Element in chemistry are substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by any chemical method by the application of heat or light. For instance, melting a piece of gold still remains the gold element. These substances are composed of a singular type of atoms i.e., they are monoatomic.
Elements are considered to be the building blocks of matter. 118 elements exist in total till now, 94 elements out of these occur in nature whereas the 24 left are prepared artificially. These elements are arranged in a table called the periodic table of elements.
In this article, we will learn about elements in chemistry, the classification of elements, metals, non-metals, and metalloids, etc in detail.

Element Definition
Elements are pure substance that contains only one type of atom that is the building block of all the matter in the universe. Elements can occur in all three states in the matter, that is, solid, liquid or gaseous state. Elements are recognized using chemical symbols and formulae. Elements maintain their homogeneity. For instance, a piece of gold is made up of only gold atoms. Atom is the smallest unit-forming element. It dictates the properties of elements. Elements also possess sharp melting and boiling points.
What is an Element?
Elements in chemistry are the building blocks of all the matter in the universe. There are 118 elements known to humans that are arranged in the table called the periodic table. There are 94 elements in the periodic table that are naturally occurring and 24 elements are artificially prepared by humans. Elements are made up of only one similar kind of atoms.
Example: Hydrogen is an example of an element that cannot be split down into two or more substances. The image added below shows the elements of two types.
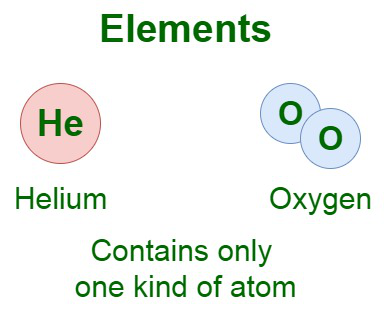
Here, Helium element contains one single atom arranged infinitely, whereas oxygen atom is formed by two atoms group together.
Origin of the Elements
The going of the elements is linked with the origin of universe. The elements in the universe are from the starting of the time and it is believed that most the elements are created in big bang. The knowledge and use of elements to humans is a relatively new affair.
Metals are known to humans since early days we known the existence of bronze and has used it a lot in a period called Bronze Age in early centuries. Apart form this Gold and Silver is known to each early civilization of human this can be proved very easily. So the question arises when is the first time we started organising and string these metals and study their properties for the betterment of human civilization. The answer to this in since Modern days.
Classification of Elements
There are various methods of classification of elements based on their various properties, i.e. there valance electrons, physical and chemical properties and others. But the most common way of classifying elements is based on the physical and chemical properties and on this basis the elemts are of three types that include,
- Metals
- Non Metals
- Metalloids
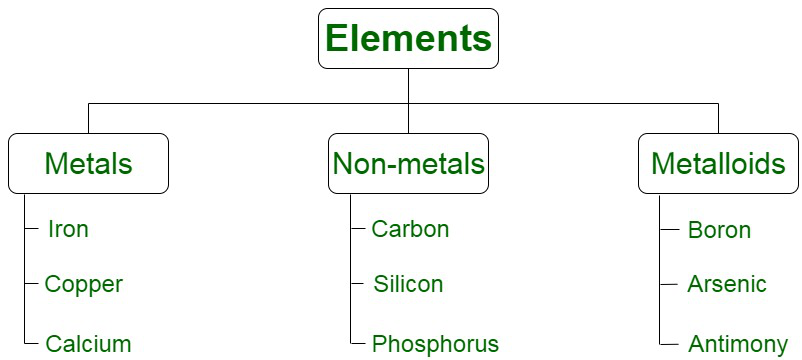
Now let’s learn about them in detail.
Most of the elements in the periodic table are metals. They form cations, that are positive ions and contain metallic bonds. Metals comprise alkali metals, lanthanides as well as transition metals. Metals are rigid substances possessing a shiny lustrous body and acting as good conductors of heat and electricity. For instance, metal is considered to be a good conductor of electricity. These can be easily hammered to form sheets and drawn into wires. Therefore, the metals are both malleable and ductile. Metals are usually crystalline solids. Metals display high chemical reactivity.
Metals tend losing electrons easily. Metals easily form a lattice of positive ions surrounded altogether by a cloud of delocalised electrons. A metal may be a chemical element, for instance, iron; or an alloy, for instance, stainless steel; or even a molecular compound, for instance, polymeric sulphur nitride.
Various characteristics of metals are,
- Possess metallic lustre; Exception: Mercury is a liquid at room temperature.
- Malleable
- Ductile; Exception: Zinc is non-malleable and non-ductile.
- Opaque
- Hard Solids; Exception: Alkali metals, lithium and potassium are soft metals that can easily be cut through a knife.
