Spring Boot – H2 Database
Last Updated :
13 Dec, 2023
H2 Database in Spring Boot is an embedded, open-source, and in-memory database. It is a relational database management system written in Java. It is a client/server application. It stores data in memory, not persist the data on disk. Here we will be discussing how can we configure and perform some basic operations in Spring Boot using H2 Database.
Features of the H2 Database:
- Very fast, open-source, JDBC API
- Embedded and server modes; disk-based or in-memory databases.
- Transaction support, multi-version concurrency
- Browser-based Console application
- Encrypted databases
- Fulltext search
- Pure Java with a small footprint: around 2.5 MB jar file size
- ODBC driver
Configure H2 Database in Spring Boot Application
Step 1: Adding the dependency
To use the H2 database in the spring boot application we have to add the following dependency in the pom.xml file:
h2 and spring-boot-starter-data-jpa dependencies:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
Step 2: Write some properties in the application.properties file
# H2 Database
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:dcbapp
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=password
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
We can also use YAML file for database configuration by adding properties to application.yml file as depicted below:
spring:
h2:
console.enabled: true
datasource:
url: jdbc:h2:mem:dcbapp
driverClassName: org.h2.Driver
username: sa
password: password
jpa:
spring.jpa.database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
Let’s understand what these properties are by opening the H2 Database console.
H2 Console: By default, the console view of the H2 database is disabled. Before accessing the H2 database, we must enable it by using the following property:
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
Once we have enabled the H2 console, now we can access the H2 console in the browser by invoking the URL http://localhost:8082/h2-console.
Note: Provide your port number in which your spring application is running
The following figure shows the console view of the H2 database.

Database Operation (CRUD Operation)
We are going to perform some basic CRUD Operations by creating a Spring Boot Application and using the H2 Database.
Steps to perform CRUD Operation using H2 database:
Step 1: Refer to this article How to Create a Spring Boot Project with IntelliJ IDEA and create a Spring Boot project.
Step 2: Add the following dependency
- Spring Web
- H2 Database
- Lombok
- Spring Data JPA
Below is the complete code for the pom.xml file. Please check if you have missed something.
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.5.5</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>com.amiya</groupId>
<artifactId>Spring-Boot-Demo-Project</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>Spring-Boot-Demo-Project</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
|
Step 3: Create 4 packages and later create some classes and interfaces inside these packages as seen in the below image
- entity
- repository
- service
- controller

