StringTokenizer Class in Java
Last Updated :
08 Jan, 2024
StringTokenizer class in Java is used to break a string into tokens. A StringTokenizer object internally maintains a current position within the string to be tokenized. Some operations advance this current position past the characters processed.
A token is returned by taking a substring of the string that was used to create the StringTokenizer object. It provides the first step in the parsing process often called lexer or scanner.
Java String Tokenization
The String Tokenizer class allows an application to break strings into tokens. It implements the Enumeration interface. This class is used for parsing data. To use the String Tokenizer class we have to specify an input string and a string that contains delimiters. Delimiters are the characters that separate tokens. Each character in the delimiter string is considered a valid delimiter. Default delimiters are whitespaces, new lines, spaces, and tabs.
Illustration:
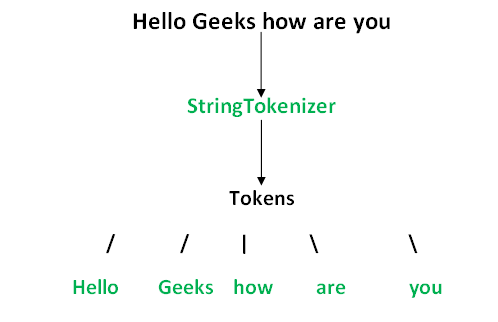
Constructors of StringToken
Let us consider ‘str’ as the string to be tokenized. In that case we have three constructor cases as mentioned below:
|
StringTokenizer(String str)
|
Default delimiters like newline, space, tab, carriage return, and form feed.
|
|
StringTokenizer(String str, String delim)
|
delim is a set of delimiters that are used to tokenize the given string.
|
|
StringTokenizer(String str, String delim, boolean flag)
|
The first two parameters have the same meaning wherein The flag serves the following purpose.
|
Cases of StringToken Constructors
1. If the flag is false, delimiter characters serve to separate tokens
Example:
Input : if string --> "hello geeks" and Delimiter is " ", then
Output: tokens are "hello" and "geeks".
2. If the flag is true, delimiter characters are considered to be tokens.
Example:
Input : String --> is "hello geeks"and Delimiter is " ", then
Output: Tokens --> "hello", " " and "geeks".
3. Multiple delimiters can be chosen for a single string.
Example:
Syntax: StringTokenizer st1 = new StringTokenizer( "2+3-1*8/4", "+*-/");
Input : String --> is "2+3-1*8/4" and Delimiters are +,*,-,/
Output: Tokens --> "2","3","1","8","4".
Examples of Java String Tokenizer Constructors
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Using Constructor 1 - ");
StringTokenizer st1 = new StringTokenizer(
"Hello Geeks How are you", " ");
while (st1.hasMoreTokens())
System.out.println(st1.nextToken());
System.out.println("Using Constructor 2 - ");
StringTokenizer st2 = new StringTokenizer(
"JAVA : Code : String", " :");
while (st2.hasMoreTokens())
System.out.println(st2.nextToken());
System.out.println("Using Constructor 3 - ");
StringTokenizer st3 = new StringTokenizer(
"JAVA : Code : String", " :", true);
while (st3.hasMoreTokens())
System.out.println(st3.nextToken());
}
}
|
Output
Using Constructor 1 -
Hello
Geeks
How
are
you
Using Constructor 2 -
JAVA
Code
String
Using Constructor 3 -
JAVA
:
Code
:
String
Methods Of StringTokenizer Class
Example of Methods of StringTokenizer Class
Below is the implementation of Methods:
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
StringTokenizer str = new StringTokenizer(
"Welcome to GeeksforGeeks");
StringTokenizer temp = new StringTokenizer("");
int count = str.countTokens();
System.out.println(count);
System.out.println("Welcome to GeeksforGeeks: "+str.hasMoreTokens());
System.out.println("(Empty String) : "+temp.hasMoreTokens());
System.out.println("\nTraversing the String:");
while(str.hasMoreTokens()){
System.out.println(str.nextElement());
}
}
}
|
Output
3
Welcome to GeeksforGeeks: true
(Empty String) : false
Traversing the String:
Welcome
to
GeeksforGeeks
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...