Types of Viruses
Last Updated :
31 Jan, 2023
A virus is a fragment of code embedded in a legitimate program. Viruses are self-replicating and are designed to infect other programs. They can wreak havoc in a system by modifying or destroying files causing system crashes and program malfunctions. On reaching the target machine a virus dropper(usually a trojan horse) inserts the virus into the system.
For more details, refer to this.
Various types of viruses:
- File Virus:
This type of virus infects the system by appending itself to the end of a file. It changes the start of a program so that the control jumps to its code. After the execution of its code, the control returns back to the main program. Its execution is not even noticed. It is also called a Parasitic virus because it leaves no file intact but also leaves the host functional.
- Boot sector Virus:
It infects the boot sector of the system, executing every time system is booted and before the operating system is loaded. It infects other bootable media like floppy disks. These are also known as memory viruses as they do not infect the file systems.
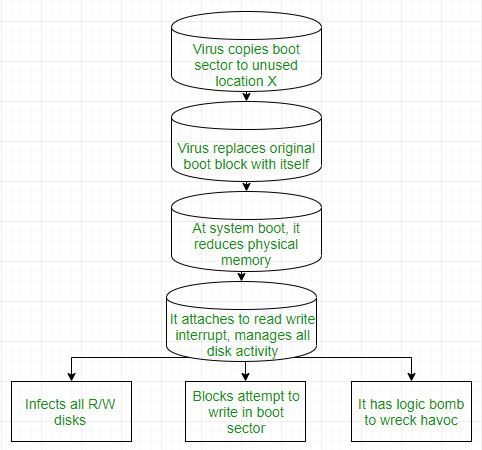
- Macro Virus:
Unlike most viruses which are written in a low-level language(like C or assembly language), these are written in a high-level language like Visual Basic. These viruses are triggered when a program capable of executing a macro is run. For example, the macro viruses can be contained in spreadsheet files.
- Source code Virus:
It looks for source code and modifies it to include virus and to help spread it.
- Polymorphic Virus:
A virus signature is a pattern that can identify a virus(a series of bytes that make up virus code). So in order to avoid detection by antivirus a polymorphic virus changes each time it is installed. The functionality of the virus remains the same but its signature is changed.
- Encrypted Virus:
In order to avoid detection by antivirus, this type of virus exists in encrypted form. It carries a decryption algorithm along with it. So the virus first decrypts and then executes.
- Stealth Virus:
It is a very tricky virus as it changes the code that can be used to detect it. Hence, the detection of viruses becomes very difficult. For example, it can change the read system call such that whenever the user asks to read a code modified by a virus, the original form of code is shown rather than infected code.
- Tunneling Virus:
This virus attempts to bypass detection by antivirus scanner by installing itself in the interrupt handler chain. Interception programs, which remain in the background of an operating system and catch viruses, become disabled during the course of a tunneling virus. Similar viruses install themselves in device drivers.
- Multipartite Virus:
This type of virus is able to infect multiple parts of a system including the boot sector, memory, and files. This makes it difficult to detect and contain.
- Armored Virus:
An armored virus is coded to make it difficult for antivirus to unravel and understand. It uses a variety of techniques to do so like fooling antivirus to believe that it lies somewhere else than its real location or using compression to complicate its code.
- Browser Hijacker:
As the name suggests this virus is coded to target the user’s browser and can alter the browser settings. It is also called the browser redirect virus because it redirects your browser to other malicious sites that can harm your computer system.
- Memory Resident Virus:
Resident viruses installation store for your RAM and meddle together along with your device operations. They behave in a very secret and dishonest way that they can even connect themselves for the anti-virus software program files.
The main perspective of this virus is to replicate and take action when it is executed. When a particular condition is met the virus will get into action and infect files in the directory that are specified in the AUTOEXEC.BAT file path.
This type of virus deletes the information contained in the file that it infects, rendering them partially or totally is useless once they have been infected.
This virus is also called called File System Virus or Cluster Virus. It infects the directory of the computer by modifying the path that is indicating the location of a file.
This kind of virus usually use the similar file name and create a different extension of it. For example, if there’s a file “Hello.exe”, the virus will create another file named “Hello.com” and will hide in the new file
The File Allocation Table is the part of the disk used to store all information about the location of files, available space , unusable space etc.
This virus affects the FAT section and may damage crucial information.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...