Note:
- Green Rounded Icon ‘I’ Buttons are Interface.
- Blue Rounded Icon ‘C’ Buttons are Classes.
Step 4: Inside the entity package
Create a simple POJO class inside the Department.java file.
Example:
Java
package com.amiya.springbootdemoproject.entity;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Entity
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class Department {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long departmentId;
private String departmentName;
private String departmentAddress;
private String departmentCode;
}
|
Step 5: Inside the repository package
Create a simple interface and name the interface as DepartmentRepository. This interface is going to extend the CrudRepository as we have discussed above.
Example Below is the code for the DepartmentRepository.java file
Java
package com.amiya.springbootdemoproject.repository;
import com.amiya.springbootdemoproject.entity.Department;
import org.springframework.data.repository.CrudRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public interface DepartmentRepository
extends CrudRepository<Department, Long> {
}
|
Step 6: Inside the service package
Inside the package create one interface named as DepartmentService and one class named as DepartmentServiceImpl.
Example 1-A
Java
package com.amiya.springbootdemoproject.service;
import com.amiya.springbootdemoproject.entity.Department;
import java.util.List;
public interface DepartmentService {
Department saveDepartment(Department department);
List<Department> fetchDepartmentList();
Department updateDepartment(Department department,
Long departmentId);
void deleteDepartmentById(Long departmentId);
}
|
Example 1-B
Java
package com.amiya.springbootdemoproject.service;
import com.amiya.springbootdemoproject.entity.Department;
import com.amiya.springbootdemoproject.repository.DepartmentRepository;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class DepartmentServiceImpl
implements DepartmentService {
@Autowired
private DepartmentRepository departmentRepository;
@Override
public Department saveDepartment(Department department)
{
return departmentRepository.save(department);
}
@Override public List<Department> fetchDepartmentList()
{
return (List<Department>)
departmentRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public Department
updateDepartment(Department department,
Long departmentId)
{
Department depDB
= departmentRepository.findById(departmentId)
.get();
if (Objects.nonNull(department.getDepartmentName())
&& !"".equalsIgnoreCase(
department.getDepartmentName())) {
depDB.setDepartmentName(
department.getDepartmentName());
}
if (Objects.nonNull(
department.getDepartmentAddress())
&& !"".equalsIgnoreCase(
department.getDepartmentAddress())) {
depDB.setDepartmentAddress(
department.getDepartmentAddress());
}
if (Objects.nonNull(department.getDepartmentCode())
&& !"".equalsIgnoreCase(
department.getDepartmentCode())) {
depDB.setDepartmentCode(
department.getDepartmentCode());
}
return departmentRepository.save(depDB);
}
@Override
public void deleteDepartmentById(Long departmentId)
{
departmentRepository.deleteById(departmentId);
}
}
|
Step 7: Inside the controller package
Inside the package create one class named as DepartmentController.
Example
Java
package com.amiya.springbootdemoproject.controller;
import com.amiya.springbootdemoproject.entity.Department;
import com.amiya.springbootdemoproject.service.DepartmentService;
import java.util.List;
import javax.validation.Valid;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RestController
public class DepartmentController {
@Autowired private DepartmentService departmentService;
@PostMapping("/departments")
public Department saveDepartment(
@Valid @RequestBody Department department)
{
return departmentService.saveDepartment(department);
}
@GetMapping("/departments")
public List<Department> fetchDepartmentList()
{
return departmentService.fetchDepartmentList();
}
@PutMapping("/departments/{id}")
public Department
updateDepartment(@RequestBody Department department,
@PathVariable("id") Long departmentId)
{
return departmentService.updateDepartment(
department, departmentId);
}
@DeleteMapping("/departments/{id}")
public String deleteDepartmentById(@PathVariable("id")
Long departmentId)
{
departmentService.deleteDepartmentById(
departmentId);
return "Deleted Successfully";
}
}
|
Accessing H2 Database
Below is the code for the application.properties file
server.port = 8082
# H2 Database
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:dcbapp
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=password
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
For application.yml file:
spring:
h2:
console.enabled=true
datasource:
url: jdbc:h2:mem:dcbapp
driverClassName: org.h2.Driver
username: sa
password: password
jpa:
spring.jpa.database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
Now run your application and let’s test the endpoints in Postman and also refer to our H2 Database.
Testing the Endpoint in Postman
Endpoint 1: POST – http://localhost:8082/departments/
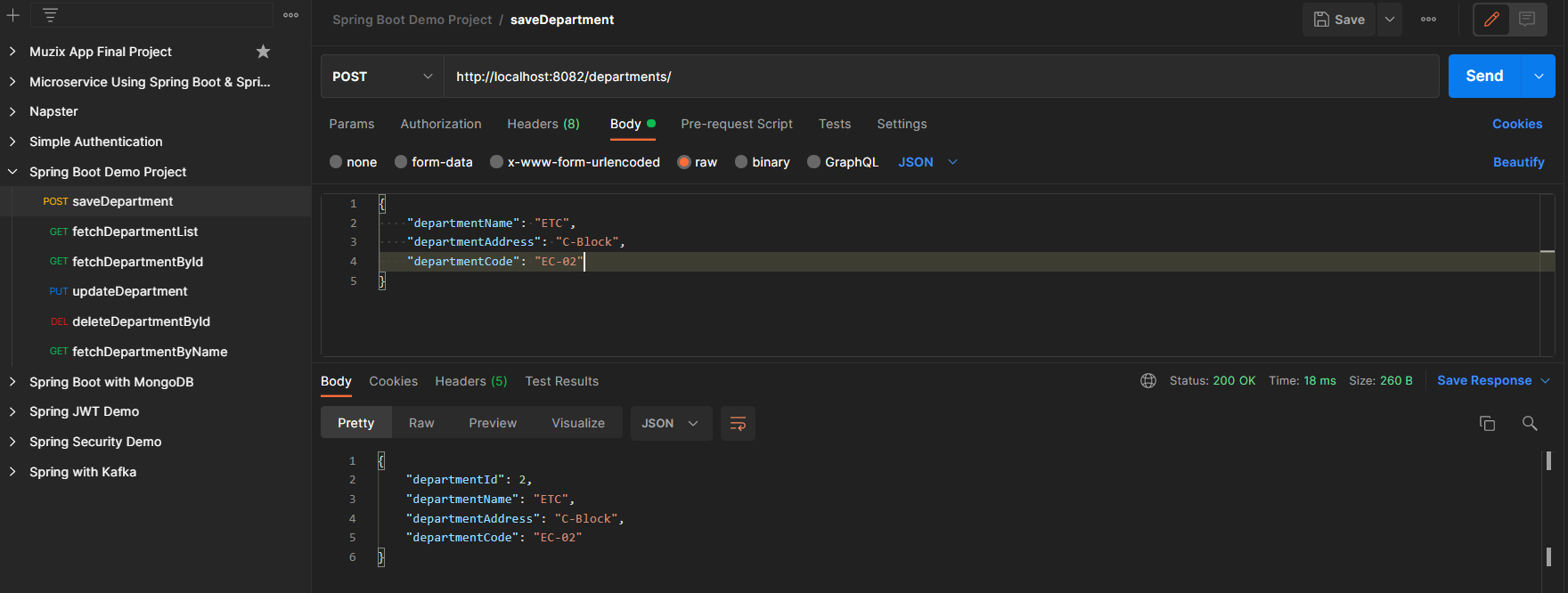
Endpoint 2: GET – http://localhost:8082/departments/

