Virtualization in Cloud Computing and Types
Last Updated :
13 Mar, 2024
Virtualization is a technique of how to separate a service from the underlying physical delivery of that service. It is the process of creating a virtual version of something like computer hardware. It was initially developed during the mainframe era. It involves using specialized software to create a virtual or software-created version of a computing resource rather than the actual version of the same resource. With the help of Virtualization, multiple operating systems and applications can run on the same machine and its same hardware at the same time, increasing the utilization and flexibility of hardware.
In other words, one of the main cost-effective, hardware-reducing, and energy-saving techniques used by cloud providers is Virtualization. Virtualization allows sharing of a single physical instance of a resource or an application among multiple customers and organizations at one time. It does this by assigning a logical name to physical storage and providing a pointer to that physical resource on demand. The term virtualization is often synonymous with hardware virtualization, which plays a fundamental role in efficiently delivering Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) solutions for cloud computing. Moreover, virtualization technologies provide a virtual environment for not only executing applications but also for storage, memory, and networking.
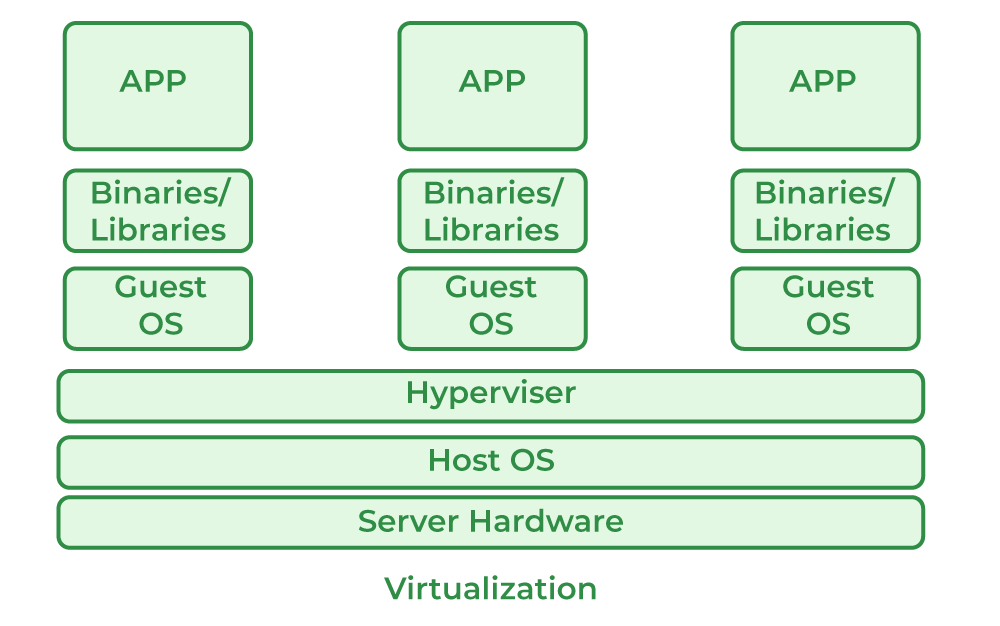
Virtualization
- Host Machine: The machine on which the virtual machine is going to be built is known as Host Machine.
- Guest Machine: The virtual machine is referred to as a Guest Machine.
Work of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Virtualization has a prominent impact on Cloud Computing. In the case of cloud computing, users store data in the cloud, but with the help of Virtualization, users have the extra benefit of sharing the infrastructure. Cloud Vendors take care of the required physical resources, but these cloud providers charge a huge amount for these services which impacts every user or organization. Virtualization helps Users or Organisations in maintaining those services which are required by a company through external (third-party) people, which helps in reducing costs to the company. This is the way through which Virtualization works in Cloud Computing.
Benefits of Virtualization
- More flexible and efficient allocation of resources.
- Enhance development productivity.
- It lowers the cost of IT infrastructure.
- Remote access and rapid scalability.
- High availability and disaster recovery.
- Pay peruse of the IT infrastructure on demand.
- Enables running multiple operating systems.
Drawback of Virtualization
- High Initial Investment: Clouds have a very high initial investment, but it is also true that it will help in reducing the cost of companies.
- Learning New Infrastructure: As the companies shifted from Servers to Cloud, it requires highly skilled staff who have skills to work with the cloud easily, and for this, you have to hire new staff or provide training to current staff.
- Risk of Data: Hosting data on third-party resources can lead to putting the data at risk, it has the chance of getting attacked by any hacker or cracker very easily.
