What factors are responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India?
Last Updated :
26 Jun, 2023
The diversity of different species on Earth is called plant and animal biodiversity. The term biodiversity was given by Walter G. Rosen in 1986 and the literal meaning of the word is biodiversity. Studying the concept of biodiversity involves counting the total number of species living in a particular area. The study of plant and animal diversity will lead to awareness of many organisms and will help conserve endangered species. There is a level of research on biodiversity because the level of research depends on the type of organism that inhabits a particular region of the ecosystem and the region we are looking at. Previously, the term “biodiversity” was used to refer to concepts such as “species abundance” or “species diversity”. Biologists have also referred to biodiversity as “the relationship of genes, species, and ecosystems throughout a particular region”.
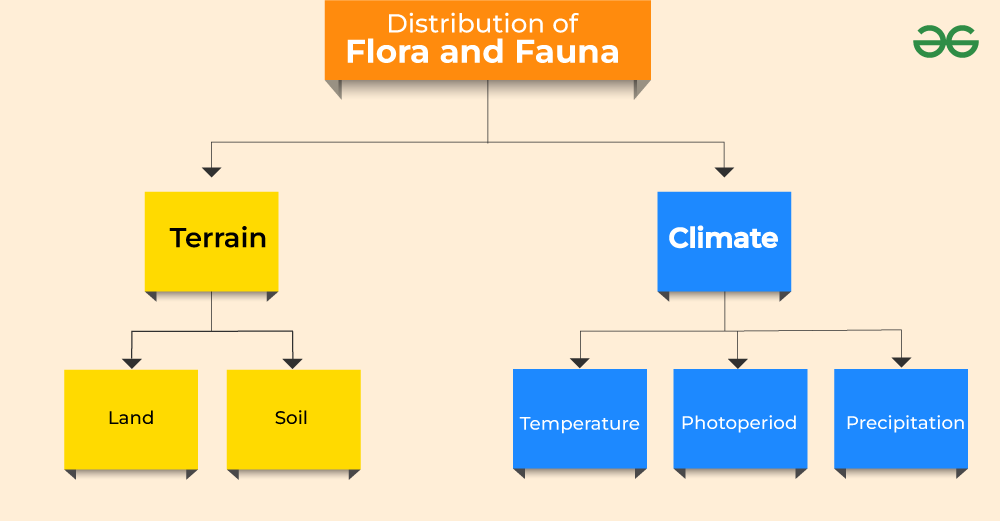
Factors responsible for the Distribution of Flora and fauna
Biodiversity Hotspots in India
Nature generously painted various landscapes throughout our country. Many of these have been identified as “biodiversity hotspots”. The area is rich and diverse in endangered flora and fauna. Officially, 4 out of 36 biodiversity hotspots worldwide are in India. Four hotspots are added to the Sundarbans as well as the grasslands of the Terai Duar Savannah, famous for its characteristic foliage and animals.
- The Himalayas
- The Western Ghats
- The Indo-Burma region
- The Sundaland
Factors Responsible for the Distribution of Plants and Animals in India
The following factors play the most important role in the distribution and diversity of flora and fauna in India.
- Terrain – Land and Soil
- Climate – Temperature, photoperiod (sunshine), precipitation
Land
Natural vegetation is directly or indirectly affected by the Earth. The type of vegetation depends on the nature of the land. Therefore, vegetation is not the same in wet areas, plateaus, mountainous areas, and plains. Agricultural activities are primarily carried out on fertile lands. Forests and grasslands develop on uneven rolling hills, providing refuge for different types of wildlife.
Soil
In space, there are differences in soil. Different types of vegetation are formed on different types of soil. Delta and mangrove vegetation is supported by deltas, wetlands, and moist soils. Prickly shrubs and cacti are supported by sandy soil. The cone tree is found in soil with some depth in hills.
Temperature
On the hills of the peninsula and on the slopes of the Himalayas over 915 m, the growth, and type of vegetation is affected by low temperatures and changes from tropical to subtropical and alpine vegetation. The degree and nature of vegetation depend primarily on temperature, soil, precipitation, and air humidity.
Photoperiod (sunshine)
Trees grow faster in summer because they can use sunlight longer. Seasons, elevation, and latitude are factors that cause differences in the amount of sunlight in different places.
Precipitation
The emergence and retreat of southwest monsoons between June and September account for almost all rainfall in India. Dense vegetation occurs in areas with high rainfall compared to areas with low rainfall.
Importance of Biodiversity
The importance of biodiversity is as follows:
- Essential for the health of ecosystems: Biodiversity is necessary to sustain the ecological processes such as nutrient cycling and climate regulation that make the planet habitable.
- Essential for the production of food: All crops are domesticated versions of plants originally found in the wild. Many animals, including cattle, pigs, and chickens, were also once wild and domesticated by humans.
- Essential for scientific research: Biodiversity allows us to study the relationships between different groups of animals and plants, which can lead to new discoveries.
- Essential for cultural reasons: Biodiversity is culturally important to us because it allows people to maintain traditional lifestyles that can be significantly affected by environmental changes. Biodiversity also plays an important role in the literary and religious traditions of various cultures.
Related Links
- What is Biodiversity?
- Reasons for the Decline of Biodiversity
Frequently Asked Questions
Q 1. What are the factors responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India?
Answer-
Factors that are responsible for the distribution of plants and animals in India would include relief and climate.
Q 2. What are the factors influencing the distribution of plants and animals?
Answer-
The factors influencing the distribution of plants and animals include climate, geology, topography, soil type and so forth.
Q 3. Why is India so rich in biodiversity?
Answer-
India is a biodiversity hotspot due to its diverse soil types, climatic conditions, and physical characteristics, making it suitable to support different types of flora and fauna.
Q 4. What factors influenced the distribution of flora and fauna in India?
Answer-
India is a multinational country with diverse flora and fauna. The main factors determining the distribution of flora and fauna are favorable relief, availability of minerals, freshwater resources, suitable climatic conditions, and soil fertility.
Q 5. How do temperature and rainfall affect the spread of natural vegetation?
Answer-
The collection of plant species in the environment is known as natural vegetation. Temperature and rainfall affect plant growth. For example, when torrential rain falls, the forest becomes dense and dense. When there is less rainfall, the size of the tree decreases.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...