What are the different MySQL database engines ?
Last Updated :
05 Jul, 2022
Database engines are MySQL components that can handle SQL operations like create, read, update data from a database. There are two types of engines in MySQL: transactional and non-transactional.InnoDB is the default engine for MySQL 5.5 and above versions. Major DBMS uses an application programming interface(API) to enable the interaction of users with database engines. It is very necessary to know about the engines for production databases and it also impacts future development. To access the list of available MySQL engines we run SHOW ENGINES; query.
There are 2 types of database engines :
- Transactional Databases: In this type, we can roll back the write operations on the database if they are left incomplete. These operations are known as transactions. Majorly, modern engines are transactional.
- Non-Transactional Databases: Unlike transactional databases, they don’t provide Rollback/Commit. Instead, we need to manually code to perform the rollback operations.
The below image illustrates the different available engines in MySQL:
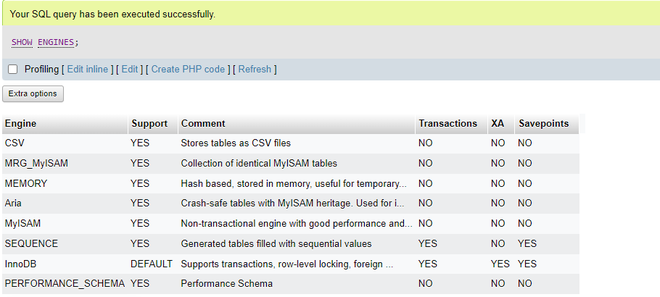
List of database engines in MySQL
In this article, we will learn about InnoDB, MyISAM, MEMORY, MERGE, CSV, and SEQUENCE engines, their features, along with knowing their advantages & disadvantages.
InnoDB: InnoDB is a storage engine for DBMS MySQL and MariaDB.It is the default storage engine for MySQL versions 5.5 and higher. It replaced MyISAM as the default engine.
Features:
- It provides standard ACID-compliant transaction features, along with foreign key support. Oracle recommends InnoDB for tables.
- It supports multi-version concurrency control, crash-recovery, and rollback operations. Multi-user performance is possible due to row-level locking.
- It is used in the MariaDB server too. To maintain data integrity and security, InnoDB supports foreign key constraints.
- InnoDB supports buffers that cache data as well as indexes.
- It offers a table locking method, which means only one user can alter the table at a time.
Advantages:
- Supports ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability) properties for securing user’s data.
- Access to multiple users with high performance and consistent reads in Oracle-style.
- Supports usage of foreign keys that help in the consistent update, insert and delete operations. Also, it helps in maintaining integrity in the contents of the tables of the database.
Disadvantages:
- Does not support full-text search.
- If performance is a priority then it is not used because it is slower than MyISAM.
- Usage of foreign key relationships makes it complex to use.
MyISAM: It is the default engine for MySQL DBMS versions prior to 5.5.MyISAM is a high-speed storage and retrieval storage engine. It doesn’t support transactions. It is easy to copy between systems and has a small data footprint. Mostly used in Web and Data Warehousing.
Features:
- MyISAM is stored in 3 files: .frm – Stores table format, .MYD – Data files, .MYI – index file.
- It supports three storage formats: Fixed, Dynamic, and Compressed.
- The maximum key length is 1000 bytes.
- The maximum number of indexes per table and columns per index are 64 and 16 respectively.
Advantages:
- MyISAM is simpler than other engines.
- It is faster than any other general-purpose database engine. It also provides a full-text searching
Disadvantages:
- It can easily lead to corruption of the table. However, we can use the REPAIR TABLE query to recover it.
- It does not support foreign key constraints or transactions.
CSV: It is used to store CSV format in a text file. It is always compiled into the MySQL server. It is lightweight and can be easily imported into spreadsheet programs.
Features:
- CSV tables use CSV format.Thus, it can be used for data exchange for eg. using the spreadsheet.
- Editing data can be performed even if the MySQL server is down using standard file editors
- Instantaneous loading of massive data in the MySQL server.
Advantages:
- Metafile is created that stores the state of the table and the number of rows that exist in the table after creating the CSV file.
- Data is stored in a text file using the common-separated value format.
Disadvantages:
- CSV engine does not support indexing.
- It does not support partitioning.
- It must have NOT NULL attributes on all columns.
MERGE: Tables created using the MERGE engine are used to handle a large volume of data easily. It is a collection of identical MyISAM tables that can be used as one. Thus, it is also known as the MRG_MyISAM engine. It is good for data warehousing environments.
Features:
- It was introduced in MySQL 3.23.25 version.
- UNION and INSERT_METHOD are two unique features of MERGE tables.
- MERGE tables do not have PRIMARY KEY or UNIQUE indexes as they cannot enforce uniqueness over all tables.
Advantages:
- It is a collection of identical MyISAM tables that can be used as one table. Memory is saved due to it.
- It can perform the most efficient repair of individual tables rather than repairing a single large table which is made by merging these individual tables.
- Merge tables are not limited to the file size of the operating system, unlike MyISAM tables.
Disadvantages:
- Only identical MyISAM tables can be used to merge.
- If the MERGE table is nontemporary, it is necessary for merge tables to be nontemporary. If the MERGE table is temporary, the MyISAM tables can be a mixture of temporary and nontemporary.
- Some MyISAM features are not available in MERGE tables.
MEMORY: It is considered to be the fastest engine used to usually create temporary tables in memory (also known as HEAP). Thus data is lost when the database is restarted. It is non-transactional. It is useful for quick looks up of references and other identifying data. It stores all data in RAM for faster access rather than storing data in disks. It is widely used for read-only caches of data from tables or for temporary usage.
Features:
- It does not create any files on disk.
- MEMORY tables cannot contain BLOB or TEXT columns.
- AUTO_INCREMENT columns are supported.
- VARCHAR is stored using fixed-length i.e. it uses fixed-length row-storage format.
Advantages:
- Data is encrypted which is implemented in the server via encryption functions.
- Supports B-tree indexes.
- Offers low-level locking and multiple-thread operation for low contention between clients.
Disadvantages:
- MEMORY tables cannot be partitioned.
- Memory can’t be reclaimed if you delete individual rows from a MEMORY table
SEQUENCE: It is the transactional engine used for creating ascending or descending sequences of positive integers with given initial, end, and increment values. It is read-only and supports XA.
Features:
- Like the MEMORY database engine, it does not create any file on a disk.
- It creates virtual tables automatically whenever we need them. There is no way to create a SEQUENCE table explicitly.
- This engine is useful with joins and subqueries.
Advantages:
- SEQUENCE engine is not bound to tables. Thus, we can use them for any other purpose too.
- Flexibility in implementation of the table.
Disadvantages:
- Additional programming is required for the AUTO_INCREMENT feature which is not available in the engine by default.
- Concurrency issue when there are multiple parallel sessions active.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...