States of a File in Git Working Directory
Last Updated :
02 Jul, 2020
Git is a free and open-source distributed version control system designed to handle everything from small to very large projects with speed and efficiency. Git relies on the basis of distributed development of software where more than one developer may have access to the source code of a specific application and can modify changes to it which may be seen by other developers.
Any Git project will consist of three sections: the Git directory, the working tree, and the staging area. The Git directory contains the history of all the files and changes. The working tree contains the current state of the project, including any changes that have made. The staging area contains the changes that have been marked to be included in the next commit.
Each file in the working directory can be in one of two states:
Untracked state
Untracked files are any files in the working directory that were not in the last snapshot and are not in the staging area. Whenever a new file is added in the working directory which doesn’t exist before, it is considered as an untracked file. This is because Git sees this as a file that didn’t have in the previous snapshot(commit).
Let’s see this with an example, suppose we add new file example.html in our repository and run git status command to see the status of the file. It shows a list of untracked files which include example.html file.
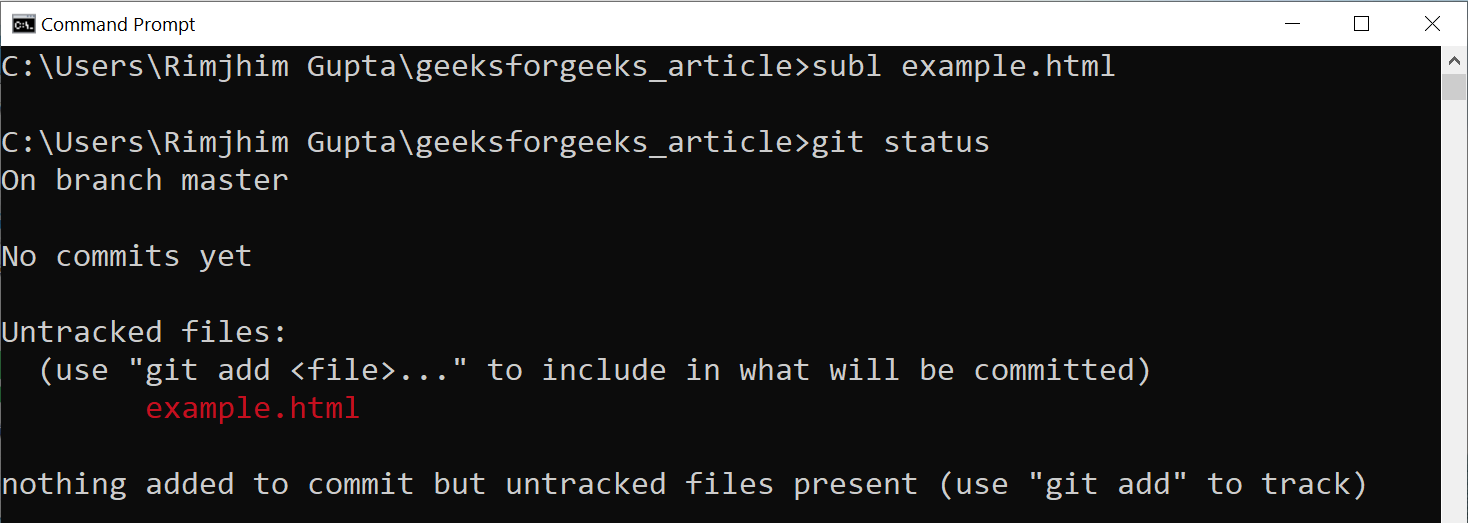
Tracked state
Tracked files are files that were in the last snapshot. These are files that Git knows about. Each track file can be in one of three sub-states, modified, staged, or committed.
Modified
A file in the modified state means that changes have been made to it that haven’t committed yet. The changes could be adding, modifying, or deleting the contents of the file. These files will be included in the next commit but will be included in their respective new form.
Let’s modify our tracked example.html file and run the git status command.

Staging
A file in the staging state means either it is not present in the last commit (e.g. newly created files) or it is “modified” file that user tells git to include in the next commit. Files are added to the staging state using git add command.Two types of files can be added to a staging state: untracked or modified.
Let’s stage our untracked example.html file and run the git status command.

Now, let’s stage our modified tracked example.html file and run the git status command.

Committed
A file in the committed state means that the changes made to it are safely stored in a snapshot in the Git directory. A file is committed using git commit command.This command creates a new snapshot in the Git directory and shows us some stats for the change made.
Let’s commit the changes we made in our example.html file.

Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...