Transpiration
Last Updated :
12 Jan, 2024
Transpiration is a process in which plants secrete out from the aerial part of the plant example leaves, stems, and flowers. Similar to other living organisms water is essential for plants to do the normal functioning of a cell. To excrete water plants also have an excretory mechanism they do it via transpiration. Transpiration occurs mainly via stomata.
What is Transpiration?
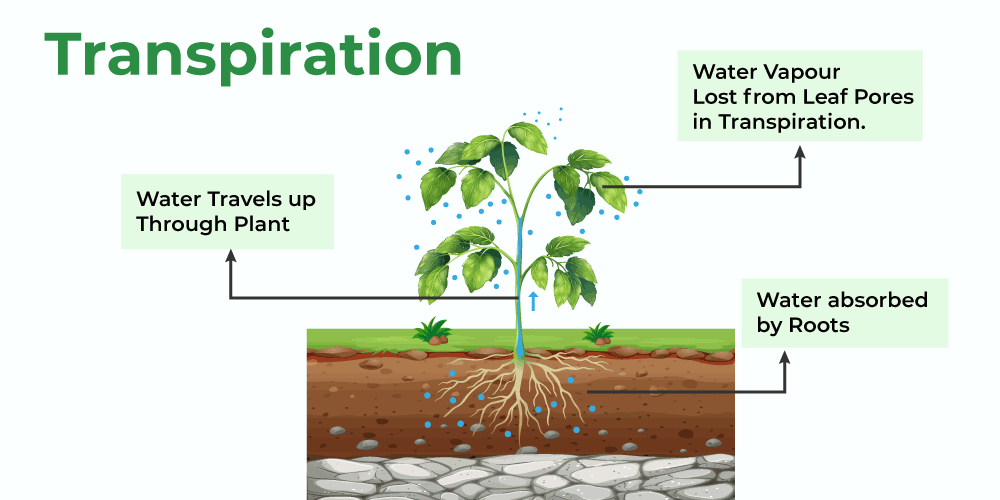
Plants release the excess water through evaporation through different plant parts such as stems or the stomata present on the surface of the leaves by the process of transpiration. The evaporation of water from leaves creates a suction pull which can pull water to great heights in the plants. Transpiration helps in cooling the plant in hot weather.
Types of Transpiration
There are mainly three types of transpiration occurs:
Stomatal Transpiration
The process of loss of water through the stomata of leaves is known as Stomatal Transpiration. When the spongy mesophyll cells become filled with water, the water moves to the intercellular space which lies just next to the mesophyll cells. When the intercellular space gets saturated with water vapors they transfer the extra water vapor to the substomatal space which is in direct contact with the stomata present on the lower epidermis. And thus the excess water moves out from the stomata. This is the whole mechanism of Stomatal Transpiration.
Cuticular Transpiration
The process of loss of water through cuticles of leaves is known as Cuticular Transpiration. Cuticular transpiration mostly takes place at night or when stomata are closed during dry conditions, and more water is transpired through the cuticles. Plants containing thin cuticles allow more cuticular transpiration.
Lenticular Transpiration
The process of loss of water through lenticels of the stem is known as Lenticular Transpiration. It is also involved in gaseous exchange. Lenticel pores consist of loosely packed cells and thin-walled cells. Their cell shape is oval and spherical.
Factors Affecting Transpiration in Plants
The factors affecting the rate of transpiration are as follows:
Environment Factors
There are some environmental factors that affect transpiration are:
- Humidity
- Wind Speed
- Temperature
- Light
Humidity
Humidity refers to the amount of water vapor present in the atmosphere at a particular time and temperature. If the atmosphere is filled with water vapors the transpiration rate decreases and vice versa. Therefore, the rate of transpiration is inversely proportional to relative humidity.
Air
If the air movement is fast, saturated air in contact with the leaf surface containing the water vapor is removed, thus increasing transpiration. But, if the air is still, the rate of transpiration is low. Therefore, the rate of transpiration is directly proportional to air movement.
Temperature
The high temperature helps in lowering the atmospheric humidity and thus increasing the rate of transpiration. So, the rate of transpiration is directly proportional to temperature.
