Summation of floor of harmonic progression
Last Updated :
13 Sep, 2022
Given an integer N, the task is to find the summation of the harmonic series 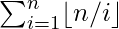 .
.
Examples:
Input: N = 5
Output: 10
floor(3/1) + floor(3/2) + floor(3/3) = 3 + 1 + 1 = 5
Input: N = 20
Output: 66
Naive approach: Run a loop from 1 to N and find the summation of the floor values of N / i. Time complexity of this approach will be O(n).
Efficient approach: Use the following formula to calculate the summation of the series:
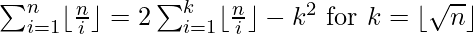
Now, the loop needs to be run from 1 to sqrt(N) and the time complexity gets reduced to O(sqrt(N))
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long int getSum(int n)
{
long long int sum = 0;
int k = sqrt(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
sum += floor(n / i);
}
sum *= 2;
sum -= pow(k, 2);
return sum;
}
int main()
{
int n = 5;
cout << getSum(n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
static long getSum(int n)
{
long sum = 0;
int k = (int)Math.sqrt(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
sum += Math.floor(n / i);
}
sum *= 2;
sum -= Math.pow(k, 2);
return sum;
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
System.out.println(getSum(n));
}
}
|
Python3
from math import floor, sqrt, ceil
def getSum(n):
summ = 0
k =(n)**(.5)
for i in range(1, floor(k) + 1):
summ += floor(n / i)
summ *= 2
summ -= pow(floor(k), 2)
return summ
n = 5
print(getSum(n))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static double getSum(int n)
{
double sum = 0;
int k = (int)Math.Sqrt(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++)
{
sum += Math.Floor((double)n / i);
}
sum *= 2;
sum -= Math.Pow(k, 2);
return sum;
}
public static void Main (String[] args)
{
int n = 5;
Console.WriteLine(getSum(n));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function getSum(n)
{
let sum = 0;
let k = parseInt(Math.sqrt(n));
for (let i = 1; i <= k; i++) {
sum += Math.floor(n / i);
}
sum *= 2;
sum -= Math.pow(k, 2);
return sum;
}
let n = 5;
document.write(getSum(n));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(sqrt(n)), since the for loop runs for sqrt(n) times.
Auxiliary Space: O(1), since no extra space has been taken.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...