What Is Poison Reverse in Networking?
Last Updated :
29 Dec, 2021
Poison Reverse is a loop avoidance method used in Routing Information Protocol (RIP) in Distance Vector Routing Protocol (DVRP) which allows a RIP enabled interface setting the cost of the route (i.e. setting hop count which generally ranges from 0 to 15) that it gets from its neighboring routers to 16 (here 16 will be considered as infinity) which shows that given route is unreachable so send the route back. When the neighboring route receives this route with cost 16, it deletes the useless routes from its routing table which further prevents the looping.
Poison Reverse is used to tackle the count-to-Infinity problems and one can imagine it as a reverse of the Split Horizon method. With the help of poison reverse, we can advertise the route advertisement which would be suppressed by a split-horizon with a distance of infinity.
Working of Poison Reverse
Distance vector routing protocols use topology exchange to dynamically learn about remote networks. The routing protocol starts the process of removing these routes from the network when one of them becomes unreachable. Poison reverse is a part of this process.
The initial advertising router linked to the downed network doesn’t simply remove the network from the routing table since this procedure should occur without generating any loop and also if we do this, the neighboring routers would simply think there is an alternate way through other portions of the network. Instead of this, the route will be advertised with an unreachable metric by the neighboring routers when they get an update from the initial advertising router. Those routers will subsequently update their routing tables to reflect the new unreachable network, effectively eliminating the possibility of a loop.
Example:
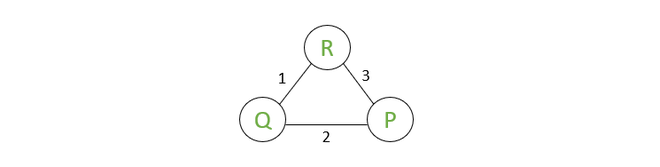
In poison Reverse, we ensure that the path should not turn back towards the same node whenever the cost changes within the network.
For example: with reference to the above diagram, the node R routes to P through destination node Q. If there is an increase in the cost between R and Q, the count-to-infinity problem may occur and to overcome this we are using Poison Reverse. As far as R routing through Q to reach node P, R will broadcast infinite cost (here 16) to node P (the node to which R is routing through).
Need of Poison Reverse
In the Autonomous system, every router must have information about all the networks in the autonomous system which is possible if every router manages to get the information of its neighboring routers. Hence each router shares its whole routing table with its neighboring one.
Consider two routers A and B. Router A has a routing table containing information related to 4 networks N1, N2, N3, N4 respectively, and the router B has a routing table with five networks namely N1, N2, N3, N4, N5 where N5 is having a direct connection with B i.e. B is the source for the network N5.
Now, whenever network A sends its routing table to B, B comes to the conclusion that A doesn’t have any path to reach N5. So, B sends a response containing information of network N5 to A. Now A will have information about N1, N2, N3, N4, and N5 as well.
If we use only the split horizon, A always will send N1, N2, N3, N4 as its routing table since what A knows is B is the source for network N5. On the other hand, B will think that A doesn’t have any path for network N5 and will be unaware of the thing that A doesn’t get the information about the network N5 because of the split horizon.
But if we use split horizon with poison reverse, A will send N1, N2, N3, N4, and N5 to B with the change of cost in N5 from 1 to 16. Now B will get to know that A knows about N5 i.e. it is connected with me(B), as, me(B) is the source of network N5, so B will simply ignore this value and the problem gets resolved.
Advantages
- We don’t have to wait until time out for breaking a loop
- Split horizon with poison reverse is way more secure than route poisoning.
Drawback
Poison Reverse won’t work all the time. Consider the below example :

Drawback of Poison Reverse
Consider the above diagram, if the connection between C and D breaks then node C will try to find a path by routing through A and hence a loop C-A-B-C will rise and we won’t able to solve this with Poison Reverse.
Protocols that use Poison Reverse
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
- Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP)
- Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (IGRP)
- Internetwork Packet Exchange Routing Information Protocol (IPX RIP)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...