What is a DNS Amplification Attack?
Last Updated :
03 Aug, 2022
DNS Amplification Attack :
In this article, we will learn about the DNS Amplification Attack and how it can be prevented.
A DNS (domain name system) Amplification Attack is basically a type of DDoS (denial-of-service) attack. It uses different technologies to attack the network by disabling it and not allowing legitimate users to use it.
For launching a DNS amplification attack, the attacker replicates the domains and sends a large number of DNS queries to the server, this results in server sending all the records of the responses of the queries to the attacker which then gains the access over the network. For example, if the attacker generates 10 MB of DNS queries, then the server sends back about 1 TB of responses to that queries.
After that, the servers become so busy in handling the queries and traffic that they cannot request any other service from the legitimate users and the attacker finally gets his thing done as the denial-of-service.
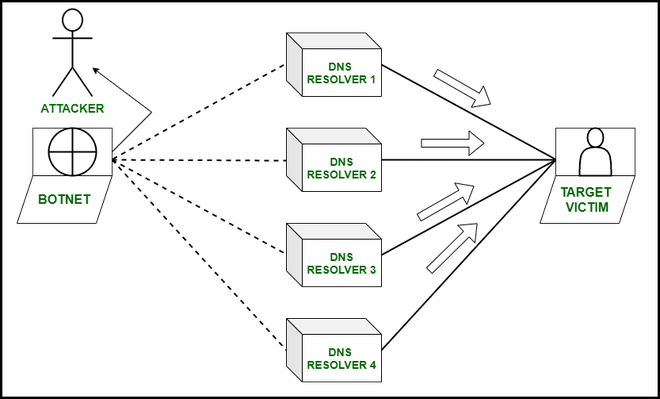
DNS AMPLIFICATION ATTACK
DNS Amplification :
- The attackers get access to all the network servers to flood the server with large amount of traffic and queries to prevent legitimate users from using the site.
- The main ninja technique that attackers use in this attack is to send a DNS lookup request to open the server with source address to be spoofed with the target address.
- When the server sends the response to the attacker’s queries, it is directly sent to the target site. Attackers then send more requests to the server at that site which produces in multiplication of more requests called the amplification effect.
- The attacker is able to increase the traffic at the target site by increasing the size of the response considerably than the requests.
- The attackers use a botnet to produce a large number of DNS addresses with spoofed IDs queries which help them to create a large amount of traffic with very little effort.
- Sometimes, it is very difficult to avoid such amplification attacks because the servers are sending legitimate information to the attackers.
Steps in a DNS Attack :
- The attacker uses a target site to send UDP (user datagram protocol) to send packets with spoofing of IP addresses which relates to the real IP address of the victim (target).
- The UDP packets sends requests with the argument type “ANY” to receive large amount of traffic responses to keep the server busy.
- The DNS resolver of the server sends responses of the queries of the attacker which in turn is a larger number of responses to the spoofed addresses.
- The spoofed IP addresses receive those responses with large amount of traffic, resulting in denial-of-service.
Mitigation of DNS Attacks :
- Using third-party mitigations services help a lot to prevent and solve DNS attacks.
- Using DNS active firewall and malware detection services help to detect these attacks in advance and play a major role in preventing in them.
- Configuring the network servers to handle the DNS requests only from within the certain allowed group of people.
- Reducing the number of DNS resolvers will help to answer the DNS queries only from within the organization and trusted sources which reduces the risk of any amplification attack.
- Source IP verification of spoofed IP addresses help to reject unknown bot traffic that may put in danger the entire DNS server. It helps in removing all the vulnerabilities by not allowing unknown IP addresses to participate to produce any DDoS attack later.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...