CI And CD is the practice of automating the integration of code changes from multiple developers into a single codebase. It is a software development practice where the developers commit their work frequently to the central code repository (Github or Stash). Then there are automated tools that build the newly committed code and do a code review, etc as required upon integration.
The key goals of Continuous Integration are to find and address bugs quicker, make the process of integrating code across a team of developers easier, improve software quality, and reduce the time it takes to release new feature updates. Some popular CI tools are Jenkins, TeamCity, and Bamboo.
Continuous Integration
There could be scenarios when developers in a team, work in isolation for an extended period and only merge their changes to the master branch once their work is completed. This not only makes the merging of code very difficult, prone to conflicts, and time-consuming but also results in bugs accumulating for a long time which are only identified in later stages of development. These factors make it harder to deliver updates to customers quickly.
With Continuous Integration, developers frequently commit to a shared common repository using a version control system such as Git. A continuous integration pipeline can automatically run builds, store the artifacts, run unit tests, and even conduct code reviews using tools like Sonar. We can configure the CI pipeline to be triggered every time there is a commit/merge in the codebase.
Continuous Delivery
Continuous delivery helps developers test their code in a production-similar environment, hence preventing any last-moment or post-production surprises. These tests may include UI testing, load testing, integration testing, etc. It helps developers discover and resolve bugs preemptively.
By automating the software release process, CD contributes to low-risk releases, lower costs, better software quality, improved productivity levels, and most importantly, it helps us deliver updates to customers faster and more frequently. If Continuous Delivery is implemented properly, we will always have a deployment-ready code that has passed through a standardized test process.
CD or Continuous Delivery is carried out after Continuous Integration to make sure that we can release new changes to our customers quickly in an error-free way. This includes running integration and regression tests in the staging area (similar to the production environment) so that the final release is not broken in production. It ensures automation of the release process so that we have a release-ready product at all times and we can deploy our application at any point in time.
Continuous Delivery automates the entire software release process. The final decision to deploy to a live production environment can be triggered by the developer/project lead as required. Some popular CD tools are AWS CodeDeploy, Jenkins, and GitLab.
Continuous Deployment
the final stage of CI and CD will be continuous deployment. It’s an extension of continuous delivery, which automate the proper code to the code repository, continuous deployment will automate the related app for production purpose because there is not having any manual gate at the stage of the pipeline before production, continuous deployment relies on high automation.
in simple language, it is a change of application that goes through the cloud which is carried by the developer and it will live within a few minutes of writing pass with the automated testing.
CI Workflow
Below is a pictorial representation of a CI pipeline– the workflow from developers checking in their code to its automated build, test, and final notification of the build status.
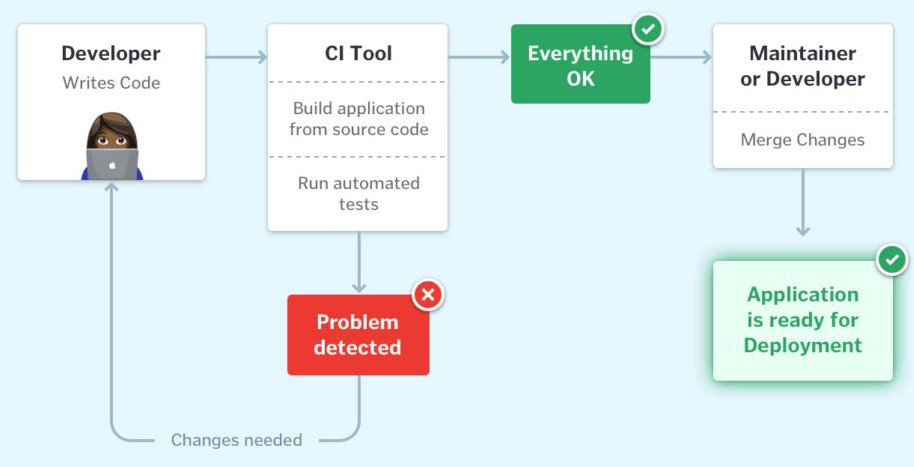
Once the developer commits their code to a version control system like Git, it triggers the CI pipeline which fetches the changes and runs automated build and unit tests. Based on the status of the step, the server then notifies the concerned developer whether the integration of the new code to the existing code base was a success or a failure.
This helps in finding and addressing the bugs much more quickly, makes the team more productive by freeing the developers from manual tasks, and helps teams deliver updates to their customers more frequently. It has been found that integrating the entire development cycle can reduce the developer’s time involved by ~25 – 30%.
CI and CD Workflow
The below image describes how Continuous Integration combined with Continuous Delivery helps quicken the software delivery process with lower risks and improved quality.

CI / CD workflow
We have seen how Continuous Integration automates the process of building, testing, and packaging the source code as soon as it is committed to the code repository by the developers. Once the CI step is completed, the code is deployed to the staging environment where it undergoes further automated testing (like Acceptance testing, Regression testing, etc.). Finally, it is deployed to the production environment for the final release of the product.
If the deployment to production is a manual step. In that case, the process is called Continuous Delivery whereas if the deployment to the production environment is automated, it is referred to as Continuous Deployment.
Why is CI/CD Important?
CI/ CD enables organizations to develop software quickly and efficiently. CI/CD enables an effective process for getting products and software to market faster than ever before, continuously moving code into production, and ensuring a steady flow of new features
What are the Benefits of CI/CD?
Automated testing enables continuous delivery that ensures software quality and safety and increases code profitability in production. CI/ CD pipelines enable a much shorter time-to-market for new product features, resulting in happier customers and reducing the burden on development.
The significant increase in overall delivery speed enabled by CI/CD pipelines improves a company’s competitive advantage.
Automation allows team members to focus on what they do best, resulting in the best end products. Companies with a successful CI/CD pipeline can attract outstanding talent. By moving away from traditional waterfall methods, engineers and developers are no longer engaged in repetitive activities that are often highly dependent on completing other tasks.
What are Some Common CI/CD Tools?
CI and CD tools can help to team with the development, deployment, and testing, some of highly recommended for the integration part and some are for the development and management of the testing and related functionality.
most of the famous tools for the CI and CD which is Jenkins. It is open source and it will help to handle all types of work and design a simple Ci server to complete the CD hub.
apart from the Jenking, many more sources are available for the proper way of managing CI and CD which are listed below:
- Concourse: It is an open-source tool to build the mechanics of CI and CD.
- GoCD: it’s used for the modeling and visualization.
- Screwdriver is a building platform for CD.
- Spinnaker: it’s a CD platform used to build a multi-cloud environment.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...