Transport in India: Transport in India refers to the system of moving people, goods, and services from one place to another within the country. India has diverse landforms and relief features, with a diverse population, which relies on various modes of transport to meet the various transportation needs of the people for supporting economic activities. Various modes of transport in India include roads, railways, airways, waterways as well as pipelines. This article gives details about transport in India.
What is Transport?
The movement of goods and services, people, from one place to the other place and by various means like air, water, and land; is known as transportation. It supports the mobility of passengers and freight.
Means of Transport Chart
.png)
Means of Transport
What is Transport in India?
The transportation system in India is a complex network of transport modes and is based on the historical developments, geographical features, and cultural and religious influences of the country. Transport plays a very important role in the economic development of the country and affects the environment due to global warming and climate change. With the advancement of technology, transport has become much cheaper and faster.
Transport in India- Overview
An overview of Transport in India is as follows:
|
Mode of Transport
|
Description
|
|
Roadways
|
Extensive road network, including national highways, state highways, and rural roads.
|
|
Railways
|
One of the largest railway networks globally, providing both passenger and freight services.
|
|
Airways
|
Domestic and international air travel facilitated by airports across the country.
|
|
Waterways
|
Inland and coastal waterways used for transportation of goods and passengers.
|
|
Pipelines
|
Pipelines for the transportation of petroleum products, natural gas, and other substances.
|
Roadway Transport in India
The second largest network of roads is present in India, accounting for 62.16 lakh km, and has preceded railways in India. Preference for roadways over railways in India is because:
- Streets will prepare higher inclinations of slants and in and of itself will cross mountains just like the chain, in addition, offers houses to deal with help, consequently, the expense of stacking and marketing may be a heap lower.
- Street transport is likewise used as a feeder to totally different strategies of transport, for instance, they furnish an association between railway line stations, and air and ocean ports.
- The development value of streets may be a heap below that of railroad lines, streets will cross nearly additional analyzed and undulating
geography,
- Street transport is reasonable in the transportation of a few individuals and moderately smaller lives of products over temporary distances.
- Provides door-to-door service as compared to railways.

Roadways
In India, roads area units are ordered in many varieties as per their capacity, they are,
- Golden Quadrilateral Super Highways: The general public authority has sent off a big street improvement project connecting Delhi-Kolkata-Chennai-Mumbai conjointly, city by six-path Super Highways. The North-South hallways connecting Srinagar (Jammu and Kashmir) and Kanyakumari (Tamil Nadu), and the East-West passageway interfacing Silchar (Assam) and Porbandar (Gujarat) area unit are necessary for this endeavor. The significant goal of those Super Highways is to decrease the time and distance between the super urban communities of India. This route comes area unit being administered by the National Highway Authority of India
- National Highways: They link the extreme parts of the country and are primary road systems and are laid as well as maintained by Central Public Works Department. Major National Highways run in direction of North-South and East-West directions. The Sher-Shah Suri Marg is called National Highway Number 1, between Delhi and Amritsar.
- State Highways: Roads that link the state capital and the different district headquarters are known as the State Highways and are maintained by State Public Works Department.
- District Roads: Roads that connect district headquarters with other places of the district are called district roads and are maintained by Zila Parishad.
- Other Roads: Other roads include the rural roads and special impetus is received from the Pradhan Mantri Grameen Sadak Yojana.
- Border Roads: Border Roads Organisation is a Government of India undertaking the construction and maintained roads in the bordering areas of the country. These roads have helped to improve the accessibility in areas of difficult terrain and economic development of the areas.
Roads can also be classified based on the material used for their construction into Metalled and Unmetalled roads. Metalled roads are made of cement, concrete, or bitumen of coal, and unmetalled roads are country roads, which are not cemented.
Railways In India
Rail routes are the necessary methodology of transportation for cargo and travelers in India. They permit people to direct totally different exercises like business, moving, or journey aboard transportation of merchandise over longer distances. Rail transport is most well-liked and coordinated over other vehicles of transport. it’s fastened courses and timetables. The Indian Railways is recognized at present into 16 zones.