Endpoint 3: PUT – http://localhost:8082/departments/1

Endpoint 4: DELETE – http://localhost:8082/departments/1
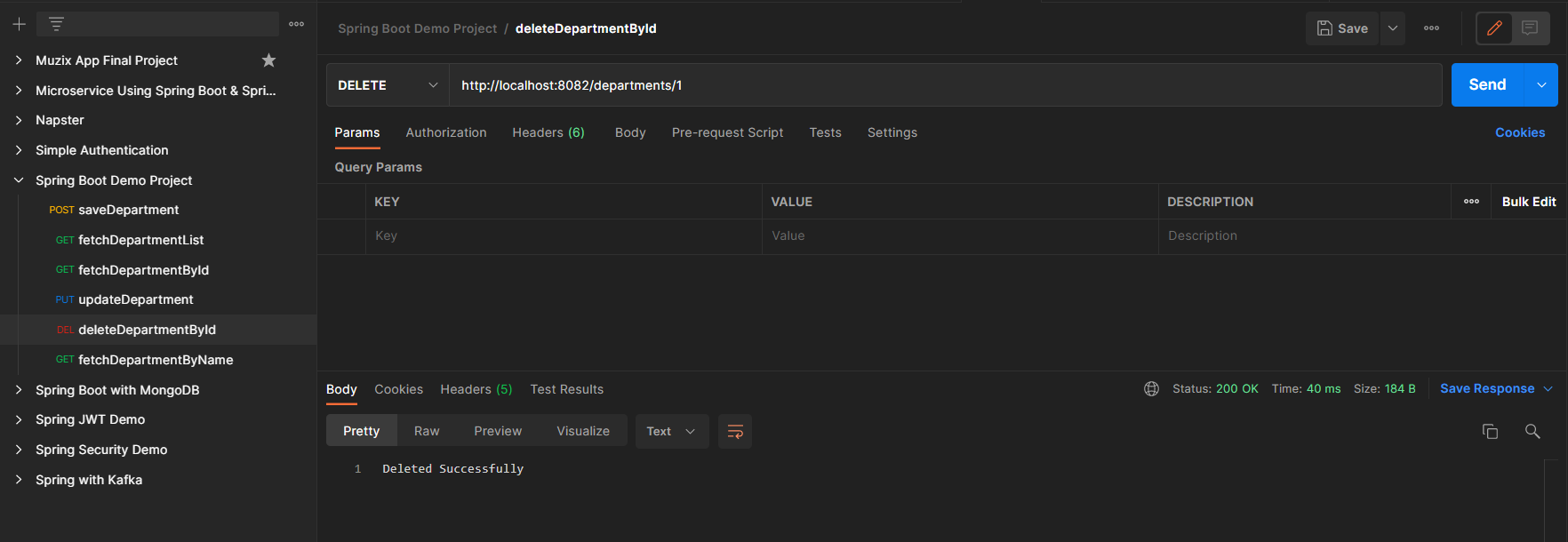
Lastly, H2 Database is as depicted in the below media as follows:

Conclusion
In this article, we have learned how to configure, access H2 Database and how to test endpoints in Postman for managing the running database.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...