Symmetric and Skew Symmetric Matrices are the types of square matrices based on the relation between a matrix and its transpose. These matrices are one of the most used matrices out of all the matrices out there. Symmetric matrices have use cases in optimization, physics, and statistics, whereas skew-symmetric matrices are used in subjects such as mechanics and electromagnetism. In this article, we will study the Symmetric and Skew Symmetric Matrices and their various properties such as eigenvalues and diagonalization.
The image below shows a symmetric and skew-symmetric matrix.
Symmetric Matrix
If for a matrix, the transposed form of that matrix is the same as the original matrix, then that matrix is said to be a Symmetric Matrix. Let, a square matrix A of size n x n is said to be symmetric if
At = A
Where,
- [aij] = [aji], for 1 ≤ i ≤ n, and 1 ≤ j ≤ n.
- [aij] is an element at position (i, j) which is ith row and jth column in matrix A, and
- [aji] is an element at position (j, i) which is jth row and ith column in matrix A.
So, [aji] represents the transpose of [aij] matrix.
For example, let consider a square matrix 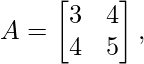
and Transpose of A = 
So, this matrix is a Symmetric Matrix, because the transposed form of this matrix is itself the original matrix.
Properties of Symmetric Matrices
Some Properties of Symmetric Matrices are as follows:
- All eigenvalues of a symmetric matrix are real.
- Eigenvectors corresponding to distinct eigenvalues of a symmetric matrix are orthogonal.
- A symmetric matrix is always diagonalizable (i.e., it can be written as a diagonal matrix with its eigenvalues on the diagonal).
- The sum and product of two symmetric matrices are symmetric.
- A symmetric matrix is positive definite if all its eigenvalues are positive.
- The spectral theorem states that every symmetric matrix can be diagonalized by an orthogonal matrix.
Property: If matrix A is a square matrix then (A + At) is always symmetric.
Prove:
To find if a matrix symmetric or not, first, we have to find the transposed form of the given matrix
So, let’s find the transpose of (A + At)
= (A + At)t
= At + (At)t
= At + A [here, (At)t = A]
= (A + At)
So, this is the same as the given matrix, so it is symmetric.
Skew Symmetric Matrix
If for a matrix, the transposed form of that matrix is the same as the negative of the original matrix, then that matrix is said to be a Skew-Symmetric Matrix. Let, a square matrix A of size n x n is said to be skew-symmetric if
At = -A
Where,
- [aij] = – [aji], for 1 ≤ i ≤ n, and 1 ≤ j ≤ n.
- [aij] is an element at position (i, j) which is ith row and jth column in matrix A, and
- [aji] is an element at position (j, i) which is jth row and ith column in matrix A.
For Example, consider 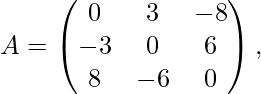
and 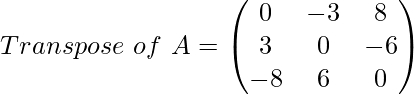
Here, in the transposed form the matrix looks like the negative of the original matrix.
Properties of Skew-Symmetric Matrices
There are some rules that come from the concept of Symmetric and Skew-Symmetric Matrices,
- All eigenvalues of a skew-symmetric matrix are either 0 or purely imaginary.
- Eigenvectors corresponding to distinct non-zero eigenvalues of a skew-symmetric matrix are orthogonal.
- The determinant of a skew-symmetric matrix is 0 if the size of the matrix is odd, and the determinant is the product of the eigenvalues if the size of the matrix is even.
- Skew-symmetric matrices with complex entries are called skew-hermitian matrices, here instead of transpose we take the conjugate transpose of the matrix.
Property: If matrix A is a square matrix then (A – At) is always skew-symmetric.
Proof:
To find if a matrix skew-symmetric or not, first, we have to find the transposed form of the given matrix
So, let’s find the transpose of (A – At)
= (A − At)t
= At − (At)t
= At − A [here, (At)t = A]
= − (A − At)
So, this form is the negative of the given matrix, so it is skew-symmetric.
Determinant of Skew Symmetric Matrix
Skew-Symmetric Matrix, is a square matrix and the determinant of the Skew-Symmetric matrices follows the condition discussed below. If we have a Skew-Symmetric Matrix then,
det (AT) = det (-A) = (-1)n det(A)
Also, every skew-symmetric matrix of odd order is a singular matrix, i.e. its determinant is zero and hence its determinant does not exist.
Eigenvalue of Skew Symmetric Matrix
The eigenvalues of a skew-symmetric matrix are zero. It is a real matrix, but the matrix can have non-real eigenvalues. Also, we can easily express every square matrix in the form of the sum of a symmetric and a skew-symmetric matrix, uniquely.
Expressing Matrix in the form of Symmetric and Skew-Symmetric Matrices
Property: Every square matrix can be expressed uniquely as the sum of symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices.
Proof:
Let A be a square matrix,
We can write, A = A/2 + A/2
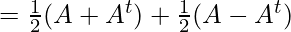
Let, A = P + Q
Where, 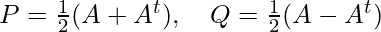
Now, find Pt and Qt
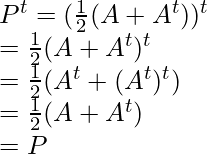
and,
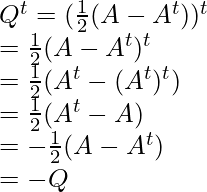
So, here P is symmetric and Q is skew-symmetric matrices and A is the sum of P and Q.