Light
During bright daylight, the stomata remain open, and thus the transpiration rate increases. The increase in light intensity also increases the temperature which in turn increases the rate at which the transpiration occurs. Thus, the rate of transpiration is directly proportional to light intensity.
Cellular factors
There are some cellular factors that affect the rate of transpiration
- The structure and direction of the leaf
- Water in the plant
- Number and distribution of stomata.
Surface Area of Leaf
The rate of transpiration is higher if the leaf has more surface area. On the other hand, if we consider the rate of transpiration per unit surface area, then, smaller leaves have a higher rate because the number of stomata in smaller leaves is higher.
Water Availability
The rate of transpiration also depends upon the rate of absorption of water from the ground by roots. With a lack of water availability, less water uptake by the root causes partial dehydration of the leaf cells resulting in wilting of the plant.
Stomata
Stomatal pores present in the leaf allow gas exchange where water vapor leaves and carbon dioxide enters the plant. So, when stomata are open the rate of transpiration increases, and when they are closed the rate decreases.
Ascent of Sap
Ascent of sap means the upward movement of water and minerals from the roots to the aerial parts of the plant through the stem. Evaporation of water vapors from the leaf cells creates a suction that pulls water from the xylem cells of roots and thus contributes to transpiration this is known as transpiration pull.
Also Read: Difference between Transpiration and Guttation
Opening and Closing of Stomata
Stomata are present on the lower part of the leaf epidermis. Less amount of stomata is seen on the upper part of the leaf. Stomata contains one pair of guard cells and in between the guard cell, an aperture is present. Stomata remain open in the daytime and closed during the night. The opening and closing of the stomata depend on the guard cells.

The aperture of the stomata is covered with the flexible inner layer of the guard cell. When the turgidity increase due to excessive water in the guard cell it leads the stomata open. The inner layer of the guard cell becomes concave and forms a crescent shape. The pattern of the microfibrils also helps in the opening of the stomata. If microfibril is radial then stomata open. When the water is lost then the turgidity of the guard cell also decreases and the stomata closed.
Significance of Transpiration
Significance of transpiration are as follows:
- Transpiration are responsible for cooling effect.
- Suction Force is experienced by plants during more transpiration.
- Plants get a proper distribution of minerals due to transpiration.
- Transpiration helps in maintaining the turgidity of the cells and thus helps in cell division.
Disadvantages of Transpiration
Even though transpiration is a very important process, it has a few drawbacks.
- Wilting of leaves: Due to excessive transpiration during high temperatures wilting and loss of turgidity is quite common which in turn reduces photosynthesis and other metabolic processes of the plant.
- Loss of energy: A lot of energy is lost during transpiration for absorption and conduction of water as 98-99% of absorbed water is lost through transpiration.
- Reduced Growth: Due to transpiration the water availability inside the plant gets reduced thus giving the plant shorten growth.
Conclusion
Transpiration in plants is a very vital process. Without transpiration, the plants will not get enough nutrients and due to the lack of loss of water, the plant cells will eventually burst. Transpiration is also responsible for maintaining the water balance of the world.
FAQs on Transpiration in Plants
1. What is Transpiration?
Answer:
Transpiration is the process of evaporation of excess water from the aerial parts of the plant such as leaves and stems.
2. Explain the different types of transpiration.
Answer:
Transpiration in plants occurs in the following three processes:
- Stomatal Transpiration: The process of loss of water through stomata of leaves.
- Lenticular Transpiration: The process of loss of water through lenticels of stem
- Cuticular Transpiration: The process of loss of water through cuticles of leaves
3. How is transpiration important to the surroundings?
Answer:
Transpiration helps in cooling the environment. Water vapors are released from the plant which in turn contributes to the rainfall of that region and thus lowering the temperature of the surroundings.
4. What are the Disadvantages of Transpiration?
Answer:
Excessive transpiration results in the wilting of leaves and loss of turgidity and also stunted growth of the plants. It can result in the desiccation of plants due to scarcity of water.
5. Where does Transpiration occur?
Answer:
Stomata are the primary location of transpiration. Various environmental factors effect the rate of transpiration.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...