For more benefits and drawbacks, you can refer to the Pros and Cons of Virtualization.
Characteristics of Virtualization
- Increased Security: The ability to control the execution of a guest program in a completely transparent manner opens new possibilities for delivering a secure, controlled execution environment. All the operations of the guest programs are generally performed against the virtual machine, which then translates and applies them to the host programs.
- Managed Execution: In particular, sharing, aggregation, emulation, and isolation are the most relevant features.
- Sharing: Virtualization allows the creation of a separate computing environment within the same host.
- Aggregation: It is possible to share physical resources among several guests, but virtualization also allows aggregation, which is the opposite process.
For more characteristics, you can refer to Characteristics of Virtualization.
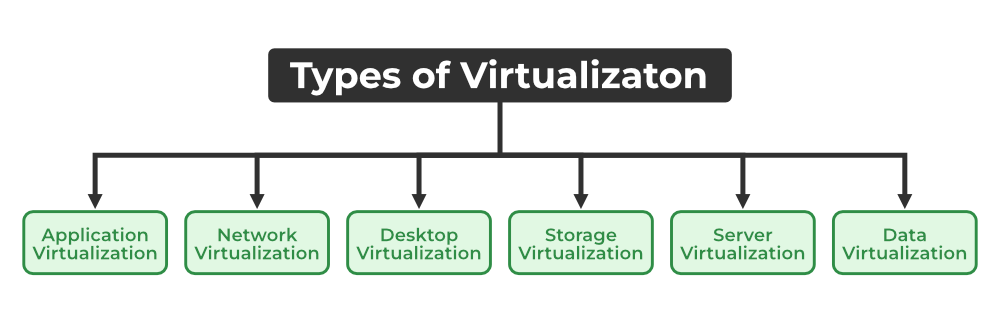
Types of Virtualization
- Application Virtualization
- Network Virtualization
- Desktop Virtualization
- Storage Virtualization
- Server Virtualization
- Data virtualization
Types of Virtualization
1. Application Virtualization: Application virtualization helps a user to have remote access to an application from a server. The server stores all personal information and other characteristics of the application but can still run on a local workstation through the internet. An example of this would be a user who needs to run two different versions of the same software. Technologies that use application virtualization are hosted applications and packaged applications.
2. Network Virtualization: The ability to run multiple virtual networks with each having a separate control and data plan. It co-exists together on top of one physical network. It can be managed by individual parties that are potentially confidential to each other. Network virtualization provides a facility to create and provision virtual networks, logical switches, routers, firewalls, load balancers, Virtual Private Networks (VPN), and workload security within days or even weeks.
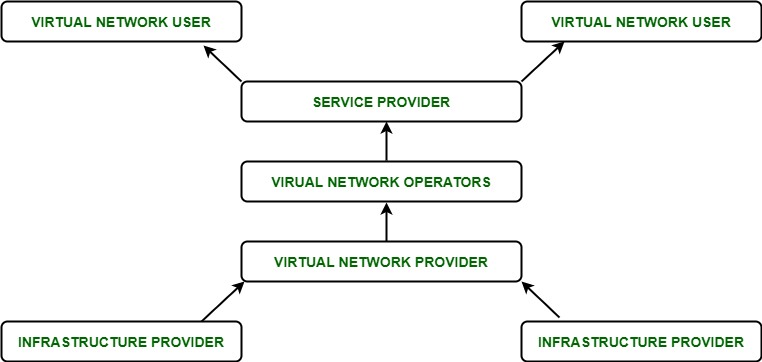
Network Virtualization
3. Desktop Virtualization: Desktop virtualization allows the users’ OS to be remotely stored on a server in the data center. It allows the user to access their desktop virtually, from any location by a different machine. Users who want specific operating systems other than Windows Server will need to have a virtual desktop. The main benefits of desktop virtualization are user mobility, portability, and easy management of software installation, updates, and patches.
4. Storage Virtualization: Storage virtualization is an array of servers that are managed by a virtual storage system. The servers aren’t aware of exactly where their data is stored and instead function more like worker bees in a hive. It makes managing storage from multiple sources be managed and utilized as a single repository. storage virtualization software maintains smooth operations, consistent performance, and a continuous suite of advanced functions despite changes, breaks down, and differences in the underlying equipment.