Example: Express matrix A as the sum of a symmetric and skew-symmetric matrix, Where
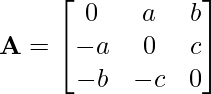
Answer:
First, find the transpose of A
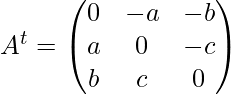
Now find (A + At) and (A – At)
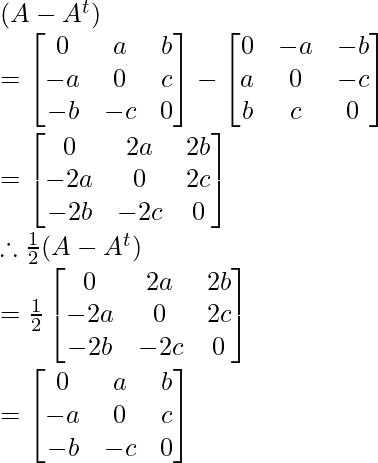
Similarly:
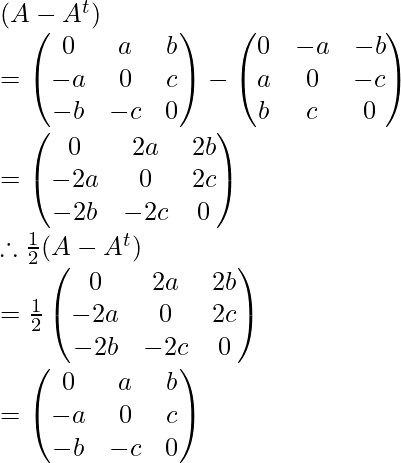
Now, check the sum of (1/2)(A + At) and (1/2)(A – At) is the same as A or not,
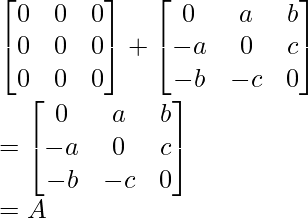
So here A is expressed as the sum of the symmetric and skew-symmetric matrix.
Difference between Symmetric and Skew Symmetric Matrices
There are some key differences between Symmetric and Skew Symmetric Matrices, which are as follows:
| Property | Symmetric Matrix | Skew-Symmetric Matrix |
|---|
| Definition | A matrix A such that AT = A | A matrix A such that AT = -A. |
|---|
| Main diagonal | Contains real numbers | Contains only zeros |
|---|
| Off-diagonal entries | Same value as a corresponding entry on the opposite side of diagonal | Opposite sign as a corresponding entry on the opposite side of diagonal |
|---|
| Eigenvalues | All eigenvalues are real | Eigenvalues come in imaginary pairs |
|---|
| Example | 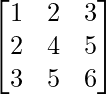 | 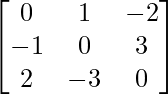 |
|---|
Read More,
Sample Problems on Symmetric and Skew Symmetric Matrices
Problem 1: Check whether the following matrix is symmetric or skew-symmetric.
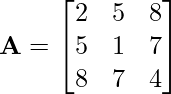
Solution:
As 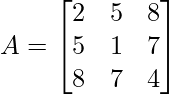
and 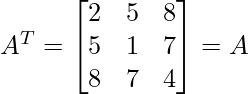
Thus, the given matrix is symmetric matrix.
Problem 2: Is the following matrix symmetric?
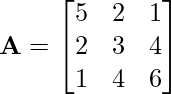
Solution:
As 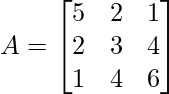
and Transpose of matrix A i.e., 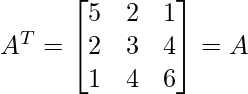
Thus, the given matrices is symmetric matrix.
Problem 3: Check whether the following matrix is symmetric or skew-symmetric.
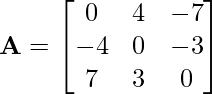
Solution:
As 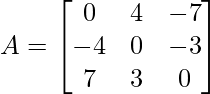
and 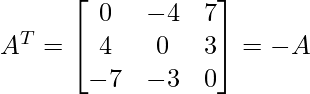
Thus, A given matrix is skew-symmetric matrix.
Problem 4: What type of matrices is the following matrix: symmetric or skew-symmetric?
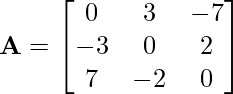
Solution:
As 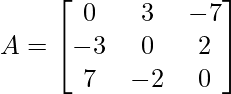
and 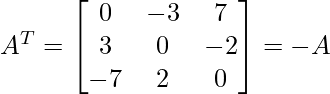
Thus, A given matrix is a skew-symmetric matrix.
FAQs on Symmetric and Skew-Symmetric Matrices
Q1: What is a Symmetric Matrix?
Answer:
A square matrix A such that AT = A, is called symmetric matrix, where AT represents the transpose of A.
Q2: What are some properties of Symmetric Matrices?
Answer:
Some of the properties of symmetric matirces are as follows:
- Eigenvalues of symmetric matrices are real.
- Eigenvectors corresponding to each distinct eiganvalue of symmetric matrices are orthogonal.
Q3: What is a Skew-Symmetric Matrix?
Answer:
A square matrix A such that AT = -A, is called skew-symmetric matrix, where AT represents the transpose of A.
Q4: What are some properties of Skew-Symmetric Matrices?
Answer:
Some of the properties of skew-symmetric matirces are as follows:
- Eigenvalues of symmetric matrices are either 0 or purely imaginary.
- Eigenvectors corresponding to each distinct eiganvalue skew symmetric matrices are orthogonal.
Q5: Can we write any Square Matrix as the summation of Symmetric and Skew-Symmetric Matrices?
Answer:
Yes, we can write any matrix as the summationof symmetric and skew-symmetric matrices. Let us consider a square matric A, then we can rewirte A as
A = (A + AT)/2 + (A – AT)/2
(A + AT)/2 is a symmetric matrix and (A + AT)/2 is a skew-symmetric matrix.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...