- Good conductors of heat and electricity; Exception: Caesium and gallium have low melting points, which melt on the palm itself. Mercury, lead, and titanic are bad conductors of electricity. Bismuth is the poorest conductor of heat.
- Most are mono-atomic, that is, contain a single type of atoms
- Low density and low melting point
- Sonorous, producing a deep or ringing sound when struck with another hard object.
Various examples of metals include, Copper, Iron, Sodium, Calcium, Iron, etc. The image added below shows some commonly used metals.

Various application of metals are,
Metals are the most commonly used materials in the construction sector. Iron and steel are two of the most commonly used metals in the construction of structures and even homes.
Because metals are good conductors of electricity, they are used to build cables and parts for electrically powered equipment and gadgets. Just a few examples include televisions, cellphones, refrigerators, irons, and computers.
Metal elements are needed for a range of processes such as nerve impulse transmission, oxygen movement, enzyme activity, and so on. Several medicines are mixed with metal compounds to treat certain deficits or disorders. Antacids contain elements that are often used in medicine, such as iron, calcium, magnesium, potassium, titanium, and aluminium.
- In Automobiles and Machinery
They are frequently used in the manufacture of industrial, agricultural, and farming machines, as well as automobiles such as road vehicles, trains, aeroplanes, and rockets. The most commonly utilised metals in this sector are iron, aluminium, and steel. The bulk of kitchen utensils are made of metals including steel, aluminium, and copper. Metals are selected because of their high temperature resistance.
Nowadays, the majority of furniture is constructed of metal. Metals are also used in the military, where they are used to make weapons and ammunition. Galvanizing prevents the rusting of metals by utilising specific metals.
Non-metals possess qualities differing from those of metals. Non-metals have a dull, coloured or colourless appearance. Non-metals are generally brittle and do not possess the properties of malleability and ductility. They usually generally lack all the characteristics of metals. At room temperature, most of the non-metals are gaseous.
Some of them may be solid. One of the non-metals, bromine is liquid at room temperature. The majority of the non-metals have a dull appearance, except iodine. Certain non-metals can occur in different forms, called allotropes. For example, carbon.
Diamond is one of the allotropes of carbon. It has a very high melting and boiling point and is the hardest naturally occurring substance. Non-metals are generally less dense in comparison to metals. Non-metals are the category of elements that form anions, that is negative ions by accepting or gaining electrons. This is because non-metals possess 4, 5, 6 or 7 electrons in their outermost shell which makes it easy to gain electrons during chemical reactions.
Various characteristics of non-metals are,
- Non-lustrous; Exception: Graphite possess lustre.
- Bad conductors of heat and electricity; Exception: Graphite is a good conductor of heat and electricity.
- Non-malleable
- Non-ductile; Exception: Carbon fibres are ductile but not malleable.
- Contains dual kinds of atoms
- May be solids, liquids or gases.
- Non-sonorous does not produce a deep or ringing sound when struck with another hard object.
Various examples of non-metals are,
- Non-metals may be solid: Carbon, Silicon, Phosphorus etc.
- Non-metals may be liquid: Bromine
- Non-metals may also be gaseous: Hydrogen, Chlorine etc.
The image added below shows the non-metals that are generally used by us in our daily life.

The applications of non-metals are listed below:
Fertilizers
Fertilizers contain nitrogen. It promotes the development of plants. It accelerates the plant’s growth. Non-metallic phosphorus can also help plants. Both of these nonmetals are required for plant growth.
Daily Life
The breathing process is helped by oxygen, which accounts for 21% of the body’s volume. It’s also used to manufacture steel and keep temperatures high during the metal manufacturing process. Oxygen cylinders are used in hospitals. Chlorine, as a bleaching agent, is good at removing stains and colour patches. Chlorine is utilised in the production of a wide range of polymers and insecticides. It aids in the filtering of water. How? When chlorine is added to drinking water, bacteria are killed. Helium is used as an inert gas in scientific studies. It is also used by weather balloons. Iodine is utilised as an antiseptic in the treatment of wounds and cuts, as well as throat infections.
- Sports and music equipment
- Crackers: Sulphur and phosphorus are used in fireworks.
- Purification of water: Chlorine
- Sulphuric acid is prepared using sulphur.
- Hydrogen is used as rocket fuel.
Learn More, Metals and Non-Metals.
Metalloids are basically the elements possessing intermediate in their properties between metals and nonmetals. They mostly act like non-metals in their physical properties. However, there are certain exceptions. For instance, metalloids are good conductors of electricity. Some of the metalloids contract when they are melted. They also possess a metallic and dull appearance. Boron, germanium, arsenic and antimony are some commonly known metalloids.
- Metalloids possess intermediate properties between metals and non-metals.
- Generally occur in solid-state.
- They are semi-conductive.
- Contain one kind of atom.