5. Server Virtualization: This is a kind of virtualization in which the masking of server resources takes place. Here, the central server (physical server) is divided into multiple different virtual servers by changing the identity number, and processors. So, each system can operate its operating systems in an isolated manner. Where each sub-server knows the identity of the central server. It causes an increase in performance and reduces the operating cost by the deployment of main server resources into a sub-server resource. It’s beneficial in virtual migration, reducing energy consumption, reducing infrastructural costs, etc.
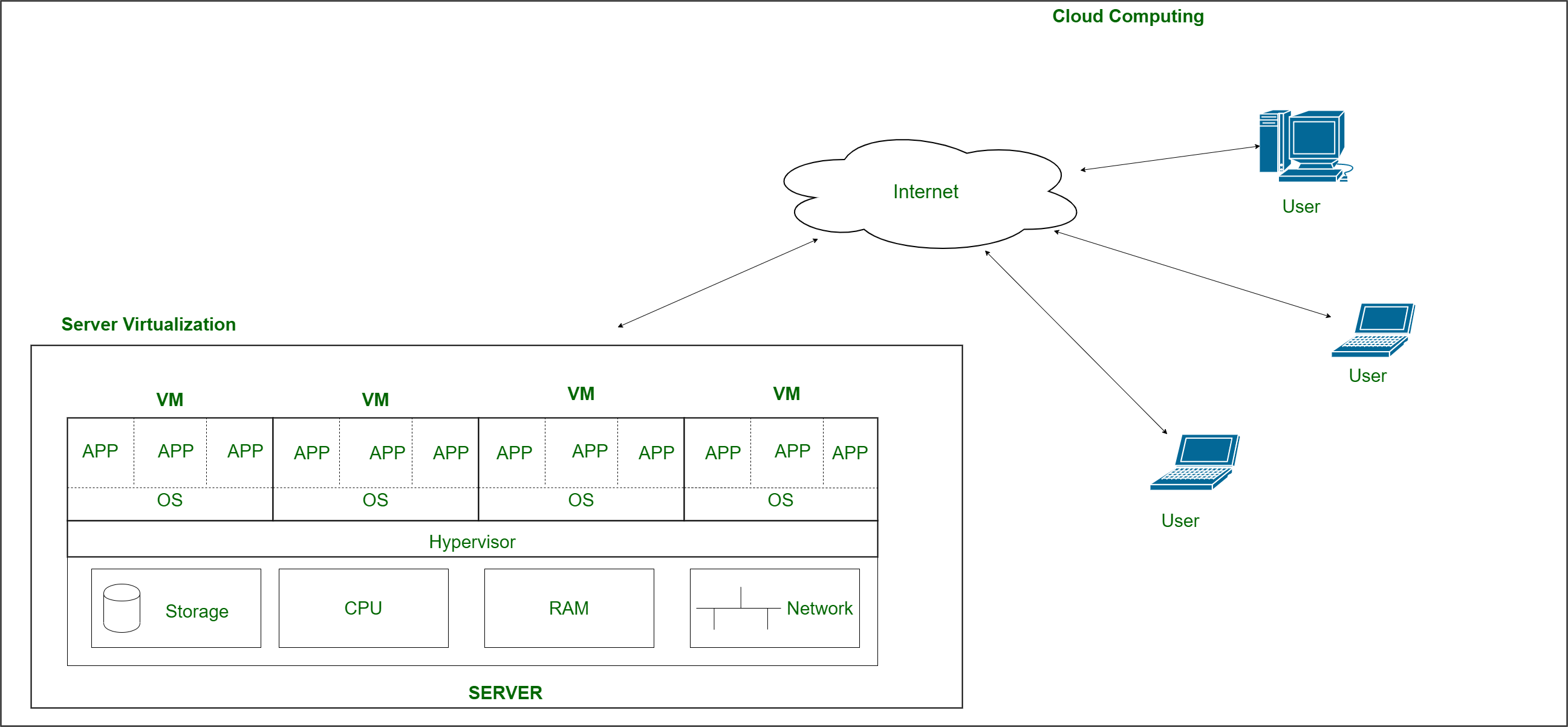
Server Virtualization
6. Data Virtualization: This is the kind of virtualization in which the data is collected from various sources and managed at a single place without knowing more about the technical information like how data is collected, stored & formatted then arranged that data logically so that its virtual view can be accessed by its interested people and stakeholders, and users through the various cloud services remotely. Many big giant companies are providing their services like Oracle, IBM, At scale, Cdata, etc.
Uses of Virtualization
- Data-integration
- Business-integration
- Service-oriented architecture data-services
- Searching organizational data
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...