In Computer Network ,there are various ways through which different components are connected to one another. Network Topology is the way that defines the structure, and how these components are connected to each other.
Types of Network Topology
The arrangement of a network that comprises nodes and connecting lines via sender and receiver is referred to as Network Topology. The various network topologies are:
- Point to Point Topology
- Mesh Topology
- Star Topology
- Bus Topology
- Ring Topology
- Tree Topology
- Hybrid Topology
Point to Point Topology
Point-to-Point Topology is a type of topology that works on the functionality of the sender and receiver. It is the simplest communication between two nodes, in which one is the sender and the other one is the receiver. Point-to-Point provides high bandwidth.
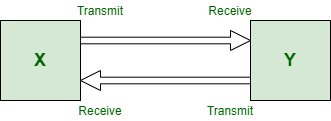
Point to Point Topology
Mesh Topology
In a mesh topology, every device is connected to another device via a particular channel. In Mesh Topology, the protocols used are AHCP (Ad Hoc Configuration Protocols), DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), etc.
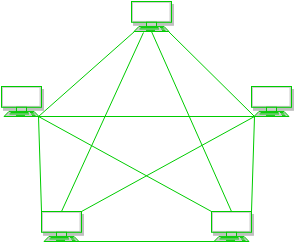
Mesh Topology
Figure 1: Every device is connected to another via dedicated channels. These channels are known as links.
- Suppose, the N number of devices are connected with each other in a mesh topology, the total number of ports that are required by each device is N-1. In Figure 1, there are 5 devices connected to each other, hence the total number of ports required by each device is 4. The total number of ports required = N * (N-1).
- Suppose, N number of devices are connected with each other in a mesh topology, then the total number of dedicated links required to connect them is NC2 i.e. N(N-1)/2. In Figure 1, there are 5 devices connected to each other, hence the total number of links required is 5*4/2 = 10.
Advantages of Mesh Topology
- Communication is very fast between the nodes.
- Mesh Topology is robust.
- The fault is diagnosed easily. Data is reliable because data is transferred among the devices through dedicated channels or links.
- Provides security and privacy.
Drawbacks of Mesh Topology
- Installation and configuration are difficult.
- The cost of cables is high as bulk wiring is required, hence suitable for less number of devices.
- The cost of maintenance is high.
A common example of mesh topology is the internet backbone, where various internet service providers are connected to each other via dedicated channels. This topology is also used in military communication systems and aircraft navigation systems.
For more, refer to the Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Topology.
Star Topology
In Star Topology, all the devices are connected to a single hub through a cable. This hub is the central node and all other nodes are connected to the central node. The hub can be passive in nature i.e., not an intelligent hub such as broadcasting devices, at the same time the hub can be intelligent known as an active hub. Active hubs have repeaters in them. Coaxial cables or RJ-45 cables are used to connect the computers. In Star Topology, many popular Ethernet LAN protocols are used as CD(Collision Detection), CSMA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access), etc.

