Umbrella of Software Defined Everything (SDx/SDE)
Last Updated :
06 Jan, 2023
Software-Defined Everything (SDx/SDE) is a broad term. Software-Defined Everything is one of the broader trends in current IT technology. It serves to group a variety of software-defined computing technologies. SDE/SDx is an advance in technology that allows virtualization of the entire technology stack computer network, storage, and security layers. Software-Defined Everything aims to make information technology (IT) infrastructures more flexible and agile.
Software-Defined Everything (SDE) is a container term where the umbrella of SDE/Sdx includes Software Defined Networking (SDN), Software-Defined Storage (SDS), and Software-Defined Data Center (SDDC).
Treating Information Technology as Software Defined reduces cost, reduces mistakes, and makes everything faster and flexible by opening new opportunities in the technological world. In a Software-Defined Everything (SDE/SDx) environment, management and control of the networking, storage, data center infrastructure, etc are automated by intelligent software rather than by hardware components of infrastructure.
Umbrella of Software Defined Everything :
The below figure illustrates the Umbrella of Software Defined Everything –
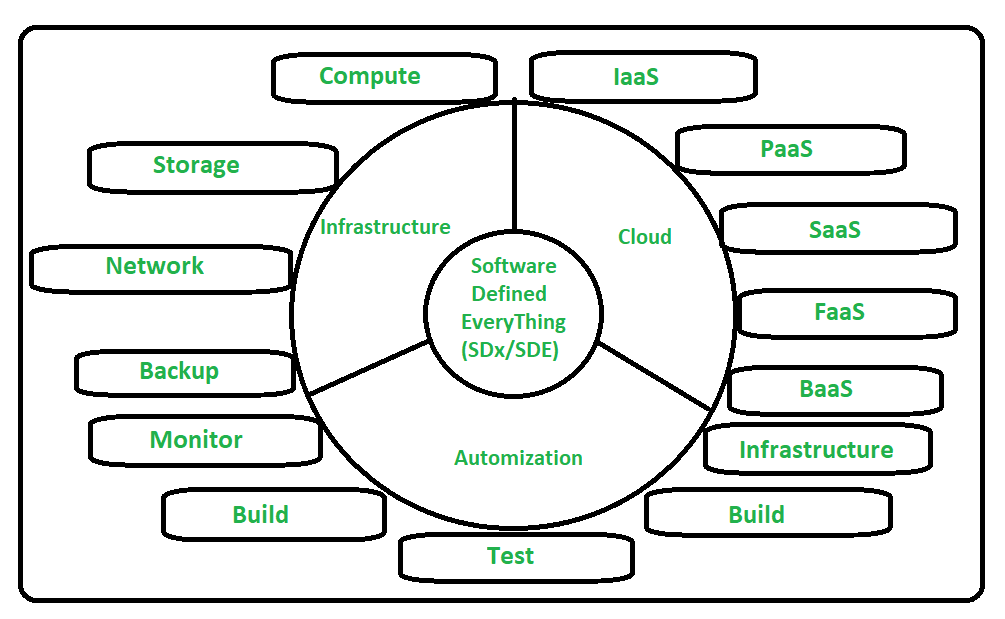
If we will see the above figure it clears that Software-Defined Everything (SDE) has more impact on Cloud, Infrastructure, and Automation.
1. Infrastructure :
Nowadays IT infrastructure can be implemented as software with the support of standard hardware where the computing infrastructure is virtualized and delivered as a service.
- Software-Defined Computer-
The virtualization of servers helps to save hardware and software costs and increases flexibility in dealing with computer resources.
- Software-Defined Storage –
In Software-Defined Storage (SDS) physical storage hardware is decoupled and uses storage media such as NVMe, SSD, or HDDs in server hardware to provide virtual storage.
- Software-Defined Network – In Software Defined Network (SDN) the network architecture is abstracted to make network devices programmable.
2. Cloud :
A wide range of on-demand IT services/computer system resources are delivered to the organizations or to the customers as per their requirements over the Internet.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) –
Virtualized computing resources over the internet. It provides instant computing infrastructure which is provisioned and managed over the internet by the vendor/service provider.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) –
The platform is provided to the customer to develop and deploy the application in the cloud. PaaS environment takes care of load balancing and scaling of the application.
- Software as a Service (SaaS) –
Users are allowed to connect and use the applications over the internet. In this service provider hosts applications for customers and makes them available to these customers via the internet.
- Function as a Service (FaaS) –
In Function as a Service (FaaS) modular pieces of code on the edge are executed. It provides a platform that allows customers to develop, run, and manage application functionalities without worrying about the complexity of building and maintaining.
- Backup as a Service (BaaS) –
In Backup as a Service (BaaS) data is backed up/ stored in cloud backup and recovery services from an online data backup provider. It refers to a modern alternative to traditional data backup approaches.
3. Automation :
Automation refers to a code approach that means everything needs to be programmed to work automatically. It enables IT to be kept more flexible, fast, secure, and stable.
- Infrastructure –
The infrastructure in the Automation approach allows you to define and manage your IT infrastructure with configurable software.
- Build and Test –
Build and test in Automation approach Build and test processes automated. In this results remain traceable.
- Installation –
The installation in the Automation approach allows the configuration of operating systems and the installation of applications to be automated.
- Monitoring –
The monitoring in Automation approach allows automatic monitoring (provides technical assistance like identifying and correcting errors etc) and data collection process.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...