Surface Areas and Volumes
Last Updated :
29 Feb, 2024
Three dimensions can be measured, length, width, and height, for any object that you can see or touch. There are certain dimensions of our home that we live in. The rectangular display screen/Monitor you’re looking at has the width and breadth of its own length. For every three-dimensional geometrical structure, surface area and volume are measured.
The area or zone covered by the object’s surface is the surface area of any given object. Whereas the quantity of space available in an object is volume.
Surface Area
The surface area and volume can be calculated for any three-dimensional (3D)geometrical shape. The surface of any area is the region occupied by the surface of an object. The volume is the amount of space available in an object. We have different types of shapes like a hemisphere, sphere, cube, cuboid, cylinder, etc. All three-dimensional shapes have area and volume. But two – dimensional shapes like square, rectangle, triangle, circle, etc. Here in two – dimensional, we can only measure the area. The area occupied by a three-dimensional object by its outer surface is called the surface area. It is measured in square units.
The area is of two types:
- Total surface area
- Curved surface area/Lateral surface area
Total surface area
The area including the base(s) and the curved portion corresponds to the overall surface area. It is the amount of the area enclosed by the object’s surface. If the form has a curved base and surface, so the sum of the two regions would be the total area. The Total Surface Area can be defined as “the total area covered by an object including its base as well as the curved part. If an object has both the base and curved area then the total surface area will be equal to the sum of a base and curved area “.
- The total surface area is the total area occupied by an object.
- For example, take cuboid as an example the cuboid has 6 faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices.
Total Surface Area = Base Area + Curved Area

- The sum of all those total of 6 areas will be our total surface area of the particular shape
Example:
Given below is a cuboid having its dimension given as length = 8 cm,breadth = 4 cm and height = 6 cm, find the TSA of a cuboid

given l = 8cm, b = 4cm, h = 6cm
TSA = 2((l * b) + (l * h) + (b * h))
= 2((8 * 4) + (8 * 6) + (4 * 6))
= 2((32) + (48) + (24))
= 2(104)
= 208
The TSA of the cuboid is 208cm.
Curved surface area/Lateral surface area
Curved surface area, except its center, corresponds to the area of only the curved portion of the shape (s). For shapes such as a cone, it is often called the lateral surface area. The Lateral Surface Area can be defined as “the area which includes only the curved surface area of an object or lateral surface area of an object by excluding the base area of an object”. The Lateral Surface Area is also known as the Curved Surface Area. Most of the Shapes or Objects refer to the curved surface area, the shape or object-like cylinder refers to it as a lateral surface area. In simple, “The area which is visible to us is called a lateral surface area”. For example, consider the cylinder as shown in the below figure.

Volume
The Volume is the amount of space in a certain 3D object. The total amount of space, that an object or substance occupies is called volume. It is measured in cubic units.
Formulae of Surface Area and Volume
The table given contains the Total Surface Area, Curved Surface Area/Lateral Surface Area, and Volume of various shapes.
Name of the shape
| Curved Surface Area
| Total Surface Area
| Volume
|
|---|
Cuboid
| 2h(l + b)
| 2(lb + bh + hl)
| l * b * h
|
|---|
Cube
| 4a2
| 6a2
| a3
|
|---|
Cylinder
| 2πrh
| 2πr(r + h)
| πr2h
|
|---|
Sphere
| 4πr2
| 4πr2
| 4/3π r3
|
|---|
Cone
| πrl
| πr(r + l)
| 1/3π r2h
|
|---|
Hemisphere
| 2πr2
| 3πr2
| 2/3π r3
|
|---|
Examples
Example 1: 2 cubes each of volume 512 cm3 are joined end to end. Find the surface area of the resulting cuboid?
Solution:
Given,
The Volume (V) of each cube is = 512 cm3
we can now imply that a3 = 512 cm3
∴ The side of the cube, i.e. a = 8 cm
Now, the breadth and length of the resulting cuboid will be 8 cm each while its height will be 16 cm.
So, the surface area of the cuboid (TSA) = 2(lb + bh + lh)
Now, by putting the values, we get,
= 2(8 × 16 + 8 × 8 + 16 × 8) cm2
= (2 × 320) = 640 cm2
Hence, TSA of the cuboid = 640 cm2
Example 2: We have a cylindrical candle, 14 cm in diameter and of length 2cm. It is melted to form a cuboid candle of dimensions 7 cm × 11 cm×1 cm. How many Cuboidal candles can be obtained?
Solution:
Dimensions of the cylindrical Candle:
Radius of cylindrical candle = 14/2 cm = 7 cm
Height/Thickness=2 cm
Volume of one cylindrical candle = πr2h = π x 7 x 7 x (2) cm3 = 308 cm3 .
Volume of cuboid candle = 7 x 11 x 1 = 77 cm3
Hence, number of Cuboidal candles = Volume of cuboid candle/Volume of one cylindrical candle = 308/77 = 4
Hence we can get 4 Cuboidal shaped candles.
Example 3: A woman wants to build a spherical toy ball of clay whose radius is equal to the radius of the bangle she wears. Given that the bangle is circular in shape, she also wants that the area of the bangle is equal to the volume of the sphere. Find out the radius of the bangle she is wearing?
Solution:
Let r be the radius of the bangle as well as the sphere,
We have been given that the volume of the sphere is equal to the area of the bangle:
Hence,
πr2 = 4/3 πr3
⇒ r = 3/4
Hence the radius of the bangle is 3/4 units.
Example 4: It is given that the slant height of a right circular cone is 25 cm and its height is 24 cm. Find the curved Surface area of the cone?
Solution:
The formula for the curved surface area of the cone is πrl. Where r is the radius of the cone and l is the slant height of the cone.
Here the cone is the Right Circular Cone.
So the radius of the cone would be :
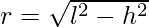
=> 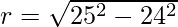
=> r = 7 cm.
Now calculating the curved surface are:
Required Area = (22/7) * 7 * 25 = 550 cm2
Hence the curved surface area of the cone is 550 cm2.
Example 5: Find the lateral surface area of a cylinder with a base radius of 6 inches and a height of 14 inches.

Solution:
Given radius r = 6, height h = 14
LSA = 2∏rh
= 2 * ∏ * 6 * 14
= 168∏
= 527.787
= 528.
The LSA of given cylinder is 528cm.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...