Near, Far and Huge Pointers in C
Last Updated :
19 Apr, 2023
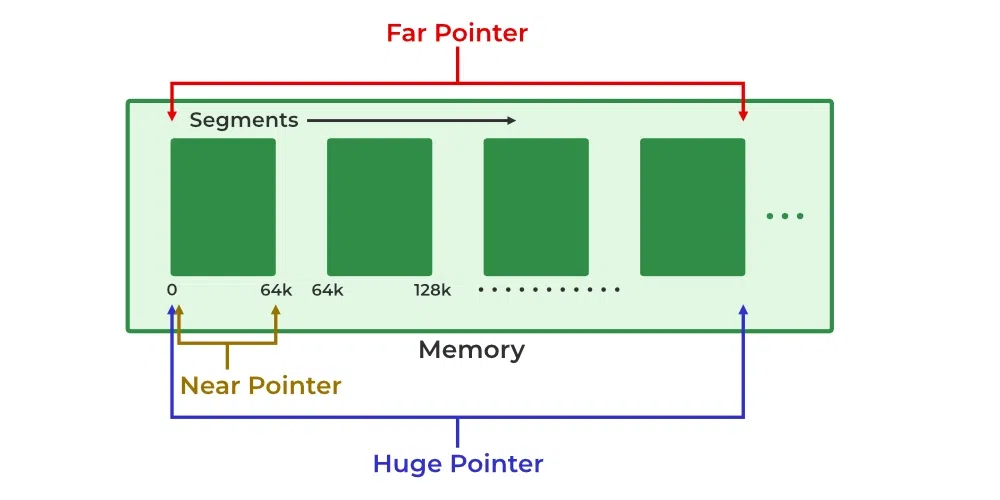
In older times, the intel processors had 16-bit registers but the address bus was 20-bits wide. Due to this, the registers were not able to hold the entire address at once. As a solution, the memory was divided into segments of 64 kB size, and the near pointers, far pointers, and huge pointers were used in C to store the addresses.
There are old concepts used in 16-bit intel architectures, not of much use anymore.
Near, Far and Huge Pointers in C
1. Near Pointer
The Near Pointer is used to store the 16-bit addresses. It means that they can only reach the memory addresses within the current segment on a 16-bit machine. That is why we can only access the first 64 kb of data using near-pointers.
The size of the near pointer is 2 bytes.
Syntax of Near Pointers in C
pointer_type near * pointer_name;
Example of Near Pointers in C
C
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int near* ptr;
printf("Size of Near Pointer: %d bytes", sizeof(ptr));
return 0;
}
|
Output
Size of Near Pointer: 2 bytes
Note: Most of the modern compiler will fail to run the above program as the concept of the near, far and huge pointers is not used anymore.
2. Far Pointer
A far pointer stores the address in two 16-bit registers that allow it to access the memory outside of the current segment. The compiler allocates a segment register to store the segment address, then another register to store offset within the current segment. The offset is then added to the shifted segment address to get the actual address.
- In the far pointer, the segment part cannot be modified as incrementing/decrementing only changes the offset but not the segment address.
- The size of the far pointer is 4 bytes.
- The problem with the far pointers is that the pointer has different values but points to the same address. So, the pointer comparison is useless on the far pointers.
Syntax of Far Pointer in C
pointer_type far * pointer_name;
Example of Far Pointer in C
C
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int far* ptr;
printf("Size of Far Pointer: %d bytes", sizeof(ptr));
return 0;
}
|
Output
Size of Far Pointer: 4 bytes
3. Huge Pointer
The huge pointer also stores the addresses in two separate registers similar to the far pointer. It has the following characteristics:
- In the Huge pointer, both offset and segment address is changed. That is why we can jump from one segment to other using a Huge Pointer.
- The Huge Pointers always compare the absolute addresses, so the relational operation can be performed on it.
- The size of the huge pointer is 4 bytes.
Syntax of Huge Pointer in C
pointer_type huge * pointer_name;
Example of Huge Pointer in C
C
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int huge* ptr;
printf("Size of the Huge Pointer: %d bytes",
sizeof(ptr));
return 0;
}
|
Output
Size of the Huge Pointer: 4 bytes
Difference between Far Pointer and Near Pointer
Following are the difference between the far pointer and near pointer in C:
- The far pointer can store the address of any memory location in the RAM whereas the near pointer can only store till first 64kB addresses.
- The far pointer uses two registers to store segment and offset addresses separately whereas the near pointer can only store addresses in a single register.
- The size of the far pointer is 4 bytes where as the near pointer is 2 bytes wide.
Difference between Far Pointer and Huge Pointer
Following are the difference between the far pointer and huge pointer in C:
- The far pointer cannot move between different segments whereas the huge pointer can move between multiple memory segments.
- The two far pointer values can point to the same location while in the case of the huge pointer, it is not possible.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...