Three way partitioning of an array around a given range
Last Updated :
20 Feb, 2023
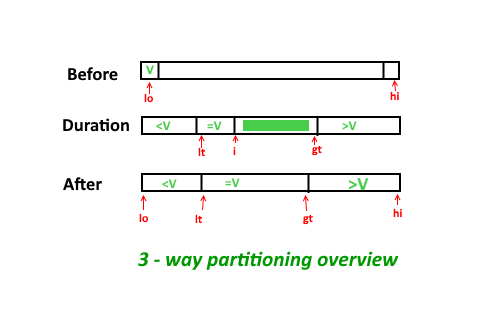
Given an array and a range [lowVal, highVal], partition the array around the range such that array is divided in three parts.
- All elements smaller than lowVal come first.
- All elements in range lowVal to highVal come next.
- All elements greater than highVal appear in the end.
The individual elements of the three sets can appear in any order.
Examples;
Input: arr[] = {1, 14, 5, 20, 4, 2, 54, 20, 87, 98, 3, 1, 32} , lowVal = 14 , highVal = 20
Output: arr[] = {1, 5, 4, 2, 1, 3, 14, 20, 20, 98, 87, 32, 54}
Explanation: all elements which are less than 14 are present in the range of 0 to 6
all elements which are greater than 14 and less than 20 are present in the range of 7 to 8
all elements which are greater than 20 are present in the range of 9 to 12
Input: arr[] = {1, 14, 5, 20, 4, 2, 54, 20, 87, 98, 3, 1, 32} , lowVal = 20 , highVal = 20
Output: arr[] = {1, 14, 5, 4, 2, 1, 3, 20, 20, 98, 87, 32, 54}
Three-way partitioning of an array using Two Pointer
The idea is based on Dutch National Flag based QuickSort. We traverse the given array of elements from left. We keep track of two pointers, first to store next position of smaller element (smaller than range) from beginning, and second to store next position of greater element from end. while traversing the array use these two pointers to place elements according to their range.
Follow the steps mentioned below to implement the idea:
- Create two variables start and end to store the index of the vacant place to store the elements according to their range.
- Traverse the array from 0 to end.
- If an element is less than lowVal then swap it with the element present at index start and increase the value of start by 1.
- If an element is greater than highVal then swap it with the element present at index end and decrease the value of end by 1.
- Print the array.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void threeWayPartition(int arr[], int n, int lowVal,
int highVal)
{
int start = 0, end = n - 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= end;) {
if (arr[i] < lowVal) {
if (i == start) {
start++;
i++;
}
else
swap(arr[i++], arr[start++]);
}
else if (arr[i] > highVal)
swap(arr[i], arr[end--]);
else
i++;
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[]
= { 1, 14, 5, 20, 4, 2, 54, 20, 87, 98, 3, 1, 32 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
threeWayPartition(arr, n, 10, 20);
cout << "Modified array \n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void
threeWayPartition(int[] arr, int lowVal, int highVal)
{
int n = arr.length;
int start = 0, end = n - 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= end;) {
if (arr[i] < lowVal) {
int temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
start++;
i++;
}
else if (arr[i] > highVal) {
int temp = arr[end];
arr[end] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
end--;
}
else
i++;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 1, 14, 5, 20, 4, 2, 54,
20, 87, 98, 3, 1, 32 };
threeWayPartition(arr, 10, 20);
System.out.println("Modified array ");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
|
Python3
def threeWayPartition(arr, n, lowVal, highVal):
start = 0
end = n - 1
i = 0
while i <= end:
if arr[i] < lowVal:
arr[i], arr[start] = arr[start], arr[i]
i += 1
start += 1
elif arr[i] > highVal:
arr[i], arr[end] = arr[end], arr[i]
end -= 1
else:
i += 1
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [1, 14, 5, 20, 4, 2, 54,
20, 87, 98, 3, 1, 32]
n = len(arr)
threeWayPartition(arr, n, 10, 20)
print("Modified array")
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i], end = " ")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
public static void
threeWayPartition(int[] arr, int lowVal, int highVal)
{
int n = arr.Length;
int start = 0, end = n - 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= end;) {
if (arr[i] < lowVal) {
int temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
start++;
i++;
}
else if (arr[i] > highVal) {
int temp = arr[end];
arr[end] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
end--;
}
else
i++;
}
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 1, 14, 5, 20, 4, 2, 54,
20, 87, 98, 3, 1, 32 };
threeWayPartition(arr, 10, 20);
Console.WriteLine("Modified array ");
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) {
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function threeWayPartition(arr, n, lowVal, highVal)
{
let start = 0, end = n - 1;
for(let i = 0; i <= end;)
{
if (arr[i] < lowVal)
{
let temp = arr[start];
arr[start] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
start++;
i++;
}
else if(arr[i] > highVal)
{
let temp = arr[end];
arr[end] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
end--;
}
else
i++;
}
}
let arr = [ 1, 14, 5, 20, 4, 2, 54,
20, 87, 98, 3, 1, 32 ];
let n = arr.length;
threeWayPartition(arr, n, 10, 20);
document.write("Modified array <br>");
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
document.write(arr[i] + " ");
</script>
|
Output
Modified array
1 5 4 2 1 3 14 20 20 98 87 32 54
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...