote Sustainable Transportation
Transportation is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions. Promoting sustainable transportation, such as public transportation, carpooling, cycling, and walking, can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality.
Conclusion – Greenhouse Effect
In conclusion, the greenhouse effect is a natural process vital for maintaining Earth’s temperature, but human activities worsen it and leads to global warming and environmental challenges. Understanding its causes and effects is crucial for implementing strategies to mitigate its adverse impacts, such as reducing carbon emissions, promoting afforestation.
FAQs on Greenhouse Gases
What are the Main Greenhouse Gases?
The major greenhouses gases are: Carbon Dioxide, Methane, Nitrous Oxide, and Hydrochloroflurocarbons
How can we Reduce the Greenhouse Effect?
Greenhouse effect can be reduce by various ways such as by using renewable resources., energy saving light bulbs, solar energy, and non-toxic household products.
What are the Major Causes of Greenhouse Effects?
Burning of fossil fuels, farming, industrial and factory waste, and deforestation, all of these play important roles in causing a greenhouse effect.
What is the Greenhouse Effect?
A greenhouse effect is when more gases, such as carbon dioxide, are trapped in the Earth’s atmosphere. These gases function as a screen, trapping heat from the sun and creating a significant temperature increase.
What is Global Warming?
Global warming refers to the overall rise in Earth’s temperature due to intensified greenhouse effect, causing environmental changes like rising sea levels and extreme weather events.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...