- Brittle
The examples of metalloids are Boron, Germanium, Antimony, Arsenic, Bismuth, Silicon, etc.
- Metalloids and metalloid compounds are frequently employed as alloys (or as a component of alloys), biological agents (which can be nutritional, toxicological, and medicinal), flame retardants, catalysts, glasses (which can be oxides or metallic in origin), and optical storage media.
- Metalloids are also used in optoelectronics, semiconductors, pyrotechnics, and electronics.
- Fluorescent lamps and infrared detectors: Germanium
- Paints and ceramic enamels: Antimony
- Insecticide and in the preservation of wood: Arsenic
- Biological agents
- Each of the six metalloid elements is recognised to be either poisonous or to have therapeutic and nutritional characteristics. Antimony and arsenic compounds, for example, are known to be very hazardous.
- Boron, arsenic, and silicon, on the other hand, are extremely essential trace elements. The four elements boron, arsenic, silicon, and antimony have numerous medical applications. The remaining two elements (germanium and tellurium) are known to have tremendous therapeutic potential.
The comparison between metal, non-metal and metalloids is tabulated below:
| Basis |
Metals |
Non-Metals |
Metalloids |
| Metallic properties |
Possess the highest degree of metallic behaviour. |
Possess metallic behaviour. |
Possess the metallic properties partially. |
| Location on the periodic table |
Left |
Right |
Between metals and non-metals. |
| Blocks |
Located in s, p, d, f, blocks. |
Located in s and p blocks. |
Located in P Block. |
| Appearance |
Lustrous |
Possess a dull appearance. |
Possess both dull and metallic appearance. |
| Electro-negativity |
Low electronegativity. |
High electronegativity. |
Neither too high nor too low. |
| Conductivity |
High thermal and electrical conductivity. |
Low thermal and electrical conductivity. |
Good thermal and electrical conductivity but less than metals. |
| Ductility |
Ductile |
Non-ductile |
Non-ductile |
| Malleability |
Malleable |
Non-malleable |
Non-malleable |
Read More,
Element Definition – FAQs
What is an Element in Chemistry?
Elements in chemistry are the basic building blocks that are combined in different form to made the universe. They are the independent blocks of matter that have some physical and chemical property and they combine together to form the world that we see.
What is the difference between Elements and Compounds?
The difference between Elements and Compounds is added in the table below:
| Elements |
Compounds |
| Consists of only one kind of atom. |
Consists of more than one kind of atom. |
| Cannot be divided into two or more simpler substances by any physical or chemical means. |
Can be divided into elements by chemical means. |
| There are only 118 types of elements known to mankind. |
An unlimited number of compounds exist |
What is a Metal?
Metals are elements in the periodic table that generally forms cations in their aqueous solution. Metals are generally solid at room temperature. They are generally electropositive in nature. Some examples of metals are, Sodium, Potassium, Iron , Copper, etc.
What is a Non-metal?
Non-metal are elements in the periodic table that are generally electronegative in nature. In general they are in liquid or gaseous state. Some examples of non metals are, Oxygen, Hydrogen, Carbon ,etc.
What are Metalloids?
The elements in the periodic table that have properties of both metals and non-metals are called metalloids. They are generally in all three state of matter, i.e. solid, liquid, and gas. Some examples of metalloids are Germanium, Boron, Silicon, etc.
What is an example of a metal and a non-metal that are liquids at room temperature.
Mercury is the metal and bromine the non-metal which is liquid at room temperature respectively.
Why Copper is a Metal and Sulphur is a Non-Metal?
This is explained by the points added below,
- Copper is malleable and ductile whereas sulphur is neither malleable nor ductile.
- Copper is a good conductor of heat and electricity whereas sulphur is a poor conductor of heat.
Why Platinum, Gold and Silver are preferred elements to make jewellery?
Platinum, gold and silver and situated at the bottom end of the reactivity series, thereby possessing very less reactivity. They do not chemically react with air and water. Because of this reason, they are termed as noble metals. Also, they possess a bright lustre, therefore, suitable for making ornaments.
What are Six Elements of Life?
The six elements of life are,
- Carbon
- Hydrogen
- Nitrogen
- Oxygen
- Phosphorus
- Sulfur
They are called so because they are responsible for the life on Earth.
What are Types of Elements?
The elements in the periodic table are generally divided into three categories that include,
- Metals
- Non-Metals
- Metalloids
What are Radioactive Elements?
Some element in the periodic table that have large nuclei are highly unstable and they release alpha, beta, and gama rays from their nuclei to transform themselves into smaller and stable nuclei. This property of the elements is called radioactivity and the elements that shows radioactivity are called Radioactive Elements. Some examples of radioactive elements are, Radium, Plotonium, Uranium, etc.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...