Volcanic Landforms: Extrusive and Intrusive
Last Updated :
08 Mar, 2024
Volcanic landforms are natural wonders shaped by the fiery power of volcanoes. They are formed from magma, the molten rock beneath the Earth’s surface, which erupts and cools to create diverse landscapes. They come in two main types: extrusive and intrusive.
Let’s learn about the volcanic landforms in detail, both above and below the Earth’s surface.
Volcanic Landforms
When magma comes out of the magma chambers, it proceeds to the cooling process. It either cools within the crust or on the surface of the earth. The formation of rocks after the cooling of magma inside the earth’s surface is called plutonic rocks. The rocks that cool on the earth’s surface and form rocks are known as Igneous rocks.
Volcanic landforms are landforms that form due to volcanic eruptions and depend on the place where it cools.
- Intrusive landforms
- Extrusive landforms
Intrusive Volcanic Landforms
The magma which cools inside the earth’s crust is known as intrusive landforms.

Intrusive Volcanic Landforms
Batholiths
- It is cooled magma inside the magma chamber.
- It is a large magma that forms into a large dome when it cools down in the deeper depth of the crust.
- After the Denudation process, it appears on the earth’s surface.
- It forms the core of the high mountain.
- It is usually granite which forms a massive upland region.
Lacoliths:
- It is a large dome-shaped with a level base and is linked by a pipe channel or conduit from below.
- It is present in deeper depth but above Batholiths.
- It is an exposed part of the Batholiths.
- The Karnataka hill is an example of such kind of Volcanic Landforms.
Lopoliths:
- Generally, lava move in an upward direction but a part of lava moves in the horizontal direction when there is weaker space.
- The horizontal movement of lava develops into different shapes but the formation of a saucer shape, concave to the sky body is known as lopolith.
Phacoliths:
- It is wavy intrusive rocks parallel to the bedding plane.
- It is found at the base of the syncline or the top of the anticline in folded igneous rocks.
- It is found in lens shape.
Sills and Sheets:
- Some lava move in the horizontal direction and the horizontal body of intrusive igneous rocks after solidification is known as sills.
- The thick deposit is known as sills and thinner ones are called sheets.
- They are not at depth but nearer to the earth’s surface.
Dikes:
- During volcanic eruption, lava moves in all possible directions in the possible cracks and fissures.
- The magma which cools in cracks and fissures forms wall-like structures known as Dykes.
- Dykes which are perpendicular to the earth’s crust, are mostly found in the western Maharashtra region.
- Deccan traps form due to the eruption of lava from these feeders.
Extrusive Volcanic Landforms
Landforms formed due to material thrown out of the surface. The materials include ash, dust, pyroclastic debris, nitrogen and sulphur compound, and a small amount of chlorine, hydrogen, and argon. The various landforms forms due to the outside solidification of lava.
Extrusive Volcanic Landforms
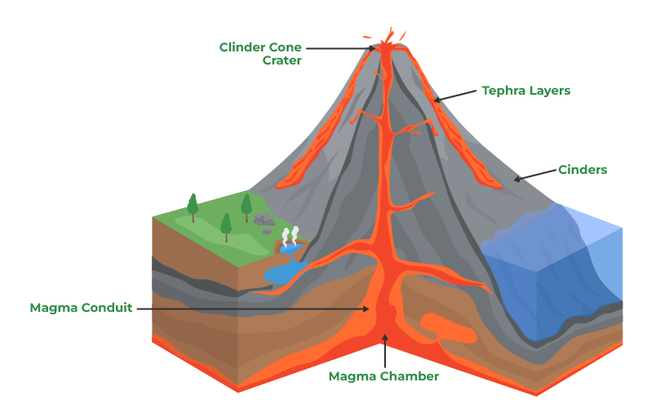
Cinder Cones:
- It is of low height and form of lava and other pyroclastic materials.
- Due to gravity it piles up in large no.
- It consists of steep straight sides and a crater at the top.

Cinder Cone Volcanoes
Conical Vent:
- A narrow, cylindrical vent through which magma erupts during an explosion.
- It is found in composite-type volcanoes.
Fissure Vent:
- A narrow, linear vent is like a conical one but the magma comes out without any explosion.
- It is common in shield-type volcanoes.
- When basaltic lava flow occurs in the region and it piles up into the shape of a large mountain known as a shield volcano. Ex- Mauna Lao
Composite-type Volcanic Landforms:
- These are conical-type landforms and are also known as stratovolcanoes because of layers of pyroclastic and lava.
- During this formation, lava comes out with a lot of pyroclastic material and ashes. The major lava is andesitic.
- Mount Fiji, mount Vesuvius is an examples.
Caldera:
- when during a volcanic eruption, magma comes out of the earth’s surface and forms an empty chamber inside the earth, and sometimes the outside material collapses into the volcanic chamber and forms a tube-like shape known as a caldera.
- When rain or snow melts in this it turns out to be caldera lake.

Caldera Lake
Crater:
- A vent through which magma flows out an eruption is known as a crater.
- It is an inverted cone shape and when it is inactive it appears as a bowl-shaped depression
- When rainwater accumulated or snow melts it is known as a crater lake. Lake Toba is the largest crater lake in the world.
Volcanic Domes:
- It is a result of the extrusion of a highly viscous gas, poor andesitic, and rhyolitic lava.
- It piles up over the vent without spreading.
Resurgent Domes:
- When the caldera is formed by collapse, magma is re-injected into the area below the caldera. One or more areas within the caldera uplift and form resurgent domes.
Flood Basalt:
- It is large volume outpourings of basaltic magma from fissure vents.
- It spread in large areas and builds up plateaus.
Read More :
FAQs on Volcanic Landforms
What are Volcanic Landforms?
A volcanic landform is a natural landscape feature formed by the eruption of magma from the earth’s crust.
How are Extrusive and Intrusive Rocks formed?
Extrusive rocks are formed when magma erupts onto the Earth’s surface, cools, and solidifies quickly into rock. Intrusive rocks are formed when magma cools and solidifies beneath the Earth’s surface, creating coarse-grained textures.
What are Intrusive Landforms?
Intrusive landforms are geological features formed from magma that cools and solidifies beneath the Earth’s surface, such as plutons, batholiths, sills, and dikes.
What are Extrusive Landforms?
Extrusive landforms are geological features formed by the cooling and solidification of lava on the Earth’s surface, including volcanoes, lava plateaus, and volcanic islands.
What is difference between Extrusive and Intrusive Volcanic Landforms?
Extrusive volcanic landforms are created by lava cooling on the Earth’s surface, while intrusive volcanic landforms result from magma solidifying beneath the surface.
What are Various Intrusive Landforms or Structures?
Various intrusive landforms include batholiths, laccoliths, sills, dikes, and plutons.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...