Transmission Impairment in Data Communication
Last Updated :
19 Sep, 2023
In communication system, analog signals travel through transmission media, which tends to deteriorate the quality of analog signal, which means that the signal at the beginning of the medium is not the same as the signal at the end of the medium. The imperfection causes signal impairment. Below are the causes of the impairment.
Causes of impairment –
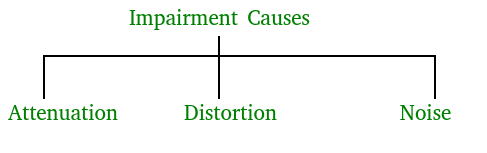
- Attenuation – It means loss of energy. The strength of signal decreases with increasing distance which causes loss of energy in overcoming resistance of medium. This is also known as attenuated signal. Amplifiers are used to amplify the attenuated signal which gives the original signal back and compensate for this loss.
Attenuation(dB) = 10log10(P2/P1)
P1 is the power at sending end and P2 is the power at receiving end.
Some where the decibel is also define in terms of voltage instead of power.In this case because power is proportional to the square of the voltage the formula is
Attenuation(dB) = 20log10(V2/V1)
V1 is the voltage at sending end and V2 is the voltage at receiving end.
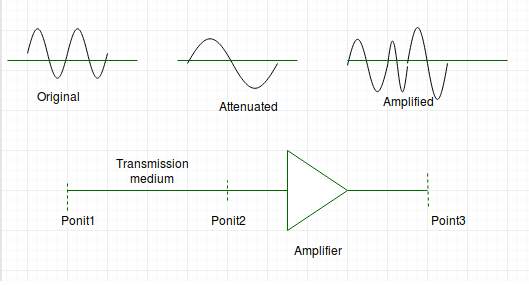
- Distortion – It means changes in the form or shape of the signal. This is generally seen in composite signals made up with different frequencies. Each frequency component has its own propagation speed travelling through a medium. And thats why it delay in arriving at the final destination Every component arrive at different time which leads to distortion. Therefore, they have different phases at receiver end from what they had at senders end.
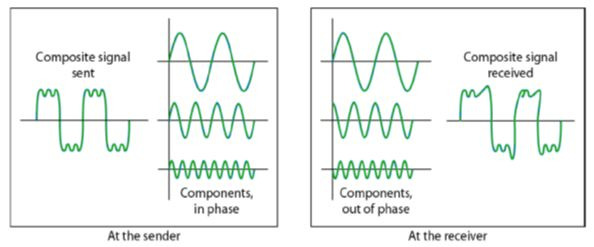
- To find the theoretical bit rate limit, we need to know the ration .The signal-to-noise ratio is defined as
SNR = AVG SIGNAL POWER / AVG NOISE POWER
SNRdB = 10Log10SNR
EXAMPLE
The values of SNR and SNRdB for a noiseless channel are
SNR = Signal Power/0 = ∞
SNRdB = 10Log10 ∞ = ∞
We can never achieve this ratio in real life ; it is an ideal.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...