What is Biometrics ?
Last Updated :
20 Mar, 2024
Biometrics is measure of biological or behavioral features which are used for identification of individuals. Most of these features are inherit and cannot be guessed or stolen.
What is Biometric System?
It is a system that takes an individual’s physiological, behavioral or both traits as input, analyzes it and identifies the individual as legitimate or malicious user.
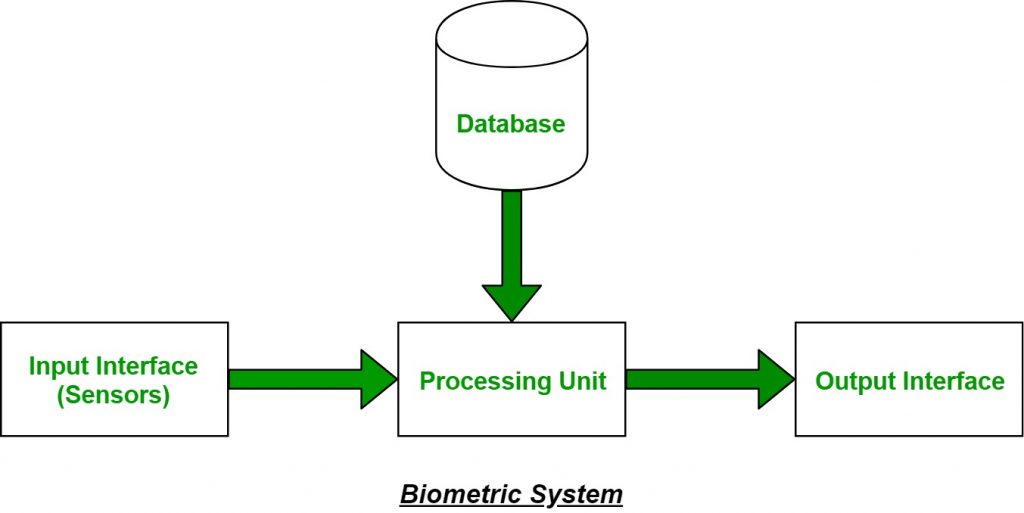
The biometric feature being used must be available in the database for all individuals in the community before the feature can be used for authentication. This is called enrollment.
Authentication can be in one of the following forms:
- Identification: Matching an individual’s features against all records to check whether his/her record is present in the database.
- Verification: To check whether the person is who he/she is claiming to be. In this case the feature of the person is matched only with the features of the person they claim to be.
How are the Biometric Systems designed?
Biometrics Systems, by their nature, are complex system with responsive decision making involved in terms of physical access controls. The two most critical issues that designers of biometric system face are:
Storage and Protection of the template: Biometric systems have to scan, store/retrieve a template and match. It is important to note that depending on the design of the system, the match is to be performed in different locations. There can be three different ‘modes of protection’ that may be used for the template: no protection, data encryption or digital signature.
Accuracy of biometric system step: The evaluation of a biometric system has to be based on the evaluation of all components: the recognition system performance communication interface, the matching and decision and other key factors such as each to use acquisition speed and processing speed.
Types of Biometrics
There are two broad categories of biometrics:
- Physiological Biometrics
- Behavioral Biometrics
Physiological Biometrics: Physical traits are measured for identification and verification in this type of biometrics. The trait should be chosen such that it is unique among the population, and resistant to changes due to illness, aging, injury, etc.
Physiological Biometric Techniques:
- Fingerprint: Fingerprints are unique for every individual. They can be measured in several ways. Minutiae-based measurement uses graphs to match ridges whereas image-based measurement finds similarities between the individuals’ fingertips image and fingerprint images present in the database. It has high level of security and used both for identification and verification. However, due to old age or diseases/injury, fingerprint may get altered. Common usage: in mobiles for verification, in offices for identification.
- Facial Recognition: Features of the face like distance between nose, mouth, ears, length of face, skin color, are used for verification and identification. Accuracy can be affected by fog, sunglasses, aging, etc.
- Iris and Retina: Patterns found in the eye are unique and can be used for both identification and recognition. Devices to analyze retina are expensive and hence it is less common. Diseases like cataract may alter iris patterns
- Voice Recognition: The pitch, voice modulation, and tone, among other things are measured. Security is medium, due to the similarity in voice of people, hence used mostly for verification. The accuracy can be hindered due to the presence of noise, or due to aging or illness.
- DNA: DNA is unique and persistent throughout lifetime. Thus, security is high and can be used for both identification and verification.
Behavioral Biometrics:
Traits of human behavior are measured in this case. Monitoring is required in this type of biometrics to prevent impersonation by the claimant.
- Signature: Signature is one of the most commonly used biometrics. They are used to verify checks by matching the signature of the check against the signature present in the database. Signature tablets and special pens are used to compare the signatures. Duration required to write the signature can also be used to increase accuracy. Signatures are mostly used for verification.
- Keystroke Dynamics: This technique measures the behavior of a person when typing on a keyboard. Some of the characteristics take into account are:
- Typing speed.
- Frequency of errors
- Duration of key depressions
Criteria for selection of Biometric:
- Universality: Each person should possess the biometric trait which is being used. For example, everyone has a face, but it is not the case with GAIT biometric (for wheelchair users).
- Uniqueness: No two persons must be same in terms of the biometric trait being used i.e. everyone must be unique in terms of the biometric trait being used.
- Permanence: Biometric trait must be invariant over time i.e. it shouldn’t change over time.
- Collectability: Biometric trait must be easily measurable.
- Performance: Processing of the biometric trait must be accurate and fast.
- Secure: It must be secure and can’t be copied.
- Acceptability: People should be willing to accept the biometric system.
Measurement of Accuracy:
Accuracy can be measured using two parameters as given below:
Benefits of using Biometric system over traditional authentication systems:
- Invariant: Biometric traits are invariant over time as smart cards get damaged over time, but biometric traits doesn’t.
- Accountability: If there is a security breach, then biometric ensures who can be the responsible person for the breach but in traditional methods, smart cards can be stolen and used by someone else. Hence, accountable person is easily identifiable nowadays by using biometric.
- Easy to use: Biometric systems are easy to use.
- Convenient: User doesn’t have to remember passwords, pins and keep safe the smart cards like before.
- More secure: Biometric trait can’t be stolen or copied.
Social Issues of the biometric system:
Clarity of purpose: It is important to clear about what the needs of application are and hoe biometric will be able to achieve them.
Interoperability and equivalence of performance and process: Process equivalence is extremely important as it impact ton system performance, especially where biometric are used international situations (e.g. border control IS).
Human Factor engineering, usability and social exclusion: Human Factor such as age, ethnicity, gender, disease ought to be studied on a case-by-case basis so as to minimize the possibility of social exclusion of a small but significant part of the population.
Element of Trust: People may temporarily accept to trade in part of their personal freedom in exchange for a more secure world.
Privacy Issues Surrounding Biometrics:
Biometrics requires data of individuals like physiological and behavioral traits be stored in order for identification and verification. This may hinder their privacy, which is considered as a basic fundamental right. Also, there is fear of the stored data being used against them. Since biometric data for an individual is mostly unique, there is fear of it being used to monitor measurement of individuals. Therefore, the data must be stored securely and access to the database must be hierarchical.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...