Railways
Distribution patterns of the railways in the country have influenced the physiographic, economic, and also administrative factors:
- Like the north plains, vast areas of flat lands and high density of populations and rich agricultural resources provide for favorable conditions of growth and development. Construction of bridges is required across rivers’ wide beds for laying railway lines.
- In hilly areas, tracts are laid through low hills, gaps, and also tunnels. It is not easy to lay rail tracts in the Himalayan mountains, the same way in the sandy plains of the states of Rajasthan, swamps of Gujarat, and forested areas of Madhya Pradesh.
- Construction of Konkan railways in recent times has facilitated movement more easily in one of the economically vital areas of the country. However, it has faced problems like sinking tracks in some stretches and also landslides in others.
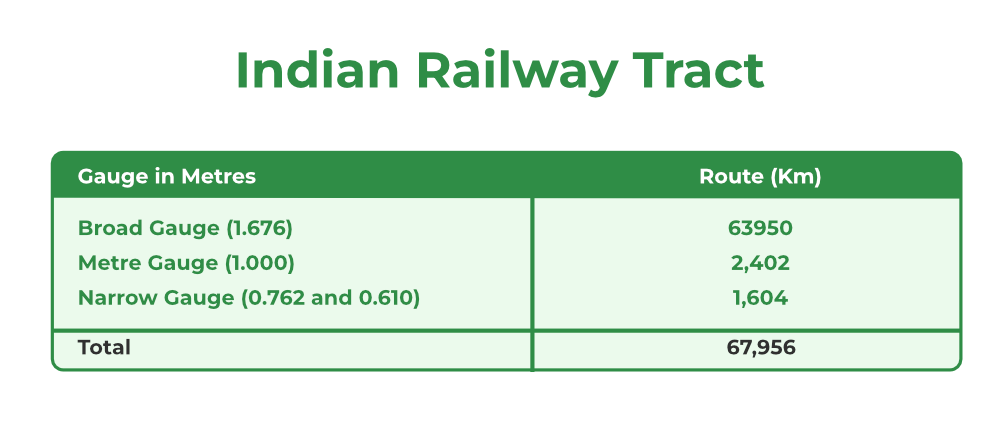
Indian Railway Tract
Rail transport has arisen collectively as the foremost trustworthy strategy of transport with regards to somewhere safe and secure. Trains are fast and also the most unimpacted by common climate turbulences like rain or haze, contrasted with alternative vehicle instruments. Rail transport is an associate degree empowering agent of financial advancement, accustomed activate merchandise further as people. Variations incorporate traveler rail lines, underground railroad metro railroads, and merchandise carriages.
Pipelines
Pipelines are new in the transport network of India. These are used for shipping unrefined crude oil, oil-based mostly commodities, and ignitible gas from oil and ignitible gas fields to process plants, manure industrial facilities, and enormous atomic energy stations. Solids will likewise be captive through a pipeline once modified over into suspension and to ship water between varied urban areas.

Pipelines
The interior locations of refineries like that of Barauni, Mathura, and also Panipat, other gas-based fertilizer plants could be only thought of because of pipelines. The cost of laying pipelines is high but the running cost is minimum and doesn’t have the provisions like that of trans-shipment losses or delays.
There are unit 3 vital organizations of pipeline transportation within the country:
- Gas pipeline from Hazira in Gujarat associates Jagdishpur in the state, by means that of Vijaipur in Madhya Pradesh. it branches to Kota in Rajasthan, Shahajahanpur, Bab-rala, and totally different spots in the state. It is 1,700 km and the first one.
- From Salaya in Gujarat to Jalandhar in a geographical region, through Viramgam, Mathura, city, and Sonipat. Its branches interface Koyali (close to Vadodara, Gujarat) Chakshu and totally different spots.
- From oil fields in higher Assam to Kanpur (Uttar Pradesh), through Guwahati, Barauni and Allahabad. it branches from Barauni to Haldia, by means of Raj-bandh, Raj-bandh to Mauri-gram, and Guwahati to Siliguri.
Overall. India’s gas pipeline infrastructure of the country has increased from 1,700 km to that 18,500 km.
Waterways
India from its ancient times was a seafaring country and one of the cheapest means of transport. They are most suitable for carrying bulky and heavy goods. They are fuel-efficient and also an environmentally friendly mode of transportation and have an inland navigation of 14,500 km in length and out of this only 5685 km are navigable. The following are declared as National Waterways by the Government:

Waterways
- N.W. No.1 – The Ganga waterway between Allahabad and Haldia (1620 km).
- N.W. No.2 – The Brahmaputra river waterway between Sadiya and Dhubri (891 km).
- N.W. No.3 – The West Coast Canal in Kerala (Kottapurma-Kollam, Udyoga Mandal and Champakkras canals-205 km).
- N.W. No.4 – Specified stretches of Godavari and Krishna waterways aboard the Kakinada Puducherry stretch of channels (1078 km).
- N.W. No.5 – Specified stretches of stream Brahmani aboard black pine waterway, delta channels of Mahanadi and Brahmani streams, and geographic region Canal (588 km).
Some important inland waterways on which much of the transport takes place include the Mandavi, Zuari, Cumberjua, Sunderbans, Barak, and also the backwaters of Kerala. Foreign trade of India is carried in the ports along the coast. Of around 95 percent of the country’s volume of trade is carried out in the sea, about 68 percent.
Major Sea Ports
- India has a long coastline of about 7,516.6 km and is dotted with 12 major and around 200 notified non-major ports and major ports handle around 95 percent of the foreign trade.
- Kandla in Kuchchh was the principal port to be created when autonomy. It is otherwise known as the Deendayal Port.
- Mumbai is the greatest port with a spacious traditional and extremely abundant secure harbor.
- Marmagao port (Goa) is the head iron metal commerce port of India. This port exports fifty percent of iron ore.
- Mangalore port, placed in Mysore takes special care of the merchandise of iron minerals. Kochi is the super southwestern port, placed at the entry of a periodic event lake.
- Kochchi is situated in the extreme southwestern port, which is located at the entrance of a lagoon with a natural harbor.
- Tuticorin port is organized in the super southeast. The city is one of the foremost established faux ports of India.
- Chennai is one of the oldest artificial ports in the country and is ranked next to Mumbai in terms of volume of trade and cargo.
- Vishakhapatnam is the most profound inland and everyone around safeguarded port nine. Paradip port placed in Odisha has sensible expertise in the product of iron metal.
- Paradwip port is located in Odisha and specializes in the export of iron ore.
- Kolkata is an inland riverine port and serves as a very large and rich hinterland for the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin. As it is a tidal port, it requires constant dredging of Hoogly.
- Haldia port was developed as a subsidiary port, to relieve the growing pressure on Kolkata port.
Airways
The air is the fastest, most agreeable, and lofty methodology of transport. It can cover undeniably difficult landscapes like high mountains, vast deserts, thick timberlands, and long maritime stretches effortlessly. Take the example of Northeast India, which is marked by dense forests, dissected relief, the presence of big rivers, etc. could be negotiated by air transport. Air transportation was nationalized in 1953.

Indian Airlines, Alliance Air (auxiliary of Indian Airlines), confidential engaged carriers, and non-planned directors offer native air administrations and Air India provides international air administrations. Indian Airlines’ tasks likewise reach bent on the contiguous nations of South and South-East Asia and also the Middle East. As aviation routes are the costlier mode, it is not within the span of average people.
Pawan-Hans Helicopters restricted provides heavier-than-air craft administrations to grease and gas Corporation (ONGC) in its seaward tasks, to distant regions and difficult landscapes just like the North-Eastern states and also the within items of Jammu and Cashmere, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand. Air transport is not mostly within the reach of common people, only in northeastern states, special provisions are made for the extension of services to common people.
Communication
Communication has evolved over time and the pace of changes has been more speedy in modern times. Long-distance communication is easier without physical movement. Personal communication and mass communication are some major means of communication in the country.

