For doing operations on data SQL has many built-in functions, they are categorized in two categories and further sub-categorized in different seven functions under each category. The categories are:
- Aggregate functions:
These functions are used to do operations from the values of the column and a single value is returned.
- AVG()
- COUNT()
- FIRST()
- LAST()
- MAX()
- MIN()
- SUM()
- Scalar functions:
These functions are based on user input, these too returns single value.
- UCASE()
- LCASE()
- MID()
- LEN()
- ROUND()
- NOW()
- FORMAT()
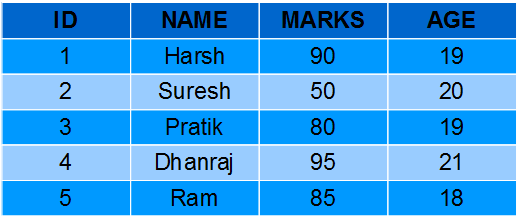
Students-Table
Aggregate Functions
AVG(): It returns the average value after calculating from values in a numeric column.
Syntax:
SELECT AVG(column_name) FROM table_name;
Queries:
- Computing average marks of students.
SELECT AVG(MARKS) AS AvgMarks FROM Students;
Output:
- Computing average age of students.
SELECT AVG(AGE) AS AvgAge FROM Students;
Output:
COUNT(): It is used to count the number of rows returned in a SELECT statement. It can’t be used in MS ACCESS.
Syntax:
SELECT COUNT(column_name) FROM table_name;
Queries:
- Computing total number of students.
SELECT COUNT(*) AS NumStudents FROM Students;
Output:
- Computing number of students with unique/distinct age.
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT AGE) AS NumStudents FROM Students;
Output:
FIRST(): The FIRST() function returns the first value of the selected column.
Syntax:
SELECT FIRST(column_name) FROM table_name;
Queries:
- Fetching marks of first student from the Students table.
SELECT FIRST(MARKS) AS MarksFirst FROM Students;
Output:
- Fetching age of first student from the Students table.
SELECT FIRST(AGE) AS AgeFirst FROM Students;
Output:
LAST(): The LAST() function returns the last value of the selected column. It can be used only in MS ACCESS.
Syntax:
SELECT LAST(column_name) FROM table_name;
Queries:
- Fetching marks of last student from the Students table.
SELECT LAST(MARKS) AS MarksLast FROM Students;
Output:
- Fetching age of last student from the Students table.
SELECT LAST(AGE) AS AgeLast FROM Students;
Output:
MAX(): The MAX() function returns the maximum value of the selected column.
Syntax:
SELECT MAX(column_name) FROM table_name;
Queries:
- Fetching maximum marks among students from the Students table.
SELECT MAX(MARKS) AS MaxMarks FROM Students;
Output:
- Fetching max age among students from the Students table.
SELECT MAX(AGE) AS MaxAge FROM Students;
Output:
MIN(): The MIN() function returns the minimum value of the selected column.
Syntax:
SELECT MIN(column_name) FROM table_name;
Queries:
- Fetching minimum marks among students from the Students table.
SELECT MIN(MARKS) AS MinMarks FROM Students;
Output:
- Fetching minimum age among students from the Students table.
SELECT MIN(AGE) AS MinAge FROM Students;
Output:
SUM(): The SUM() function returns the sum of all the values of the selected column.
Syntax:
SELECT SUM(column_name) FROM table_name;
Queries:
- Fetching summation of total marks among students from the Students table.
SELECT SUM(MARKS) AS TotalMarks FROM Students;
Output:
- Fetching summation of total age among students from the Students table.
SELECT SUM(AGE) AS TotalAge FROM Students;
Output:
Scalar Functions
UCASE(): It converts the value of a field to uppercase.
Syntax:
SELECT UCASE(column_name) FROM table_name;
Queries:
- Converting names of students from the table Students to uppercase.
SELECT UCASE(NAME) FROM Students;
Output:
| NAME |
| HARSH |
| SURESH |
| PRATIK |
| DHANRAJ |
| RAM |
LCASE(): It converts the value of a field to lowercase.
Syntax:
SELECT LCASE(column_name) FROM table_name;
Queries:
- Converting names of students from the table Students to lowercase.
SELECT LCASE(NAME) FROM Students;
Output:
| NAME |
| harsh |
| suresh |
| pratik |
| dhanraj |
| ram |
MID(): The MID() function extracts texts from the text field.
Syntax:
SELECT MID(column_name,start,length) AS some_name FROM table_name;
specifying length is optional here, and start signifies start position ( starting from 1 )
Queries:
- Fetching first four characters of names of students from the Students table.
SELECT MID(NAME,1,4) FROM Students;
Output:
| NAME |
| HARS |
| SURE |
| PRAT |
| DHAN |
| RAM |
LEN(): The LEN() function returns the length of the value in a text field.
Syntax:
SELECT LENGTH(column_name) FROM table_name;
Queries:
- Fetching length of names of students from Students table.
SELECT LENGTH(NAME) FROM Students;
Output:
ROUND(): The ROUND() function is used to round a numeric field to the number of decimals specified.NOTE: Many database systems have adopted the IEEE 754 standard for arithmetic operations, which says that when any numeric .5 is rounded it results to the nearest even integer i.e, 5.5 and 6.5 both gets rounded off to 6.
Syntax:
SELECT ROUND(column_name,decimals) FROM table_name;
decimals- number of decimals to be fetched.
Queries:
- Fetching maximum marks among students from the Students table.
SELECT ROUND(MARKS,0) FROM table_name;
Output:
NOW(): The NOW() function returns the current system date and time.
Syntax:
SELECT NOW() FROM table_name;
Queries:
- Fetching current system time.
SELECT NAME, NOW() AS DateTime FROM Students;
Output:
| NAME |
DateTime |
| HARSH |
1/13/2017 1:30:11 PM |
| SURESH |
1/13/2017 1:30:11 PM |
| PRATIK |
1/13/2017 1:30:11 PM |
| DHANRAJ |
1/13/2017 1:30:11 PM |
| RAM |
1/13/2017 1:30:11 PM |
FORMAT(): The FORMAT() function is used to format how a field is to be displayed.
Syntax:
SELECT FORMAT(column_name,format) FROM table_name;
Queries:
- Formatting current date as ‘YYYY-MM-DD’.
SELECT NAME, FORMAT(Now(),'YYYY-MM-DD') AS Date FROM Students;
Output:
| NAME |
Date |
| HARSH |
2017-01-13 |
| SURESH |
2017-01-13 |
| PRATIK |
2017-01-13 |
| DHANRAJ |
2017-01-13 |
| RAM |
2017-01-13 |
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...