Watcherd Shell Listener for Directory Changes in Linux
Last Updated :
29 Jan, 2021
Watcherd is a tool for Linux that helps to monitor directory changes and print whatever changes are done like adding and deleting for a particular directory and execute commands and shell scripts according to a particular event.
Installing Watcherd on Linux
Step 1: Downloading watcherd.
Since watcherd is a Github repository you can use wget command to download its zip and extract it. To do so execute the command:
wget https://github.com/devilbox/watcherd/archive/master.zip
Step 2: Unzipping and extracting.
After downloading unzip the file using the command:
unzip master.zip
In case you do not have to unzip installed then you can install it by using:
sudo apt-get install unzip
Step 3: Copy to the bin location.
Once unzipping is finished now you need to copy the files to the bin directory, to do so use the command:
sudo cp watcherd-master/watcherd /usr/bin/
Step 4: Check the tool is installed properly or not.
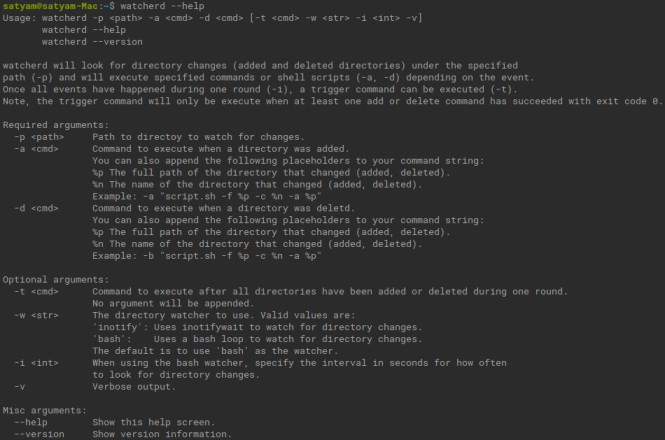
You can check the user manual by using the help command:
watcherd --help
Output:
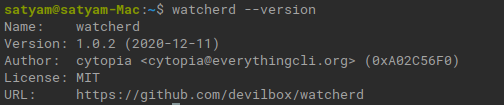
Or you can check with –version
watcherd --version
Output:
Watcherd Working:
Step 1: Create a directory.
Make a directory named test in your current working directory
mkdir sample
Step 2: Now start watcherd.
Now deploy watcherd using the following parameters:
watcherd -v -p ~/sample -a "echo added %n" -d "echo deleted %n" -t "ls -l ~/sample" &
Output:

where
- -v stands for verbose which will verbosify the output of the command
- -p stands for the path to directory, and we have used test for the subject
- -a stands for executing the command if any directory path is created , we have used echo for printing but you can also add any other way of scripting and make the best use out of it.
- -d stands for executing the command if any directory path is deleted and vice versa.
- %n will be substituted with directory name or you can use %p to get a full path to the created or deleted directory
- -t “ls -l ~/test” execute command after triggering
- & run in background
Step 3: After executing the command check if it’s running by using the command:
ps ax | grep watcherd
Output:

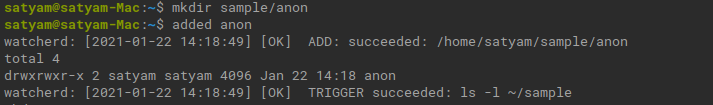
Now let’s do some adding and deleting directory in our test folder and see what happens, directory can be named anything, for instance we are using anon.
mkdir sample/anon
Output:
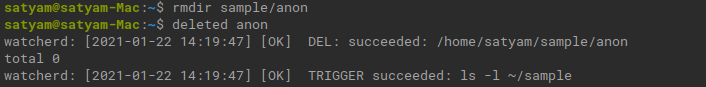
rmdir sample/anon
Output:
After executing the command you will be able to see an output generated by watcherd.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...