Indian postal services are one of the largest in the world and handle parcels as well as personal written communications:
- First-class mails include cards and envelopes and are airlifted between stations covering both land and air routes.
- Second-class mail includes book packets, newspapers, and periodicals; which are carried by surface mail, covering land and water transport.
For the facilitation of quick delivery of mail in the case of larger towns and cities, six mail channels have been introduced recently, namely: Rajdhani Channel, Metro Channel, Green Channel, Bussiness Channel, Bulk Mail Channel, and Periodical Channel.
India has one of the largest telecom networks in Asia; the exclusion of urban spaces, around two-thirds of villages in India, have already been covered under Subscriber Trunk Dialling (STD) facility. The government has also made provision to extend the 24 hours STD facilities to every village in the country and a uniform rate of STD facilities around India. This is possible because of the advancement of space and communication technology.
Mass Communication
Mass communication provides both entertainment and also created awareness about the different policies and missions. It includes radio, television, newspaper, and so forth. All India Radio, which is Akashwani broadcasts a variety of programs in different languages to different categories of people. Doordarshan, a national television channel is one of the largest terrestrial networks and also broadcasts a variety of programs for people of different age groups.
Newspapers are published in more than 100 languages and are also the largest producer of feature films in the world. The Central Board of Film Certification is the authority for the certification of both Indian as well as foreign movies.
International Trade
The exchange of goods among people, states, and also countries is referred to as trade and these exchanges usually take place in the markets. Trade between two countries is known as international trade and may take place through land, water, or air routes. Improvement and development of trade of a country is an index to the economic development and prosperity of the country and is considered one of the economic barometers of the country.
Exports and imports are the main two components of trade and the balance of trade in a country is the difference between export and import. When the value of export is above that of import, it is a favorable balance of trade. India has trade relations with the major trading blocks in the world and commodities exported from India include gems and jewelry, chemicals, agriculture, etc. Commodities imported are petroleum, gems, chemicals, base metal, electronics, agriculture, etc. India has developed significantly in the context of software development and is earning huge foreign exchange through the export of information technology.
Tourism as a Trade
Tourism is growing substantially in India over the last three decades and more. Many millions of people are engaged in the tourism industry. Tourism helps to promote the aspects of national integration, support to the indigenous and handicrafts, and also in the pursuits of culture and spirituality. It helps to develop a sense of international understanding of culture and heritage.

Foreign travelers visit India for its heritage tourism, eco-tourism, cultural tourism, business tourism as well as medical tourism. Due to the vast diversity present in India, tourism has the potential to grow many folds in India and efforts have been taken up by the government to promote the tourism industry in India.
Importance/ Significance of Transport in India
The importance and significance of Transport in India are as follows:
- Economic Growth- An efficient form of communication would help in movement of goods, services and people.
- Accessibility and Connectivity- Well developed form of transportation helps in connection of remote areas.
- Employment Generation- Transport sector helps in creation of a direct and indirect forms of employment.
- Trade and Commerce- Transport infrastructure enables in smooth function of goods and trade.
Points to Remember about Transport in India
Some important points on transport in India are:
- India has diverse transportation which has roadways, railways, airways etc.
- Indian Railway is one of the largest networks in global level.
- National highways and state highways are backbone of the economy.
- Inland waterways help in cargo movement.
FAQs on Lifelines of the National Economy
What is the main transportation in India?
The main transportation in India is the roads.
Why transportation is important in country like India?
Transportation helps in improving the connectivity between different states and in a big country like India it allows people to move from one place to another for opportunities in jobs as well education.
How many transport are there in India?
The transport in India include rail transport, road transport, air transport, water and portal connectivity.
What is the rank of India in transport?
The rank of India in transport is 6.70 million kilometer and this puts India in 2nd place in global ranking.
Which state has best transport in India?
The state which has best transport in India is Kerela and Tamil Nadu.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...