What is a Web Address?
Last Updated :
23 Nov, 2021
The web address was developed by Sir Tim Berners-Lee and the URL working group of IEFT (Internet Engineering Task Force) in the year 1994. It is a name that points to the location of a particular web page in the internet world. It can be the address of anything like the address of a particular file, directory, photo, video, etc. Every web page on the internet has a unique web address, with the help of which the user accesses those web pages. It is the same as the address of your house or school or any place on this planet. Web Address is also known as URL i.e. uniform resource locator. For example:

Here, https is the scheme, www.geeksforgeeks.org is the domain name and in combination, it is known as the web address of geeksforgeeks website.
Components of a web address
A web address is written in the following format:
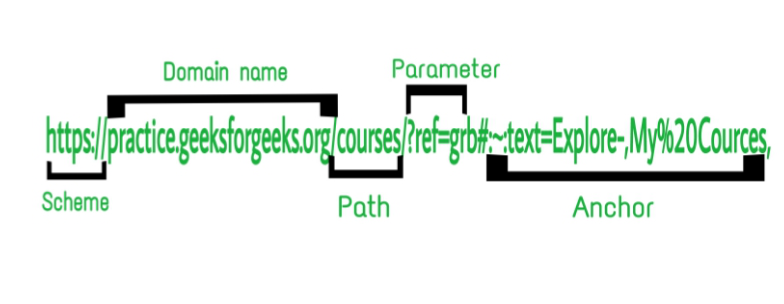
Scheme://Domain name/Path/?Parameters#Anchor
Now we discuss each part in detail:
- Scheme: It is the protocol that is associated with every URL. It tells the browser what type of address the user is trying to access so that the browser connects correctly. Generally, http or https protocol is used to connect with the browser, but other types of the protocol are also available like rtp, dns, chrome, etc.

- Domain name: A domain name is a text name that corresponds to the numeric IP (Internet Protocol) address of the website, followed by the top-level domain name(eg: .gov, .org, .com, etc). Domain names are used to make it easier for the user to access a particular website. Basically, it tells which web server is being requested. For example, the domain name to access GeeksForGeeks is geeksforgeeks.org, where .org is the top-level domain name.

- Path: Path specifies the entire path to a particular web page that the user wants to access. The user can define the entire path of the particular web page (if he/she knows). If no path is specified and only the domain name is entered by the user then the browser loads the default page, also known as the home page, of the website from where the user can navigate to the desired web page.

- Parameters: Parameters are the query string that begins with a question mark(?) after the Path. This is the list of key pairs separated by an ampersand(&) sign. You must have seen it when you have searched for a query on Google or on youtube or any platform. Each web browser has its own rules for passing the parameters. For example, https://www.google.com/search?q=gfg+login&rlz=1C1CHBD_enIN919IN919&… , here are the strings after the question mark(?) is the query string or the parameters.

- Anchor: Anchors are like bookmarks it tell the browser which particular part of a web page the user wants to access. They are written after the Parameters and begin with a hashtag(#).

If we combine all the above parts of the web address then the web address looks like this:
Types of Web Address
There are two types of web addresses:
- Absolute web address: An absolute web address is the web address that contains the domain name and the entire address of the file/directory to which it points. It is the web address that is normally seen in the address bar of the browser and it can be accessed from anywhere in the world. It begins with the protocols like “http”, “https”, “ftp” etc, and have the structure like:
Protocol://Domain name/Path
- Relative web address: Relative web address is the web address that can be accessed only if you are on the home page or on any web page of the particular website. It tells the web address is in relation to the current user location(hence it is named Relative web address). Since it is assumed that the user is already present on the website, a relative web address only contains the domain name and the location, e.g.
<a href = "./geeksforgeekscourses.html"
How to use a Web Address?
Web addresses can be accessed in 4 simple steps:
Step 1: Go to your web browser.
Step 2: Type the website name in the address bar, or you can type the entire web address of the web page you want to access(if you know the entire web address).
Step 3: Press Enter.
Step 4: This will take you to the home page of the respective website. You can navigate to the desired web page from the home page of the website.
Example:
Let’s say we want to access the GeeksForGeeks website so the above steps can be followed as:
- Open the Chrome browser (or any browser which you use).

- Type “www.geeksforgeeks.org” or you can directly write your desired web page name after the domain name, for e.g. “www.geeksforgeeks.org/courses”.

Type “www.geeksforgeeks.org” in the address bar.

Type “www.geeksforgeeks.org/courses” in the address bar.
- Press Enter.
- This will take you to the respective web pages of geeksforgeeks.

The address “www.geeksforgeeks.org” takes you to the home page of geeksforgeeks.
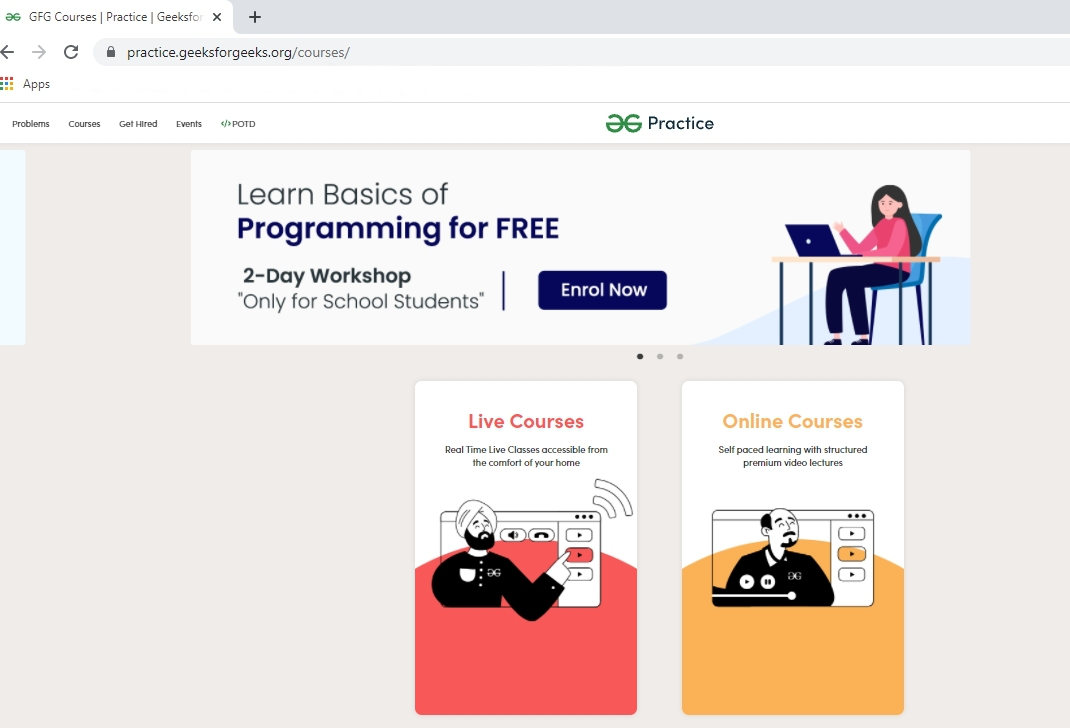
The web address “www.geeksforgeeks/courses” takes you to the courses web page of geeksforgeeks.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...