Star Topology
Figure 2: A star topology having four systems connected to a single point of connection i.e. hub.
Advantages of Star Topology
- If N devices are connected to each other in a star topology, then the number of cables required to connect them is N. So, it is easy to set up.
- Each device requires only 1 port i.e. to connect to the hub, therefore the total number of ports required is N.
- It is Robust. If one link fails only that link will affect and not other than that.
- Easy to fault identification and fault isolation.
- Star topology is cost-effective as it uses inexpensive coaxial cable.
Drawbacks of Star Topology
- If the concentrator (hub) on which the whole topology relies fails, the whole system will crash down.
- The cost of installation is high.
- Performance is based on the single concentrator i.e. hub.
A common example of star topology is a local area network (LAN) in an office where all computers are connected to a central hub. This topology is also used in wireless networks where all devices are connected to a wireless access point.
For more, refer to the Advantages and Disadvantages of Star Topology.
Bus Topology
Bus Topology is a network type in which every computer and network device is connected to a single cable. It is bi-directional. It is a multi-point connection and a non-robust topology because if the backbone fails the topology crashes. In Bus Topology, various MAC (Media Access Control) protocols are followed by LAN ethernet connections like TDMA, Pure Aloha, CDMA, Slotted Aloha, etc.
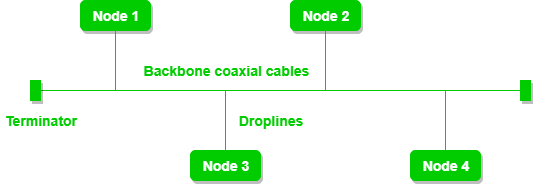
Bus Topology
Figure 3: A bus topology with shared backbone cable. The nodes are connected to the channel via drop lines.
Advantages of Bus Topology
- If N devices are connected to each other in a bus topology, then the number of cables required to connect them is 1, known as backbone cable, and N drop lines are required.
- Coaxial or twisted pair cables are mainly used in bus-based networks that support up to 10 Mbps.
- The cost of the cable is less compared to other topologies, but it is used to build small networks.
- Bus topology is familiar technology as installation and troubleshooting techniques are well known.
- CSMA is the most common method for this type of topology.
Drawbacks of Bus Topology
- A bus topology is quite simpler, but still, it requires a lot of cabling.
- If the common cable fails, then the whole system will crash down.
- If the network traffic is heavy, it increases collisions in the network. To avoid this, various protocols are used in the MAC layer known as Pure Aloha, Slotted Aloha, CSMA/CD, etc.
- Adding new devices to the network would slow down networks.
- Security is very low.
A common example of bus topology is the Ethernet LAN, where all devices are connected to a single coaxial cable or twisted pair cable. This topology is also used in cable television networks. For more, refer to the Advantages and Disadvantages of Bus Topology.
Ring Topology
In a Ring Topology, it forms a ring connecting devices with exactly two neighboring devices. A number of repeaters are used for Ring topology with a large number of nodes, because if someone wants to send some data to the last node in the ring topology with 100 nodes, then the data will have to pass through 99 nodes to reach the 100th node. Hence to prevent data loss repeaters are used in the network.
The data flows in one direction, i.e. it is unidirectional, but it can be made bidirectional by having 2 connections between each Network Node, it is called Dual Ring Topology. In-Ring Topology, the Token Ring Passing protocol is used by the workstations to transmit the data.
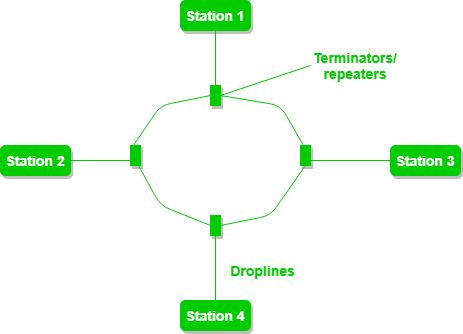
Ring Topology
Figure 4: A ring topology comprises 4 stations connected with each forming a ring.
The most common access method of ring topology is token passing.
- Token passing: It is a network access method in which a token is passed from one node to another node.
- Token: It is a frame that circulates around the network.
Operations of Ring Topology
- One station is known as a monitor station which takes all the responsibility for performing the operations.
- To transmit the data, the station has to hold the token. After the transmission is done, the token is to be released for other stations to use.
- When no station is transmitting the data, then the token will circulate in the ring.
- There are two types of token release techniques: Early token release releases the token just after transmitting the data and Delayed token release releases the token after the acknowledgment is received from the receiver.
Advantages of Ring Topology
- The data transmission is high-speed.
- The possibility of collision is minimum in this type of topology.
- Cheap to install and expand.
- It is less costly than a star topology.
Drawbacks of Ring Topology
- The failure of a single node in the network can cause the entire network to fail.
- Troubleshooting is difficult in this topology.
- The addition of stations in between or the removal of stations can disturb the whole topology.
- Less secure.
For more, refer to the Advantages and Disadvantages of Ring Topology.
Tree Topology
This topology is the variation of the Star topology. This topology has a hierarchical flow of data. In Tree Topology, protocols like DHCP and SAC (Standard Automatic Configuration ) are used.

Tree Topology
Figure 5: In this, the various secondary hubs are connected to the central hub which contains the repeater. This data flow from top to bottom i.e. from the central hub to the secondary and then to the devices or from bottom to top i.e. devices to the secondary hub and then to the central hub. It is a multi-point connection and a non-robust topology because if the backbone fails the topology crashes.
Advantages of Tree Topology
- It allows more devices to be attached to a single central hub thus it decreases the distance that is traveled by the signal to come to the devices.
- It allows the network to get isolated and also prioritize from different computers.
- We can add new devices to the existing network.
- Error detection and error correction are very easy in a tree topology.
Drawbacks of Tree Topology
- If the central hub gets fails the entire system fails.
- The cost is high because of the cabling.
- If new devices are added, it becomes difficult to reconfigure.
A common example of a tree topology is the hierarchy in a large organization. At the top of the tree is the CEO, who is connected to the different departments or divisions (child nodes) of the company. Each department has its own hierarchy, with managers overseeing different teams (grandchild nodes). The team members (leaf nodes) are at the bottom of the hierarchy, connected to their respective managers and departments.
For more, refer to the Advantages and Disadvantages of Tree Topology.
Hybrid Topology
This topological technology is the combination of all the various types of topologies we have studied above. Hybrid Topology is used when the nodes are free to take any form. It means these can be individuals such as Ring or Star topology or can be a combination of various types of topologies seen above. Each individual topology uses the protocol that has been discussed earlier.

Hybrid Topology
Figure 6: The above figure shows the structure of the Hybrid topology. As seen it contains a combination of all different types of networks.
Advantages of Hybrid Topology
- This topology is very flexible.
- The size of the network can be easily expanded by adding new devices.
Drawbacks of Hybrid Topology
- It is challenging to design the architecture of the Hybrid Network.
- Hubs used in this topology are very expensive.
- The infrastructure cost is very high as a hybrid network requires a lot of cabling and network devices.
A common example of a hybrid topology is a university campus network. The network may have a backbone of a star topology, with each building connected to the backbone through a switch or router. Within each building, there may be a bus or ring topology connecting the different rooms and offices. The wireless access points also create a mesh topology for wireless devices. This hybrid topology allows for efficient communication between different buildings while providing flexibility and redundancy within each building.
For more, refer to the Advantages and Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...