Time Complexity Analysis | Tower Of Hanoi (Recursion)
Last Updated :
15 Feb, 2023
Tower of Hanoi is a mathematical puzzle where we have three rods and n disks. The objective of the puzzle is to move the entire stack to another rod, obeying the following simple rules:
1) Only one disk can be moved at a time.
2) Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the stacks and placing it on top of another stack i.e. a disk can only be moved if it is the uppermost disk on a stack.
3) No disk may be placed on top of a smaller disk.
Algorithm
• Move the top n – 1 disks from Source to Auxiliary tower,
• Move the nth disk from Source to Destination tower,
• Move the n – 1 disks from Auxiliary tower to Destination tower.
• Transferring the top n – 1 disks from Source to auxiliary tower can again be thought of as a fresh problem and can be solved in the same manner. Once we solve Towers of Hanoi with three disks, we can solve it with any number of disks with the above algorithm.
Pseudo Code
TOH(n, x, y, z)
{
if (n >= 1)
{
// put (n-1) disk to z by using y
TOH((n-1), x, z, y)
// move larger disk to right place
move:x-->y
// put (n-1) disk to right place
TOH((n-1), z, y, x)
}
}
Analysis of Recursion
Recursive Equation : 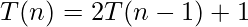 ——-equation-1
——-equation-1
Solving it by Backsubstitution :
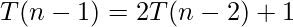 ———–equation-2
———–equation-2
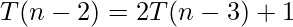 ———–equation-3
———–equation-3
Put the value of T(n-2) in the equation–2 with help of equation-3
 ——equation-4
——equation-4
Put the value of T(n-1) in equation-1 with help of equation-4
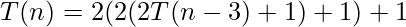

After Generalization :
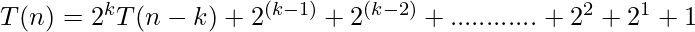
Base condition T(1) =1
n – k = 1
k = n-1
put, k = n-1

It is a GP series, and the sum is 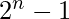
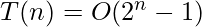 , or you can say
, or you can say  which is exponential
which is exponential
for 5 disks i.e. n=5 It will take 2^5-1=31 moves.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...